Question: Can someone help me understand how to do this Here, you will make use of some statistical functions to determine critical values for distributions. Unless
Can someone help me understand how to do this
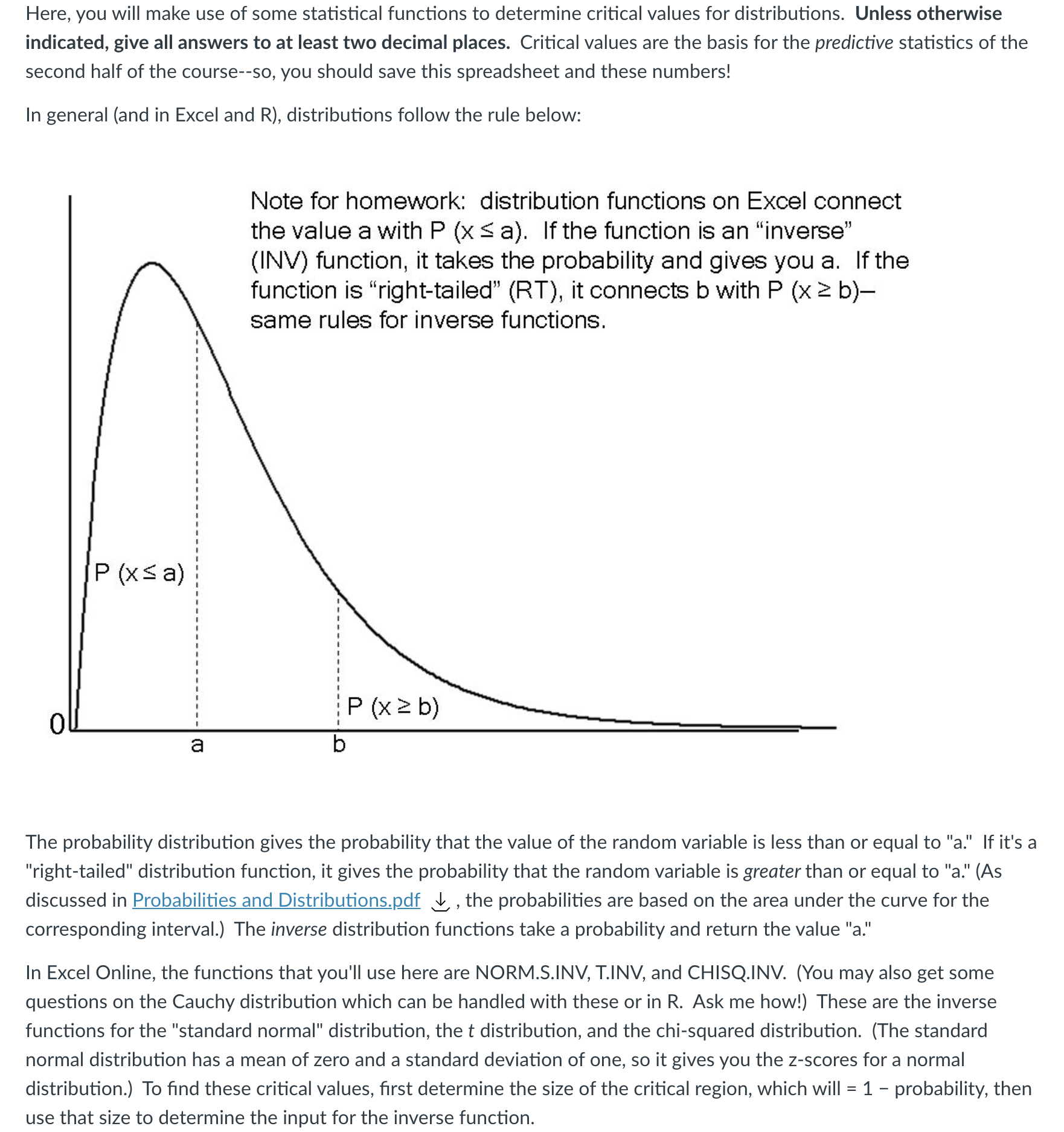
Here, you will make use of some statistical functions to determine critical values for distributions. Unless otherwise indicated, give all answers to at least two decimal places. Critical values are the basis for the predictive statistics of the second half of the course--so, you should save this spreadsheet and these numbers! In general (and in Excel and R), distributions follow the rule below: Note for homework: distribution functions on Excel connect the value a with P (x s a). If the function is an \"inverse" (INV) function, it takes the probability and gives you a. If the function is \"right-tailed" (RT), it connects b with P (x 2 b) same rules for inverse functions. m _-_-___---_-_-_---_-_----__-_----_-____--_---_ The probability distribution gives the probability that the value of the random variable is less than or equal to "a." If it's a "right-tailed" distribution function, it gives the probability that the random variable is greater than or equal to "a." (As discussed in Probabilities and Distributions.pd_f 3L , the probabilities are based on the area under the curve for the corresponding interval.) The inverse distribution functions take a probability and return the value "a." In Excel Online, the functions that you'll use here are NORM.S.|NV, T.|NV, and CHISQJNV. (You may also get some questions on the Cauchy distribution which can be handled with these or in R. Ask me how!) These are the inverse functions for the "standard normal" distribution, the t distribution, and the chi-squared distribution. (The standard normal distribution has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one, so it gives you the z-scores for a normal distribution.) To nd these critical values, rst determine the size of the critical region, which will = 1 - probability, then use that size to determine the input for the inverse function. In R, the function that determines critical values is the quantile function, which takes as input a list of probabilities (so you'll have to use c() to make a list) and returns a list of critical values. In R Assignment 5 (Probability Distributions)_,* you use dsomething to generate the probability distribution; you use qsomething to get the critical values. (Example: you use dnorm to generate a normal distribution and you use qnorm to get the critical values for a normal distribution.) You'll determine the probabilities to enter using the same method described in the last paragraph. Things to remember: the difference between a left-tailed and right-tailed critical value; for a two-tailed critical value, you must cut the critical region in half; normal and t distributions are symmetrical. This will all be easier if you draw the distributions and the critical regions before you start! *This will be released Sunday night for students in the Monday lab section, so it will be available to you soon. Again, you can take this again if you make a mistake, but if you do, that time counts. D Question 1 1.25 pts Find the two-tailed critical values for a t distribution at 95% probability and 16 degrees of freedom. (There will be a positive and negative critical value here. Only give the positive number.) D Question 2 1.25 pts Find the two-tailed critical values for a normal distribution at 99.9% probability. (There will be a positive and negative critical value here. Only give the positive number.) Question 3 1.25 pts Find the two-tailed critical values for a t distribution at 95% probability and 9 degrees of freedom. (There will be a positive and negative critical value here. Only give the positive number.) Question 4 1.25 pts Find the two-tailed critical values for a chi-squared distribution at 99% probability and 16 degrees of freedom, and give the higher critical value as your answer. Question 5 1.25 pts Find the two-tailed critical values for a chi-squared distribution at 99% probability and 16 degrees of freedom, and give the lower critical value as your answer. S D Question 6 1.25 pts Find the left-tailed critical value for a Cauchy distribution at 95% probability. D Question 7 1.25 pts Find the left-tailed critical value for a chi-squared distribution at 99% probability and 11 degrees of freedom. D Question 8 1.25 pts Find the two-tailed critical values for a Cauchy distribution at 99% probability. (There will be a positive and negative critical value here. Only give the positive number.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


