Question: C++ Code help: Use the following C++ for correct output producer_consumer.cpp #include #include #include using namespace std; #define MAX 10 #define N 4 // Data
C++ Code help:
Use the following C++ for correct output
producer_consumer.cpp
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
#define N 4
// Data structure to represent a simplified Order
// that has an order number and an item number.
struct Order
{
int order_num;
int item_num;
};
Order new_orders [N]; // array of elements of type Order to be used as a shared buffer
int num_new_orders = 0; // count of number of new (i.e., unprocessed) orders
int order_num = 0; // global variable used to generate unique order numbers
// TODO: Define and initialize necessary mutex and condition variables here
void* takeOrders(void* arg)
{
int item;
int index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i
// Beginning of critical region 1
// Get user input
cout
cin >> item;
// Print new order's details
cout
// End of critical region 1
// Beginning of critical region 2
// Put new order into new orders buffer and update number of new orders
new_orders[index].order_num = order_num;
new_orders[index++].item_num = item;
++num_new_orders;
// End of critical region 2
// Update order number so that next order gets a different number
++order_num;
// If the end of the new orders buffer is reached, wrap back around
if(index == N)
index = 0;
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
void* processOrders(void* arg)
{
int item;
int index = 0;
int o_num;
for(int i = 0; i
// Beginning of critical region 3
// Retrieve new order details from buffer and update number of new orders
o_num = new_orders[index].order_num;
item = new_orders[index++].item_num;
--num_new_orders;
// End of critical region 3
// Beginning of critical region 4
// Print retrieved order's details
cout
// End of critical region 4
// Suspend self for 1 second
sleep(1);
// If the end of the new orders buffer is reached, wrap back around
if(index == N)
index = 0;
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main()
{
// Create threads to take and process orders
pthread_t id1, id2;
pthread_create(&id1, NULL, processOrders, NULL);
pthread_create(&id2, NULL, takeOrders, NULL);
// TODO: Add code to wait for both threads to finish
// Print goodbye message
cout
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
Complete the following below.
Copy producer_consumer.cpp into a new file named producer_consumer_with_synchronization.cpp and modify the copy as instructed below.
Protect access to shared (i.e., global) data variables used in the processOrders and takeOrders threads. As part of this:
Create a global pthread mutex variable named data_mutex and initialize it to default attributes using the macro provided by the pthread library.
Insert mutex lock/unlock statements before/after regions of code using shared data in the two pthread functions. Note: the beginning and end of all critical regions are marked. Identify and protect critical region(s) that are relevant to this task.
Protect access to the console in the processOrders and takeOrders threads
Create a global pthread mutex variable named console_mutex and initialize it to default attributes using the macro provided by the pthread library.
Insert mutex lock/unlock statements before/after regions of code where the console is accessed in the two pthread functions.
Use condition variables to synchronize operations between the processOrders and takeOrders threads. As part of this:
Create necessary global pthread condition variables and initialize all of them to default attributes using the macro provided by the pthread library.
Insert pthread condition wait statements in processOrders and takeOrders threads such that:
no new orders are put into the buffer unless there is at least one space in the buffer, i.e., no new orders are put into the buffer if the buffer is full;
orders are not retrieved from the buffer unless there is at least one new order, i.e., orders are not retrieved if the buffer is empty.
Insert corresponding condition signal statements in processOrders and takeOrders threads so that the above waits will end when the conditions being waited for are satisfied.
In the main function, after both threads are created and before printing the goodbye message, insert code to ensure that the main thread waits for both pthreads to complete.
Build and run your program. When prompted, enter 10 unique integers in the range of 1 to 50. If you have put in all synchronization statements correctly, your program must adhere to the following:
Print statements must not be interleaved (i.e., a cout statement in a given thread must be not interrupted by a cout statement in a different thread).
Only orders that have been placed must get processed.
All orders that are placed must get processed, in the order in which they were placed.
Multiple orders may be placed before the first one gets processed.
The message Phew! Done with orders for today! must always be printed and printed last.
If above is correct output should the same as the one listed below:
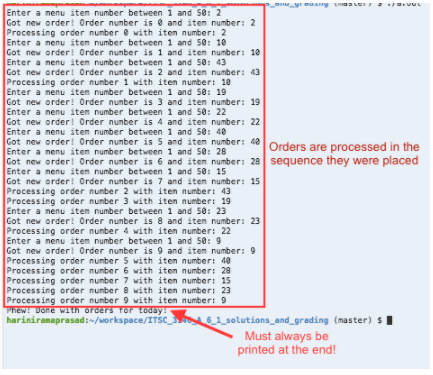
Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 50:2 Got new order! Order number is and iten number: 2 Processing order nunber with iten number: 2 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 58: 1 Got new order! Order nunber is 1 and iten number: 1e Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 58: 43 Got new order! Order number is 2 and iten number: 43 Processing order number 1 with iten numbert 10 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 58: 19 Got new order! Order nunber is 3 and iten number: 19 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 50: 22 Got new order! Order number is 4 and item number: 22 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 50: 40 Got new order! Order number is 5 and iten number: 4 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 50: 28 Got new order! Order nunber is 6 and item number: 28 sequence they were placed Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 58: 15 Got new order! Order nunber is 7 and iten number: 15 Processing order number 2 with iten number: 43 Processing order nunber 3 with iten number: 19 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 58: 23 Got new order! Order nunber is 8 and iten number: 23 Processing order number 4 with iten number: 22 Enter a nenu iten number between 1 and 50:9 Got new order! Order number is 9 and iten number:9 Processing order number S with iten number: 40 Processing order nunber 6 with iten number: 28 Processing order nunber 7 with iten number: 15 Processing order nunber 8 with iten number: 23 Processing order nunber 9 with item numbers Phew! Donc with orcers For today hariniramaprasad:-/workspace/ITSC 6 1 sotutions and grading (master) Must always be printed at the end
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


