Can I have answers with clear explanations? Thank you!
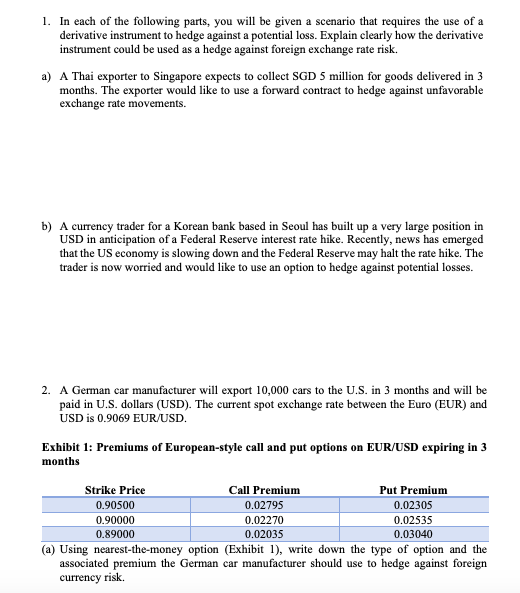

1. In each of the following parts, you will be given a scenario that requires the use of a derivative instrument to hedge against a potential loss. Explain clearly how the derivative instrument could be used as a hedge against foreign exchange rate risk. a) A Thai exporter to Singapore expects to collect SGD 5 million for goods delivered in 3 months. The exporter would like to use a forward contract to hedge against unfavorable exchange rate movements. b) A currency trader for a Korean bank based in Seoul has built up a very large position in USD in anticipation of a Federal Reserve interest rate hike. Recently, news has emerged that the US economy is slowing down and the Federal Reserve may halt the rate hike. The trader is now worried and would like to use an option to hedge against potential losses. 2. A German car manufacturer will export 10,000 cars to the U.S. in 3 months and will be paid in U.S. dollars (USD). The current spot exchange rate between the Euro (EUR) and USD is 0.9069 EUR/USD. Exhibit 1: Premiums of European-style call and put options on EUR/USD expiring in 3 months Strike Price Call Premium Put Premium 0.90500 0.02795 0.02305 0.90000 0.02270 0.02535 0.89000 0.02035 0.03040 (a) Using nearest-the-money option (Exhibit 1), write down the type of option and the associated premium the German car manufacturer should use to hedge against foreign currency risk. (b) In 3 months, if the spot exchange rate is 0.91450 EUR/USD, compute the intrinsic value of the option you have selected in part (a). Would the German car manufacturer exercise this option? 3. Which of the following is the most likely advantage of investing in currency futures contracts over investing in currency forward contracts? A. There is more flexibility in contract size. B. There is more liquidity. C. There are more currencies available. 4. Why is a currency put or call option not profitable to exercise when it is at-the-money (ATM)? A. When an option is ATM, the exchange market charges higher transaction fees to trade options to prevent arbitrage opportunities. B. When an option is ATM, the spot price equals the strike price but the premium is not recovered if exercised. C. When an option is ATM, the spot price will always be higher (lower) than the strike price for the put (call) option, and hence there is no profit to be made. 1. In each of the following parts, you will be given a scenario that requires the use of a derivative instrument to hedge against a potential loss. Explain clearly how the derivative instrument could be used as a hedge against foreign exchange rate risk. a) A Thai exporter to Singapore expects to collect SGD 5 million for goods delivered in 3 months. The exporter would like to use a forward contract to hedge against unfavorable exchange rate movements. b) A currency trader for a Korean bank based in Seoul has built up a very large position in USD in anticipation of a Federal Reserve interest rate hike. Recently, news has emerged that the US economy is slowing down and the Federal Reserve may halt the rate hike. The trader is now worried and would like to use an option to hedge against potential losses. 2. A German car manufacturer will export 10,000 cars to the U.S. in 3 months and will be paid in U.S. dollars (USD). The current spot exchange rate between the Euro (EUR) and USD is 0.9069 EUR/USD. Exhibit 1: Premiums of European-style call and put options on EUR/USD expiring in 3 months Strike Price Call Premium Put Premium 0.90500 0.02795 0.02305 0.90000 0.02270 0.02535 0.89000 0.02035 0.03040 (a) Using nearest-the-money option (Exhibit 1), write down the type of option and the associated premium the German car manufacturer should use to hedge against foreign currency risk. (b) In 3 months, if the spot exchange rate is 0.91450 EUR/USD, compute the intrinsic value of the option you have selected in part (a). Would the German car manufacturer exercise this option? 3. Which of the following is the most likely advantage of investing in currency futures contracts over investing in currency forward contracts? A. There is more flexibility in contract size. B. There is more liquidity. C. There are more currencies available. 4. Why is a currency put or call option not profitable to exercise when it is at-the-money (ATM)? A. When an option is ATM, the exchange market charges higher transaction fees to trade options to prevent arbitrage opportunities. B. When an option is ATM, the spot price equals the strike price but the premium is not recovered if exercised. C. When an option is ATM, the spot price will always be higher (lower) than the strike price for the put (call) option, and hence there is no profit to be made








