C++





The input file ex:

The Output:
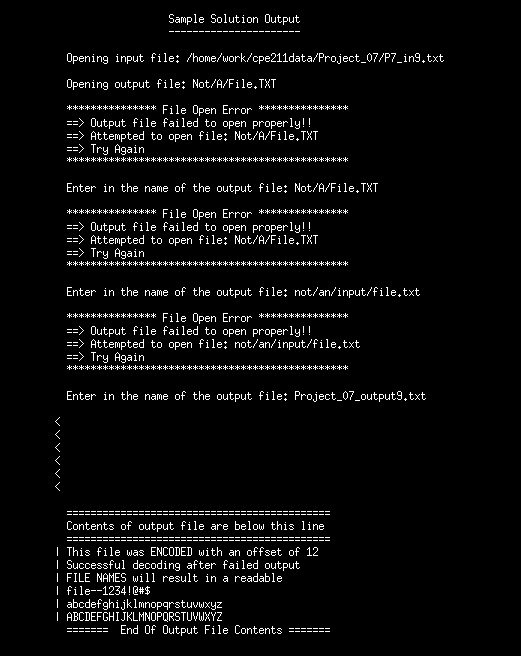
(1) Using command line arguments for an input file and output file name (see command line argument slides and page 3), print out the oormmand line input file name(see re sangle solution for the output to use) and open the input file provided. Verify that the tile opered suocessfully (ie stream is valid. If it did not open successfully, enter a while loop that outputs an error message, resets the input le stream being apened and prompts the user to enter another input file name. This file name is read, echa printed and opened. The loop continues until the input tile is successfully opened. (same procedure as used in project 6). Be sure to test for correct number of arguments as the first action in main (2) " the input fie isuccessfully opened, print out the command line output tile name and open the output tie provided Venity that the output tile opened successfully. If it did not open suocessfully, enter a whle loop that outputs an error message, resets the output file stream being opened and prompts the user to enter anather output fle name. This file name is read, echo printed and opened. The loop contnues until the output tile is successfully opened. Use the filename mad/tLlo to cause the open function to (3) The input file contains multiple lines the first line contains a single character E or D for encode or decode. After reading this character test the status of the tie stream to see if the end-o-le has been reached. f it has, then the input file is empty. Print out an empty file message to the terminal only and terminate the program. If a character was successfully read, verify that it is E ar D. I it is any other character, output an error message to the terminal and terminate the pragram. (4) The next ine in the file contains an integer offset value between 0 and 25 inclusive. There are two possible errors to check for after this read. The first error is if the input file does not contain an offset value or any other data after the E or D that was read trom the first line. For this case output the appropriate error message to the terminal and terminate the program. The second error is if the offset is present, but it is not an integer. In this case output the appropriate error message to the terminal and (5) After successfully reading the affset, the rest of the file is read character by character. For each character read, it is either (E)ncoded or (Djecoded according to the tollowing rules a. If the character read from the file is a letter(upper or lower case), it is changed based on the offset value read. For (Elncoding the offset is added to the integer value of the character. For (D)ecoding the offset is subtracted from the integer value of the character. A new letter is obtained from this value and written to the output file. See page 4 for more infomation on the character conwersion. b. If the character read from the input file is not a letter, then it is written to the output file as is (no (6) Continue to read all characters from the input tile unbl the end of the file is reached which ends the Project 7 C++ Hints 1. Testing tor an empty input file is performed by tesing the status of the file stream and the EOF bit status after reading the encode or decode character. I the input file is determined to be empty. print out an appropriate message to the terminal and terminate the program. 2. There are 5 types of possible problems with the input file that need to be tested: Empty file condition, Invalid code symbol- a character other than E or D, an Invalid offset - only have to verify that it was not an integer if it is an integer, it will be between 0 and 25), a missing offset value- for these file the only data in the fie is the code symbol of E or D, No data to convert - input file contains no data after the offset see hint #3) 3. After reading the oftset value, ignore the newline character that comes after it before you start reading the data to encode or decode. The no data to convert error occurs if there is no data to read after the newline character associated with the offset value. 4. The get function must be used to read the data that is to be encoded or decaded. 5. The offset value has 3 possibilities: it will be missing, it will be an invalid character (non-digit) or it ill be an integer between 0 and 25 inclusive. 6. Only letters are encoded or decoded. All other characters are written to the output file as they 7. Look at project 6 for the test for the correct number of command line arguments. The test needs to be the first lines in your main function Project 7 Letter Encoding and Decodin For this project letters will be encoded or decoded by using the Cesar Cipher algonthm. This algorithm adds an offset to a letter for encoding and subtracts an offset for decoding. If the offset value is 1, then for encoding, A7B, B3C Z7A. I the Offset value is 1, then for decoding, AFZ, BHA C7B 29Y Note that the letters wrap around when you reach either end of the alphabet. To perform the encoding or decoding of letters, a few functions from the cctype header file are needed. These functions are isalpha(char), islower(char) and isupper(Char)char here represents a character variable that must be used as the argument in the function cal Al three of these funcions return a boolean value of false if the character passed in is not a letter, not lower case or not upper case respectively. Likewise, these functions retum a Boolean value of true if the character passed in is a letter, a lower case letter or an upper case letter respectively. These functions can be used to determine what is to be done with the character being tested. For characters that are letters, a simple algorithm is used to madity the letterto its new value. The algorithm has to be written twice - once tor upper case letters and ance for lower case letters If a character read is a letter, the pracedure for a lower case letter is as tollows 1) Convert the character to an integer value between 0 and 25-0 representing 'a' and 25 representing 2' (same can be done with upper case letters). To do this conversion, use intVar- charRead- 'a' (you can use whatever variable names you want intVar is an integer variable and chariead is a character variable 2) For encoding the offset is added to intVar. For decoding the offset is subtracted from intvar 3) This new integer value must then be converted to a number between 0 and 25 inclusive. For example if the offset is 2 and the letter to encode is 'z, then you have intVar 25+ 2-27. This value of 27 must be converted to a number that will represent the letter that 'z' with an oftset at 2 should be converted to. In this case, the number to convert to is 1(there are 2 ways to get this value) which wil represent 'b 4) Once the number has been obtained in step 3, it must be converted back to the correct integer value for the letter it is to represen. That is easly done by taking newCharVar'a'ntvar Just add the integer value calculated(which must be between O and 25) to the integer value representing a 5) Same procedure is done for encoding upper case letters except A' is used instead of a 6) For decoding the offset is subtracted from intVar which can result in a negative number. Far negative numbers, they need to be converted back to posiive values that represent the end of the alphabet (the z end not the 'a end. For example if the offset is 2 and the letter to decode is 'a', then we have intVar 0-2 =-2. This value of-2 must be donverted to a number that represents the letter 'a' decoded to with an attset of 2. In this case that value is 24 which represents the letter'y' Once the corrected integer value is obtained it is used to abtain the newCharVar as described in step 4 7) Enooding and decoding examples: using an offset of 5 b. Decoding: AW, BhW, CPX, F9A G Enooding: Atodetghjklmnapgrstuvwxyz Fghjkmnopgrstuvwxyzabcde ABCOEFGHUKLMNOPORSTUVwxyz VWXYZABCDEFGHlJKLMNOPORstu For this project letters will be encoded or decoded by using the Cesar Cipher algorithm. This algorithm adds an offset to a letter far encoding and subtracts an aftset tor decading. If the offset value is 1, then for encoding. A B, B3C29A. If the ottset value is 1, then tor decoding. APZ BA, C7B 29Y Note that the letters wrap around when you reach either end of the alphabet. One way to look at the encoding or decoding is to look at two rows of the alphabet. The top row will be the character to encode or decode and the botom row will show the letter to use for the encoding or decoding. The bottom row will show the alphabet three times to make it easier to see what happens when encoding is used top row shifts right) or decoding is used (top row shifts lett Here is the initial start point with ofset 0. abcdefghijklnnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklnnoparstuvwxyz Here is what happens for encoding with a shitt of 7 (a becomes h, b becomes i, etc) abcdefghijklnnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklnnoparstuvwxyz Here is what happens for abcdefghijklnnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijklnnoparstuvwxyz abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz with a shift of 7 (h becomes a, i becomes b, etc) abcdefghijklnnopqrstuvwxyz Lower case letters will be used for the rest af the information, although it is simple to change the same algorithm for upper case letters First, read a character and determine if it is a letter. If it is a letter, then determine if it is upper case or lower case (use tunctions isalpha(char), islower(char) and isupperichar) from the cetype header file) The tollowing applies for lower case letters: Let charRead be the character variable holding the lower case letter read. For the asci character set, the nteger value representing the lower case letters are shown below 115 b 98k10116 97 106 S 108 u 110w 111X 100 m109 101 102 | o 103 104 105 118 120 121 122 112 114 These numeric values can be changed to 0 to 25 by subtracting 'a'trom charRead as shown below 18 k 1019 12 13 21 23 24 25 15 nfVar is an integer vaniable, and it can be assigned a value between 0 and 25 by the tollowing equation: intVar charRead-'a If charead contains 'g'then charRead- a is done using the integer variables representing g and 'a'or 103-97 6. When you add (encode) or subtract (decode) the offset fram this value, you get a new integer value that may still be in the range af 0 to 25 ar it may have to be converted back to a range ot 0 to 25. For example charRead is 'g' as above so intVar contains . If the offset value is 22, then we have the ollowing possibilibies For encoding: newintVar- intVar +22-2B For decoding: newIntVar-intvar-22--16 Both of these numbers are outside the range 0 to 25, so they have to be converted back to that range. can look at the shifting of the alphabet on page 1 to get an idea of what you will have to do. You Once newintVar is in the range of 0 to 25, that value can be added to 'a' to obtain the character to write (newchar) to the output file. newChar anewintVar For example, if charRead is 'g' and the oftset is 22 and we are encoding, newintvar 28, and this value has to be converted to the value between 0 and 25 that represents the character we want to encode to. The letter 'gencoded with offset of 22 shauld be converted to c' which means newintVar needs to be modified to a value of 2 (it is a simple math formula to do this conversion). So newCar-a'newintVar is assigning the numeric value of 972-99 to newChar and a character variable assigned an integer value of 99 is the letter c. Likewise, for decoding with the above example 'g' would be decoded to 'k' which means newintVar needs to be modified from -16 to 10. Once newIntVar has a numeric value between 0 and 25, its value is added to a' to obtain the asci character represented by that integer value - in this case 107 which is the letter k Same procedure is done with upper case letters - just replace a with 'A'and the ascii character integer values range trom 65 (A) to90 (Z) ] P7,in9.txt 13 12 Ftue ruxq ime QZOAPQP iuft mz arreqf ar 12 Egooqeergx pqoapuzs mrfqd rmuxqp agfbgf RUXQ ZMYQE iuxx dqegxf uz m dqmpmnxq ruxq_1234 !@#$ mnopqrstuvwxyzabcdefghijkl MNOPQRSTUVWXYZABCDEFGHIJKL Sample Solution Output Opening input file: /home/work/cpe211data/Project 07/P7_in9.txt Opening output file: Not/A/File.TXT Output file failed to open properly!! ==> Attempted to open file: Not/A/File.TXT Try *t Enter in the name of the output file: Not/A/File.TXT Output file failed to open properly!! ==> Attempted to open file: Not/A/File.TXT Try *t Enter in the name of the output file: not/an/input/file.txt Output file failed to open properly!! ==> Attempted to open file: not/an/input/file.txt Try *t Enter in the name of the output file: Project 07_output9.txt Contents of output file are below this line I This file was ENCODED with an offset of 12 Successful decoding after failed output FILE NAMES wil1 result in a readable l file--1234!@#$ I abcdefghijklmnoprstuvwxyz I ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPORSTUVWXYZ End Of Output File Contents













