Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Calculating Flux for Hemispheres of Different Radii the integral. That is, d = || |d cos(0). where is the angle between E and dA
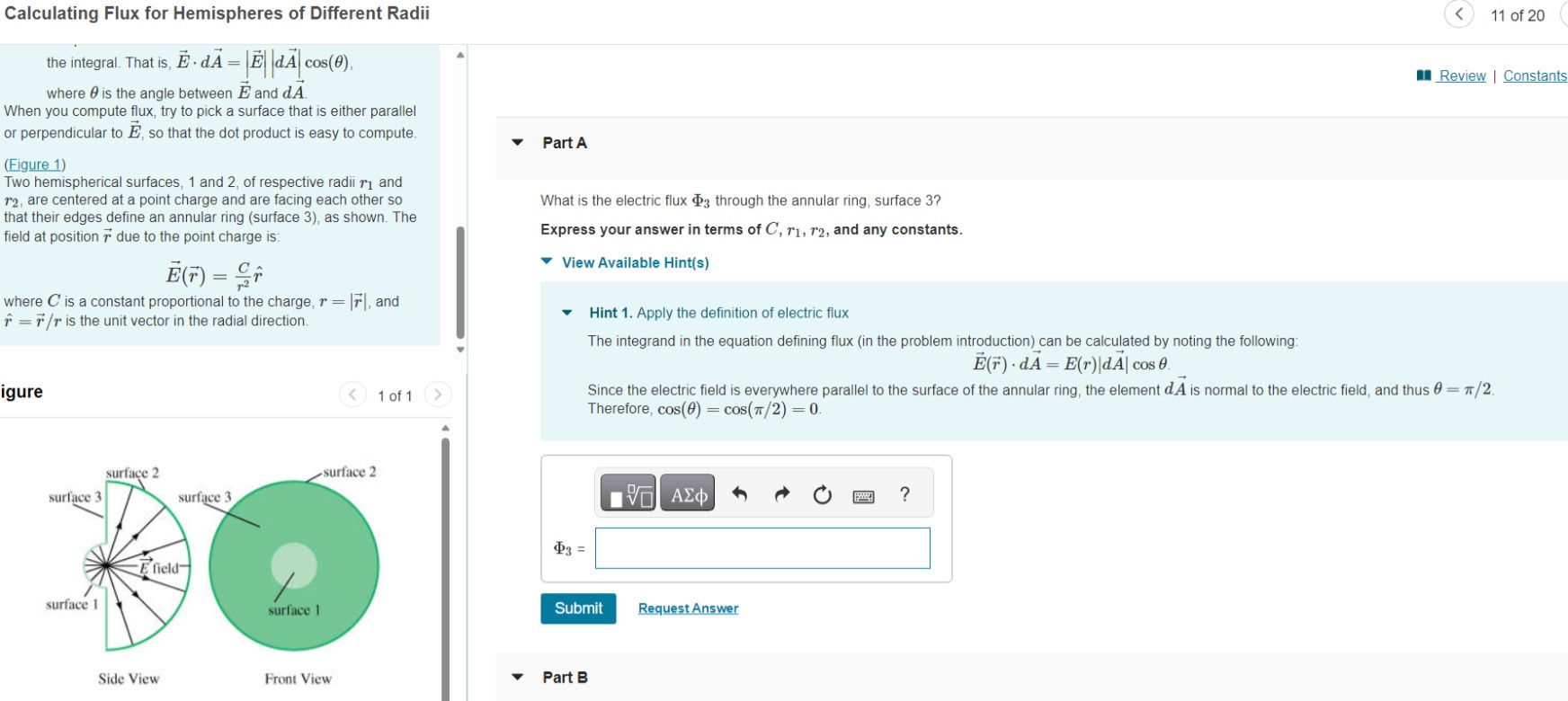
Calculating Flux for Hemispheres of Different Radii the integral. That is, d = || |d cos(0). where is the angle between E and dA When you compute flux, try to pick a surface that is either parallel or perpendicular to , so that the dot product is easy to compute. (Figure 1) Two hemispherical surfaces, 1 and 2, of respective radii and r2, are centered at a point charge and are facing each other so that their edges define an annular ring (surface 3), as shown. The field at position due to the point charge is: (T) = where C' is a constant proportional to the charge, r = [7], and * = */r is the unit vector in the radial direction. igure surface 3 surface 1 surface 2 surface 3 E field Side View surface 1 < surface 2 Front View 1 of 1 Part A What is the electric flux 3 through the annular ring, surface 3? Express your answer in terms of C, r1, 72, and any constants. View Available Hint(s) 3 = Hint 1. Apply the definition of electric flux The integrand in the equation defining flux (in the problem introduction) can be calculated by noting the following: (F) dA = E(r)|dA| cos 0. Submit Part B Since the electric field is everywhere parallel to the surface of the annular ring, the element dA is normal to the electric field, and thus 0 = /2. Therefore, cos(0) = cos(/2) = 0. VE ) Request Answer < ? 11 of 20 Review | Constants
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
A Electric flux through surfac...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


