Question
C++ - Using the STL For those of you going to study Computer Science and are thinking about the data structures class this is another
C++ - Using the STL
For those of you going to study Computer Science and are thinking about the data structures class this is another project will give you an introduction. There are two important data structures that you will learn and use. The first is a stack, it is a LIFO (Last In First Out) structure. You saw this in Lab 14. As a reminder, you can think of a stack like a stack of plates. You pile plates on top of each other when you put them away and you take a plate from the top of the pile when you need to use one. This functionality is called push (add to the top of the stack) and pop (remove from the top of stack). There is one last function that most stacks have. This function is called peek because it will allow you to see what is at the top of the stack without removing it.
The other popular data structure is called a queue. The queue is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure and you can think of it like standing in line at Disneyland. If you are fortunate enough to be first in line, then you are the first person to get on the ride. You will see the stack and the queue all over computers if you study operating systems. The stack is used to store and keep track of variables and the queue is used to store data that is waiting to be processed. This is just to name a couple ways they are used. In the operating system, tasks that are being scheduled to run are put into the queue. There is a slight difference in that many of these queues are called priority queues in that each task added to the queue is assigned a priority. The higher the priority a task has, the closer it gets to the front of the queue.
In this assignment you are going to create a priority queue class called priQue. To do this you could create a class that uses an array or a vector to store the items but then have to write a sort function and sort all of items in the queue based on their priority. This may not sound like a daunting task but you might as well use some of the built in functionality. As you recall from the lecture the STL has associative containers that sort the items as you insert them. This all works well with primitives but for the priQue class you are going to have to create a node that contains both data and the priority. What this means is that you are going to have to write some code to get the container class to sort on the priority and not the data. This is not too bad of a task. Consider the following code:
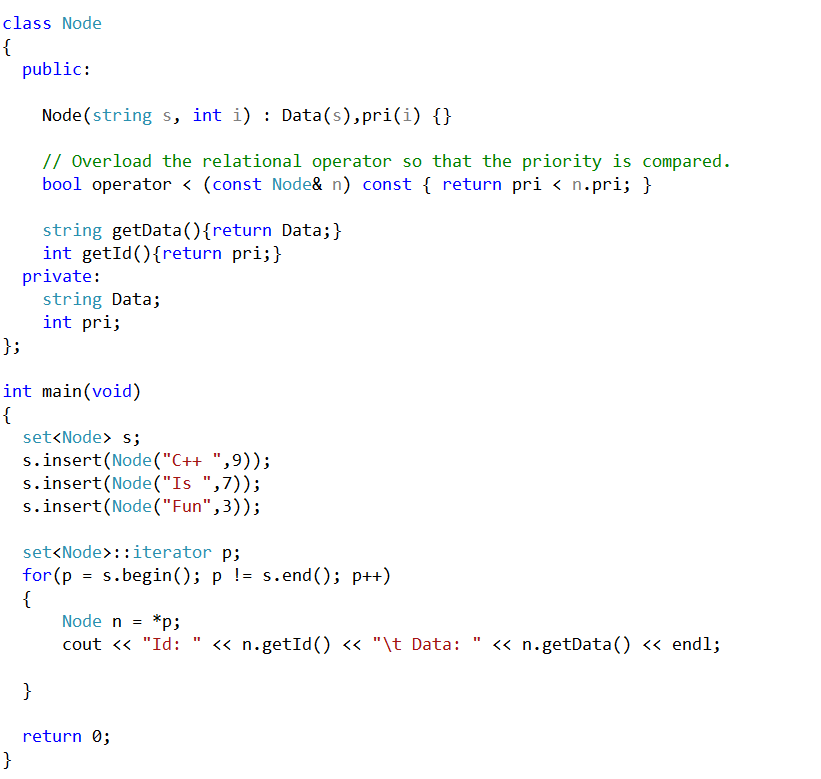
Here a class called Node has been created that will hold the priority and a string for the data. What is important about this code is the overloaded relational operator
pri
Class Details:
Your class should be constructed as a template class so that the type of data the queue operates on can easily be changed:
priQueue iQueue; // holds ints
priQueue sQueue; // holds string.
Your priority queue should be sorted by priority based on a value from 1 to 10. If a number is assigned that is outside the range of 1 to 10 you should give the element a value of 5. What this means is that each time an element is added to the queue it should be put in order by priority. If multiple elements are given the same priority their position relative to each other is unimportant as long as they are prioritized relative to other elements in the queue. Fortunately for you this is done for you simply by using the STL!
Your priQueue should have the following functionality:
enqueue - Add an element to the queue
dequeue - Remove element from the front of the queue
peek - Return value at front of queue do not remove it
size - Returns the number of items in the queue.
Specifics
You should modify the Node class so that it is a template type. This means the data section of your Node should have the ability to hold any type. The priority variable type should be an int.
Don't use a set!
If you were to run the example code and put in duplicate priorities, you would notice that the set does not allow for insertion of duplicate keys. This is a problem for us but fortunately the multiset does allow duplicate key values. So your priQueue class is going to be composed of a multiset not a set. The enqueue function should be adding a Node so that the data and the priority are coupled. This needs to be done so that the data and priority are related for sorting. Here is an example:
priQueue que;
que.enqueue("Hello", 3); que.enqueue("Goodbye", 9); // You are passing a string and an int but you should
//store a Node in the multiset.
string s = que.dequeue();
The string s at this point should hold "Goodbye" even though it was put in last because it has a higher priority.
LAB 14- TEMPLATE _______
MAIN.cpp
#include
#include "stack.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
Stack nums;
cout
for (int i = 1; i
{
cout
nums.push(i);
}
cout
cout
while (!nums.empty())
{
cout
nums.pop();
}
cout
cout
string f[] = { "apple", "banana", "orange", "pineapple" };
Stack fruits;
cout
for (int i = 0; i
{
cout
fruits.push(f[i]);
}
cout
cout
while (!fruits.empty())
{
cout
fruits.pop();
}
}
STACK.h
#ifndef stack_h
#define stack_h
#include
#include
#include
using std::exception;
using std::vector;
using std::string;
class StackException : public exception
{
private:
string message;
public:
StackException() : message("StackException") {}
StackException(string msg) : message(msg) {}
virtual const char *what() {
return message.c_str();
}
};
template
class Stack : public vector
{
public:
void push(T value)
{
this->push_back(value);
}
void pop()
{
if (this->empty())
throw StackException("Empty stack! Can't pop");
this->pop_back();
}
T peek()
{
if (this->empty())
throw StackException("Empty stack! Can't peek");
return this->back();
}
};
#endif
class Node public: Node (string s, int i) : Data(s),pri(i) { // Overload the relational operator so that the priority is compared. bool operator s; s.insert (Node("C++ ",9)); s.insert (Node("Is ",7)); s.insert (Node(" Fun",3)); setStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


