Question
C++ PLEASE #include using namespace std; vector split_string(string); // Complete the countingSort function below. vector countingSort(vector arr) { } int main() { ofstream fout(getenv(OUTPUT_PATH)); int
C++ PLEASE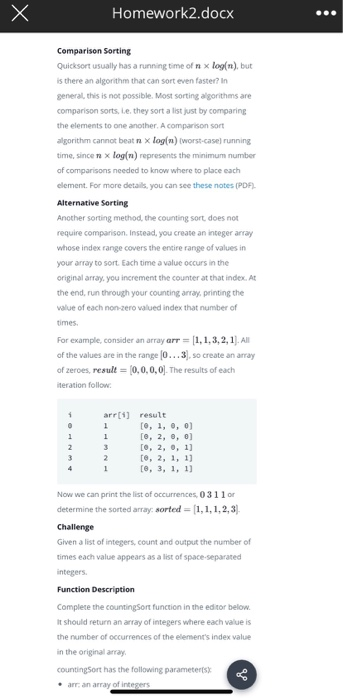

#include
using namespace std;
vector
// Complete the countingSort function below.
vector
}
int main()
{
ofstream fout(getenv("OUTPUT_PATH"));
int n;
cin >> n;
cin.ignore(numeric_limits
string arr_temp_temp;
getline(cin, arr_temp_temp);
vector
vector
for (int i = 0; i
int arr_item = stoi(arr_temp[i]);
arr[i] = arr_item;
}
vector
for (int i = 0; i
fout
if (i != result.size() - 1) {
fout
}
}
fout
fout.close();
return 0;
}
vector
string::iterator new_end = unique(input_string.begin(), input_string.end(), [] (const char &x, const char &y) {
return x == y and x == ' ';
});
input_string.erase(new_end, input_string.end());
while (input_string[input_string.length() - 1] == ' ') {
input_string.pop_back();
}
vector
char delimiter = ' ';
size_t i = 0;
size_t pos = input_string.find(delimiter);
while (pos != string::npos) {
splits.push_back(input_string.substr(i, pos - i));
i = pos + 1;
pos = input_string.find(delimiter, i);
}
splits.push_back(input_string.substr(i, min(pos, input_string.length()) - i + 1));
return splits;
}
Homework2.docx Comparison Sorting Quicksort usually has a running time of n x log(n), but is there an algorithm that can sort even faster? In general, this is not possible. Most sorting algorithms are comparison sorts. e. they sort a list just by comparing the elements to one another. A comparison sort algorithm cannot beat n x login) (worst case running time, sincer x log(n) represents the minimum number of comparisons needed to know where to place each clement. For more details, you can see these notes (PDF) Alternative Sorting Another sorting method, the counting sort does not require comparison. Instead, you create an integer array whose index range covers the entire range of values in your array to sort. Each time a value occurs in the original array. you increment the counter at that index. At the end, run through your counting array printing the value of each non-zero valued index that number of times For example, consider an array arr = [1,1,3,2,1). All of the values are in the range 0...3. so create an array of zeroes, result = (0,0,0,0]. The results of each iteration follow arr(1) 0 1 11 result [0, 1, 0, 0] [@, 2, 0, 0) [0, 2, 0, 1) [e, 2, 1, 1) [0, 3, 1, 1) Now we can print the list of occurrences, 0311 or determine the sorted array: sorted = (1,1,1,2,3) Challenge Given a list of integers, count and output the number of times each value appears as a list of space-separated integers Function Description Complete the counting Sort function in the editor below. It should return an array of integers where each value is the number of occurrences of the element's index value in the original array counting Sort has the following parameters arran array of integers 11:53 Homework2.docx Input Format The first line contains an integer n. the number of items in arr. Each of the next n lines contains an integer arr li where 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


