Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
c programming seashell For this question, you may NOT use recursion. You must use the provided STACK ADT module and iteration. Write a program that
c programming seashell
For this question, you may NOT use recursion. You must use the provided STACK ADT module and iteration.
Write a program that reads in ints, and prints the numbers in their original order and then in reverse order.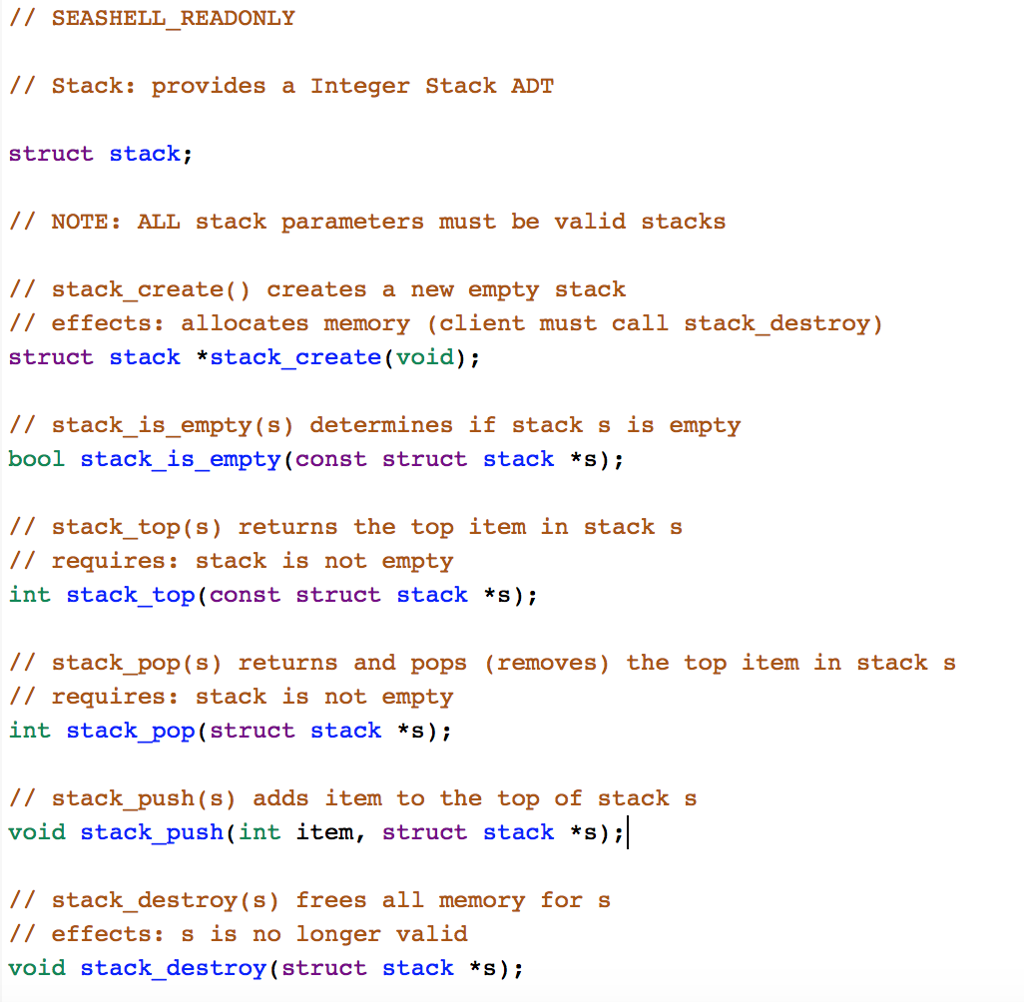 a example
a example
read in: 1 2 3
print: 1 2 3 3 2 1
/I SEASHELL _READONLY // Stack: provides a Integer Stack ADT struct stack; /NOTE: ALL stack parameters must be valid stacks // stack_create() creates a new empty stack // effects: allocates memory (client must call stack_destroy) struct stack *stack_create(void); // stack_is_empty(s) determines if stack s is empty bool stack_is_empty(const struct stack *s)i // stack_top(s) returns the top item in stack s // requires: stack is not empty int stack_top(const struct stack *S)i // stack pop(s) returns and pops (removes) the top item in stack s // requires: stack is not empty int stack_pop(struct stack *s); // stack push(s) adds item to the top of stack s void stack_push(int item, struct stack *s); // stack_destroy(s) frees all memory for s // effects: s is no longer valid void stack_destroy(struct stack *S)i /I SEASHELL _READONLY // Stack: provides a Integer Stack ADT struct stack; /NOTE: ALL stack parameters must be valid stacks // stack_create() creates a new empty stack // effects: allocates memory (client must call stack_destroy) struct stack *stack_create(void); // stack_is_empty(s) determines if stack s is empty bool stack_is_empty(const struct stack *s)i // stack_top(s) returns the top item in stack s // requires: stack is not empty int stack_top(const struct stack *S)i // stack pop(s) returns and pops (removes) the top item in stack s // requires: stack is not empty int stack_pop(struct stack *s); // stack push(s) adds item to the top of stack s void stack_push(int item, struct stack *s); // stack_destroy(s) frees all memory for s // effects: s is no longer valid void stack_destroy(struct stack *S)i
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


