Question
Bob Marsden manages the Victorian plant of George Manufacturing. He has been approached by a representative of Garfield Engineering regarding the possible replacement of a
Bob Marsden manages the Victorian plant of George Manufacturing. He has been approached by a representative of Garfield Engineering regarding the possible replacement of a large piece of manufacturing equipment that George uses in its process with a more efficient model. While the representative made some compelling arguments in favour of replacing the 3-year-old equipment, Bob is hesitant. He is hoping to be promoted next year to manager of the larger New South Wales plant, and he knows that the accrual-basis net operating income of the Victorian plant will be evaluated closely as part of the promotion decision. The following information is available concerning the equipment replacement decision:
The historical cost of the old machine is $300,000. It has a current carrying amount of $120,000, two remaining years of useful life and a market value of $72,000. Annual depreciation expense is $60,000. It is expected to have a salvage value of $0 at the end of its useful life.
The new equipment will cost $180,000. It will have a two-year useful life and a $0 salvage value. George uses straight-line depreciation on all equipment. The new equipment will reduce electricity costs by $35,000 per year and will reduce direct manufacturing labour costs by $30,000 per year.
For simplicity, ignore income taxes and the time value of money.
Required: 1. Assume that Bob Marsden’s priority is to receive the promotion, and he makes the equipment replacement decision based on next year’s accrual-based net operating income. Which alternative would he choose? Show your calculations. (4 marks)
2. What are the relevant factors in the decision? Which alternative is in the best interest of the company over the next two years? Show your calculations. (4 Marks)
3. At what cost of the new equipment would Bob Marsden be willing to purchase it? Explain. (4 Marks)
Chan uses a standard costing in its manufacturing plant for car parts. The standard cost of a particular car part, based on a denominator level of 4000 output units per year, included 6 machine hours of variable manufacturing overhead at $8 per hour and 6 machine hours of fixed manufacturing overhead at $15 per hour. Actual output produced was 4400 units. Variable manufacturing overhead incurred was $245,000. Fixed manufacturing overhead incurred was $373,000.Actual machine hours were 28,400.
1. Prepare an analysis of all variable manufacturing overhead and fixed manufacturing overhead variances, using a 4 variance analysis (4marks)
2. Describe how individual fixed manufacturing overhead items are controlled from day to day.(2marks)
3. Discuss possible causes of the fixed manufacturing overhead variance.(4 marks)
 _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 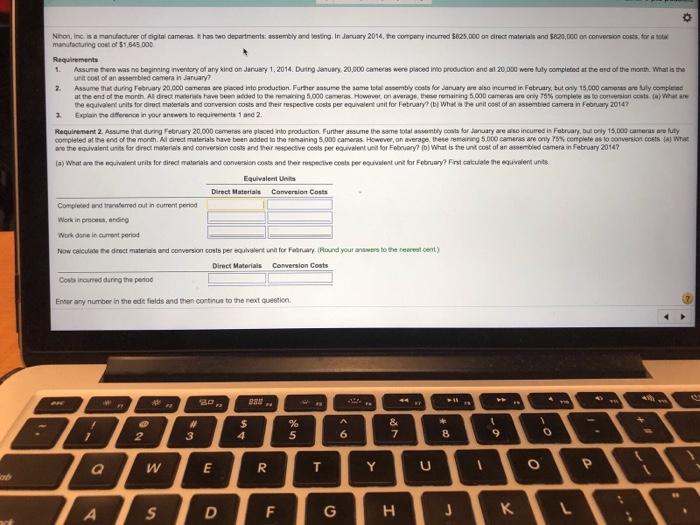
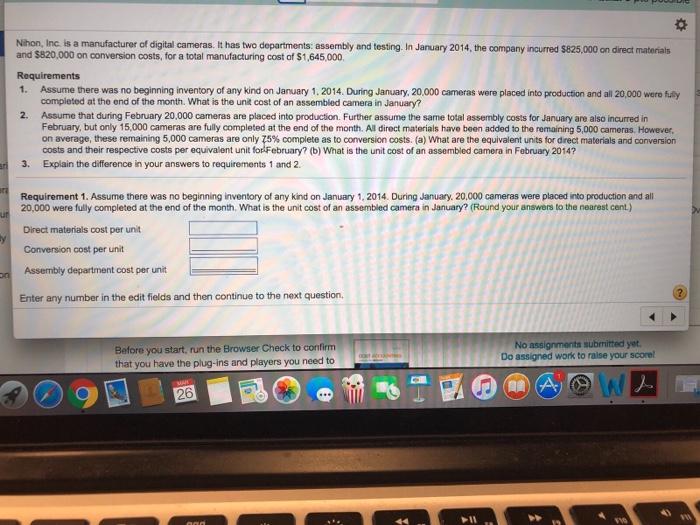
Nihon, Inc. is a manufacturer of digital cameras. It has two departments: assembly and testing. In January 2014, the company incurred $825,000 on direct materials and $820,000 on conversion costs, for a total manufacturing cost of $1,645,000. Requirements 1. Assume there was no beginning inventory of any kind on January 1, 2014. During January, 20,000 cameras were placed into production and all 20,000 were fully completed at the end of the month. What is the unit cost of an assembled camera in January? 2. Assume that during February 20,000 cameras are placed into production. Further assume the same total assembly costs for January are also incurred in February, but only 15,000 cameras are fully completed at the end of the month. All direct materials have been added to the remaining 5,000 cameras. However, on average, these remaining 5,000 cameras are only 75% complete as to conversion costs. (a) What are the equivalent units for direct materials and conversion costs and their respective costs per equivalent unit for February? (b) What is the unit cost of an assembled camera in February 2014? 3. Explain the difference in your answers to requirements 1 and 2. Requirement 1. Assume there was no beginning inventory of any kind on January 1, 2014. During January, 20,000 cameras were placed into production and all 20,000 were fully completed at the end of the month. What is the unit cost of an assembled camera in January? (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) ut Direct materials cost per unit By Conversion cost per unit on Assembly department cost per unit Enter any number in the edit fields and then continue to the next question. Before you start, run the Browser Check to confirm that you have the plug-ins and players you need to 26 No assignments submitted yet. Do assigned work to raise your score! A A
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


