Question
C++ requirements The store number must be of type unsigned int. The sales value must be of of type long long int. Your program must
C++ requirements
The store number must be of type unsigned int. The sales value must be of of type long long int.
Your program must properly check for end of file.
Your program must properly open and close all files.
You are required to have your main function and two additional functions. One of the two additional functions will be a read function and the other will be a display function.
Failure to follow the C++ requirements could reduce the points received from passing the tests.
General overview
In this program you will be reading sales information from a file and writing out a bar chart for each of the stores. The bar charts will be created by writing out a sequence of X characters.
You will have to create input files for your program. You can use a text editor such as Notepad or Notepad++ to create this. There may also be an editor in your IDE that you can use. You can use the TextEdit program on macOS but you will need to change the format to Make Plain Text. You will not be uploading these text files to zyBooks/zyLabs. The submit tests will be using their own files.
Reading in files
When reading data from a file you need to make sure you are checking for end of file properly. The general method shown in the Gaddis text book is:
ifstream inputFile; inputFile.open("input.txt"); int num; if (inputFile) { // the file opened successfully while (inputFile >> num) { // process the num value cout If you want to read in two values with every read you can simply replace inputFile >> num with something like inputFile >> num1 >> num2 as shown here:
while (inputFile >> num1 >> num2) { // process the num1 and num2 values cout Text files are more complicated that they seem. Different operating systems handle text files differently. On Windows lines of text end with followed by . On Unix (or Linux) the lines end with just . On old Macs lines ended with but now use the Unix convention. The use of the >> operator takes care of these line ending issues for you.
But it is still more complicated than that. Most text files have every line ending with either (for Windows) or (for Unix/Linux and MacOS) but it is also possible to create a text file where the last line does NOT have the line ending characters. The use of the following code will work for all line endings even when the last line of text input does not end with any line endings.
if (inputFile >> num1 >> num2) { // executes only if the read worked } or
while (inputFile >> num1 >> num2) { // executes while the read works } There are other ways to test for end of file but you have to make sure your code will work for all of the cases discussed above. It is STRONGLY recommended that you use the process outlined above.
General overview (continued)
You will also be using functions in this program.
You are required to have your main function and two additional functions.
main function
Your main function will be read in a file name from cin. It will then open the input file.
Your program must also open an output file called saleschart.txt. You will write the bar char headings and data to this file.
You main will then have a processing loop that will call the read function.
The processing loop will read the input data and process it until it gets and end of file indication from the read function.
Assuming you have read in valid data AND this is the first sales data being processed your main function should output some headings to the output file before processing the data. The headings are as follows:
SALES BAR CHART (Each X equals 1,000 dollars)
Note: Your program must not output the headings to the output file if all of the data in the input file is invalid, or if there is not data in the input file.
You need to come up with a way of keeping track if this is the first valid read or not. .
Assuming you have valid data the processing will consist of calling the display function.
Once the loop has completed you need to close the input file.
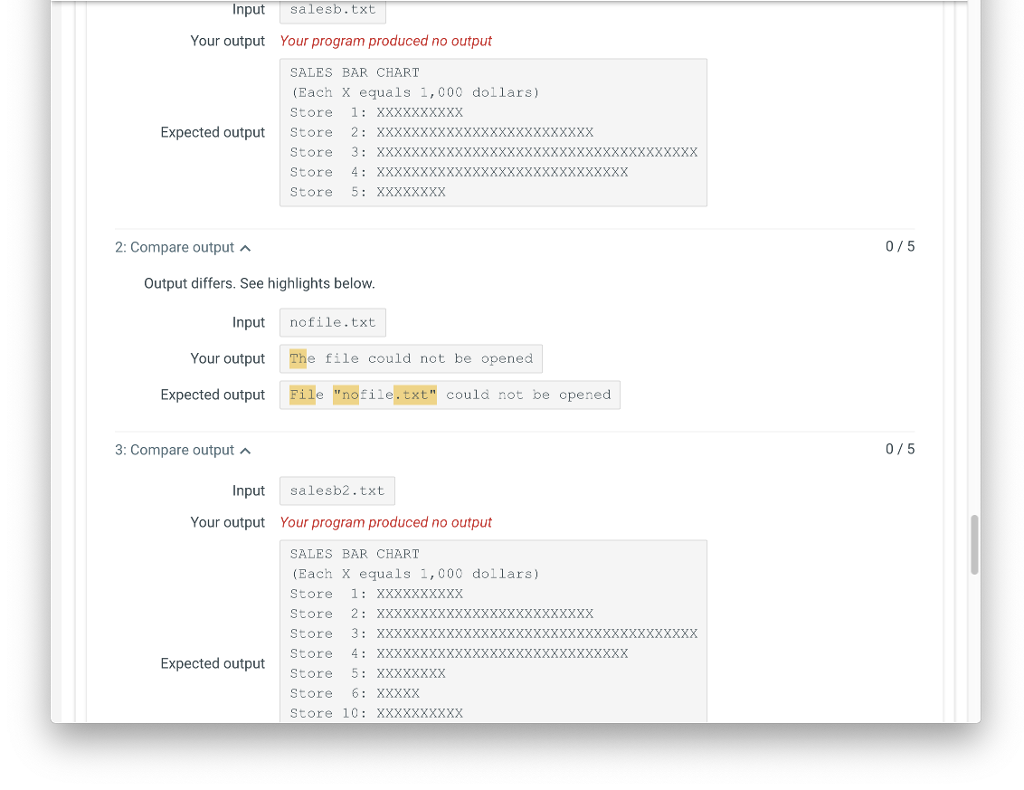
If the input file could not be opened your program should output an error message to cout. Assume the file we are reading in from is called sales.txt, and the file does not exist. The error message written to cout is:
File "sales.txt" could not be opened
Don't forget to close both files, if they were opened.
read function
The read function will return a value of true if data has been read, and will return a value of false if you have reached end of file.
The input file (of type ifstream) must be passed to the function by reference. A long long int value also needs to be passed by reference to the read function. This is where the sales data will be stored. A third parameter of type unsigned int needs to be passed by reference as well. This will be the store number. The store number is an unsigned int in the range of 1 to 99.
The data in the input file is in the order store number followed by the store sales. There will be zero or more of these input pairs in the file.
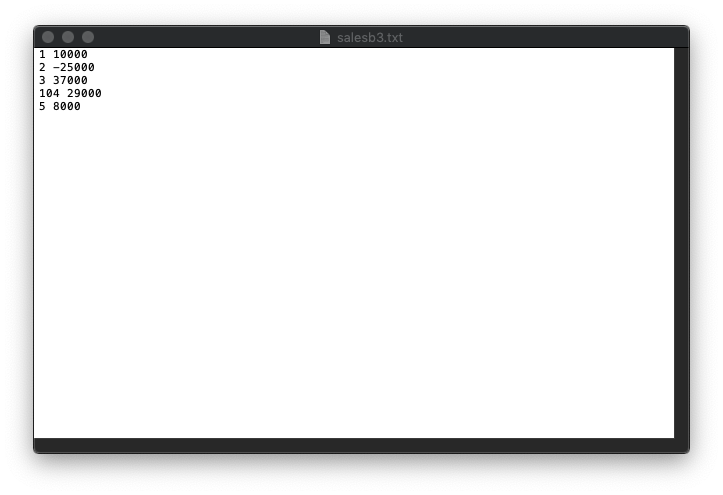
Here is the contents of a sample input text file:
1 10000 2 25000 3 37000 4 29000 5 8000
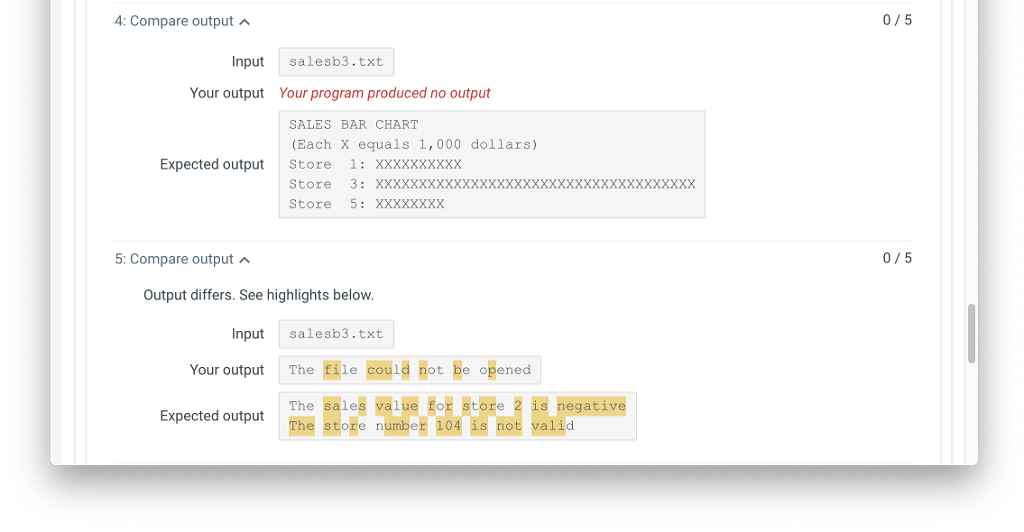
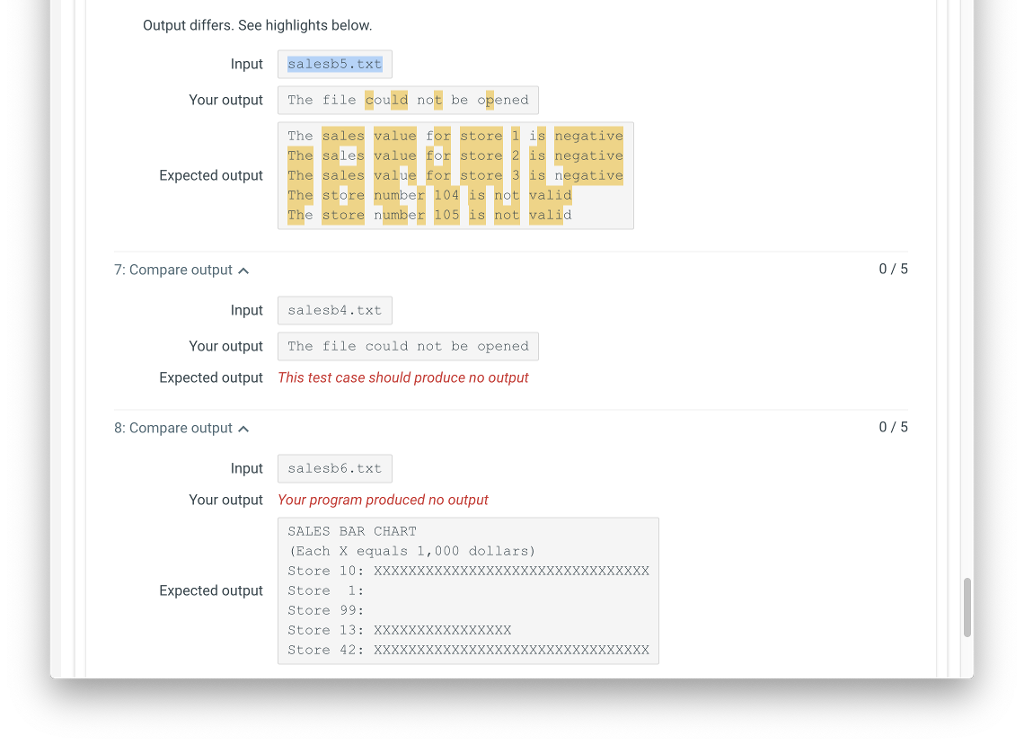
If the store number is less than 1 or greater than 99 you need to output the following message to cout:
The store number xx is not valid
Where xx is the store number.
If the sales data is less than 0 you need to output the following message to cout:
The sales value for store xx is negative
Where xx is the store number.
If either (or both) of these values are invalid your read function should loop and read in the next store number and sales value and validate them.
Every time you read from the input file you need to read in both the store number and the store sales value. After you have read in the two values you need to check to see if they are valid.
display function.
You will be outputting a string of X (upper case X) characters where each X represents $1,000 in sales for that store. For each 1,000 in sales you output one X. You do not round up the sales, so sales of $6,000 and sales of $6,999 would both output 6 X characters.
You will output the sales bar chart to the output file.
The output file is passed to you by reference. The store number and store sales are also passed to you but they are passed by value.
Assuming a store number of 9 and sales of $6,999. the display function will write the following to the output file:
Store 9: XXXXXX
Note that the store width is 2 characters, so the output is:
Store yy: XXXXXXX
The yy has a width of 2 even if the store number is 1 through 9.
Here is an example run. Assume the following input being read in from cin:
sales.txt
Assume that the content of the file sales.txt are as follows:
1 10000 2 25000 3 37000 4 29000 5 8000
The output (to file saleschart.txt) for this input would be:
SALES BAR CHART (Each X equals 1,000 dollars) Store 1: XXXXXXXXXX Store 2: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Store 3: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Store 4: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX Store 5: XXXXXXXX
You are reading from an input file and you are writing to an output file. Make sure you close both files after you are finished using them. You must do this in your program, you cannot just let the operating system close the files for you.
In this lab. and some future labs, you will be creating an output file. There could be output to cout as well.
For tests where there is output written to an output file the contents of the output file will determine if you passed that test or not. For cases where you have written out to cout the tests will check the output sent to cout.
In part 1 tests 2, 5, 6, and 7 check the output sent to cout. The rest of the tests check the output sent to filesaleschart.txt.
Failure to follow the requirements for lab lessons can result in deductions to your points, even if you pass the validation tests. Logic errors, where you are not actually implementing the correct behavior, can result in reductions even if the test cases happen to return valid answers. This will be true for this and all future lab lessons.
Expected output
There are eight tests. Each test will have a new set of input data. You must match, exactly, the expected output.Tests 2, 5, 6, and 7 check the output sent to cout. Tests 1, 3, 4, and 8 check the output sent to file saleschart.txt.
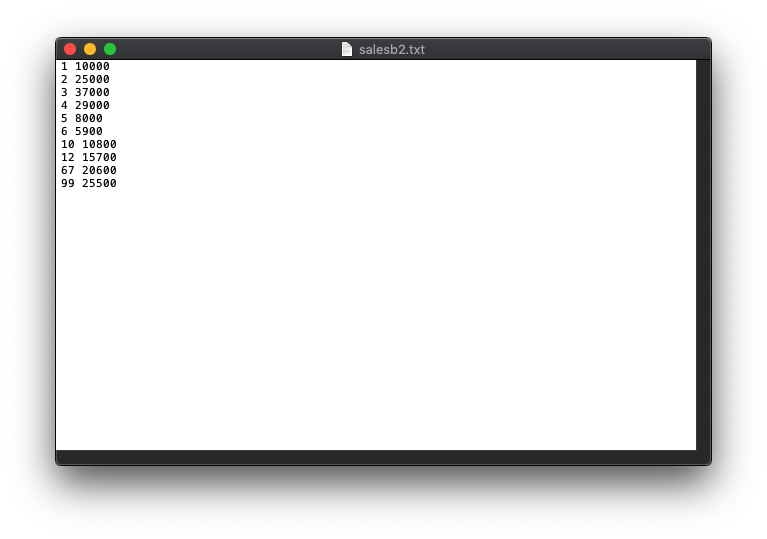
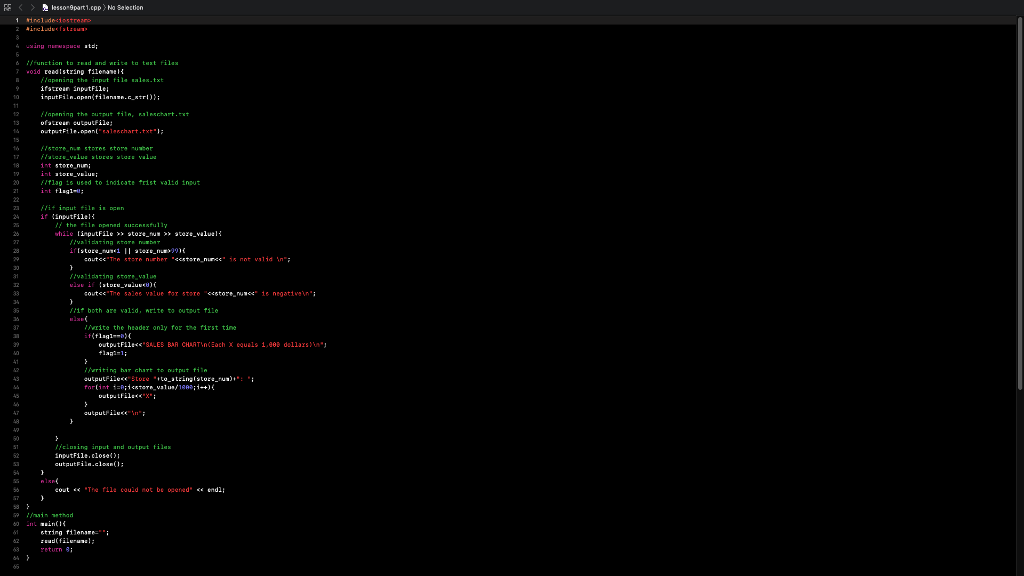
salesb2.txt 1 10000 2 25000 3 37000 4 29000 5 8000 6 5900 10 10800 12 15700 67 20600 99 25500 Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


