Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
can you answer the question c part and and be and show all of the work. these are the unit conversions to solve the problem

can you answer the question c part and and be and show all of the work.
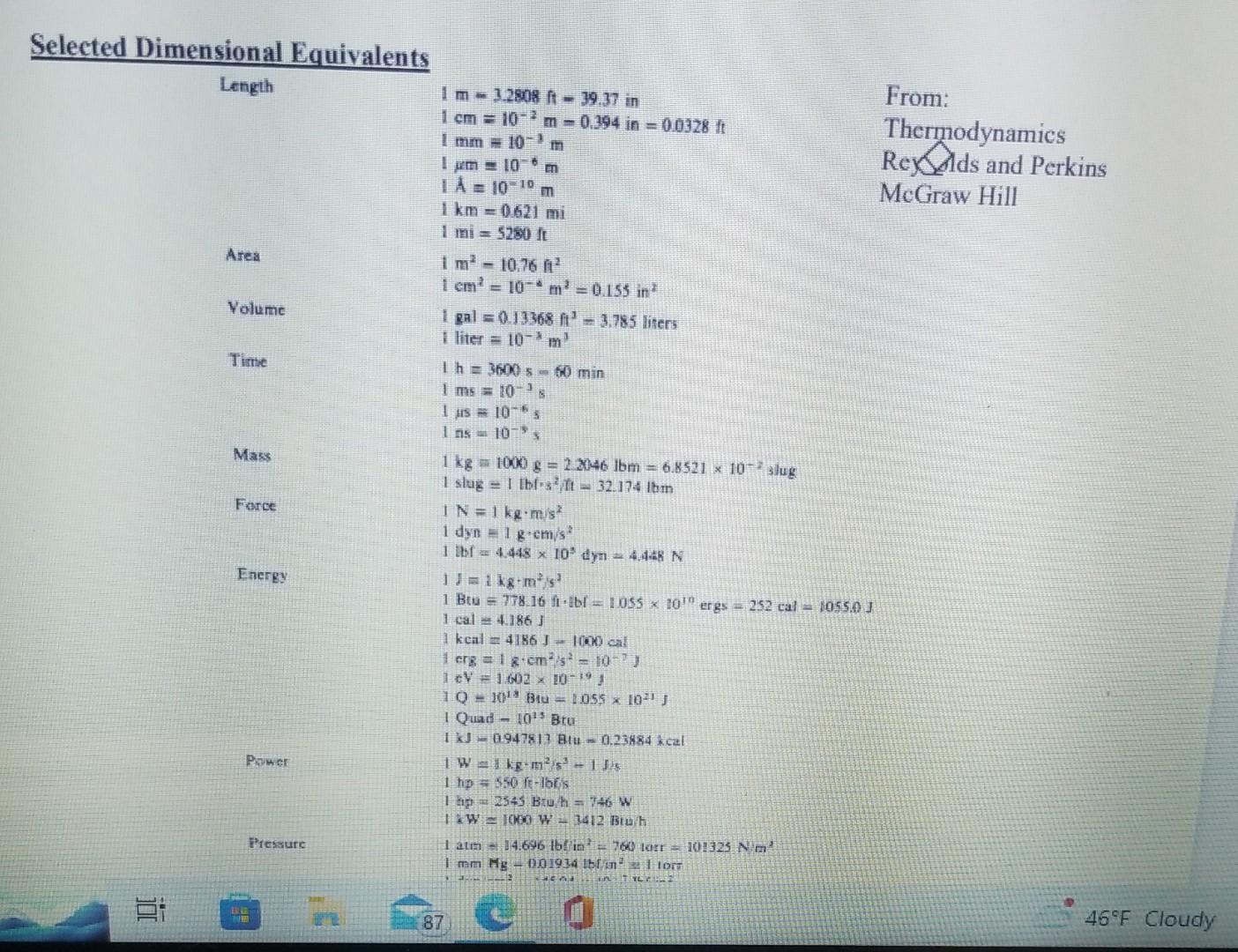
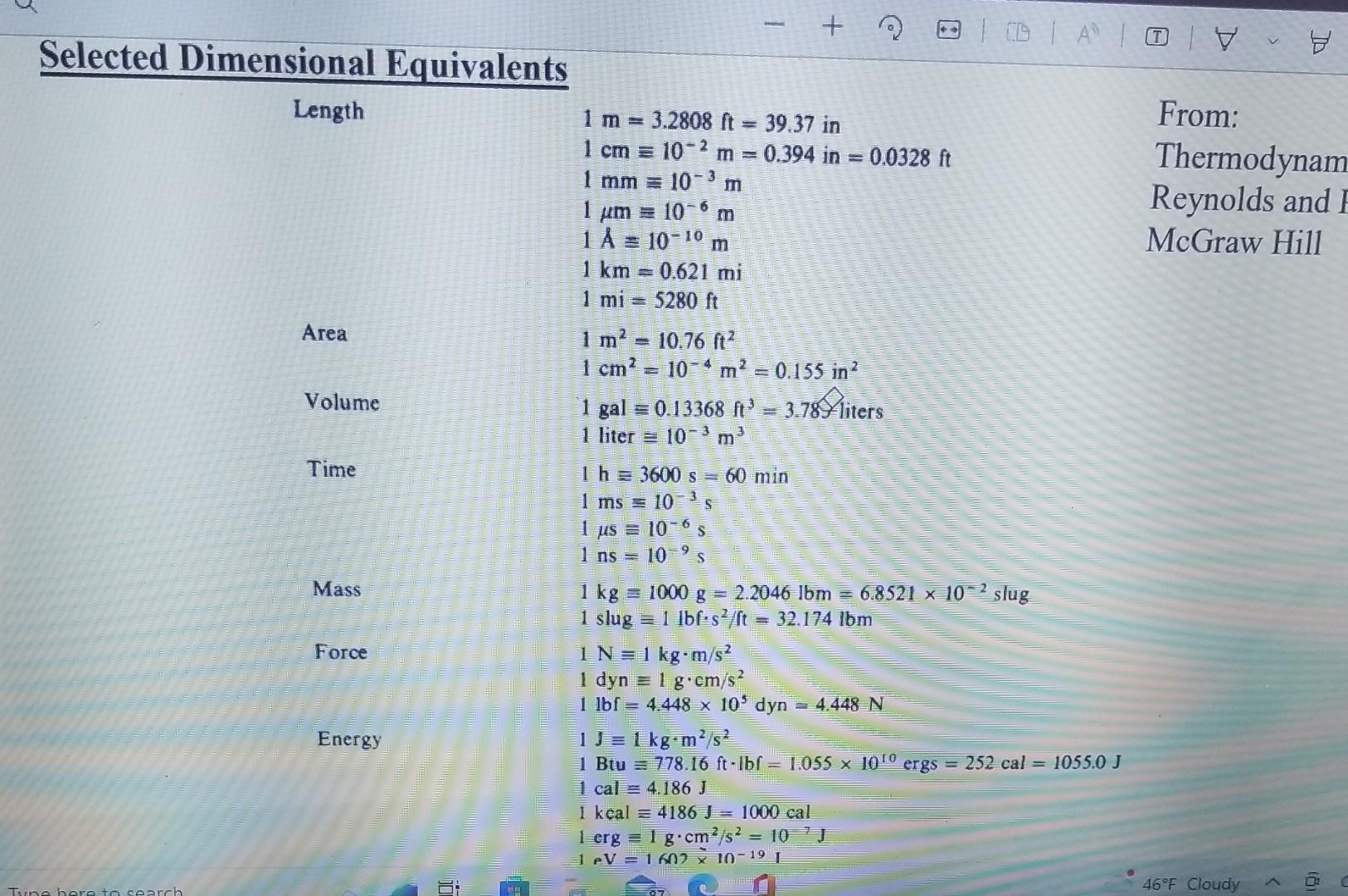


these are the unit conversions to solve the problem the final units have to be in miles or km?
1. A 1-ton (2000lbm) spacecraft is in a circular orbit around the Earth. Its velocity relative to the center of the Earth is 17,000MPH (miles per hour). a) What is its velocity, v, in m/s (meters /sec) ? Ans: 7,600 b) What is the kinetic energy, Ek, of the spacecraft relative to the center of the Earth in units of: (i) ftlbf ? Ans: 1.931010 (ii) Btu? Ans: 24.8106 (iii) kW-hrs? Ans: 7.27103 (iv) HP-hr? Ans: 9.75103 c) The centrifugal force, Fc=Msv2/r, is equal to the gravitational force, Fg=kgMsMd/r2, acting on the orbiting spacecraft, where: Ms= mass of the spacecraft (1 ton) Me= mass of the Earth (5.981024kg) kg= universal gravitational constant (6.671011m3/kgs2) r= separation distance between center of mass of the Earth and center of mass of the spacecraft If the mean diameter of the Earth, dc, is 12,742km, find the height, h, of the spacecraft above the surface of the Earth in units of: (i) km (ii) miles Ans: 332 Selected Dimensional Equivalents Length1m=3.2808ft39.37inFrom:1cm=102m=0.394in=0.0328ftThermodynamics1mm=103m1m=106m1A=1010mMcGrawHill1km=0.621mi1mi=5280ftArea1m210.76m21cm2=106m2=0.155in2Volume1gal=0.13368f3=3.785liters1liter=10xm3Time1h=3600s60min1ms=103sI1is=106s1as=104sMass1kg=1000g=22046lbm=6.8521107,slug1slug=1lbfs2ft32.174lbm1N=1kgm/s21dyn=1gcm/s31bbt=4.448103dyn=4.448NjJ=1kgm2/s21Btu=778.16ftbbr=10ss1010ergs=252cal=1055JJ1cal=4.186J1kcal=4186J1000cal1crg=1gcm2/s2=107}1cV=1.6021019J1Q=1018B14=1.0551021J1Quad-1013Btu1kJ0.947813Btu=0.23884kcal1w=1kgm2/s31js1thp=s50fe-lofisithp=2545Bru/h=746W1kw=1000w3412BB/h1atm+34.696lb/cm2=760larr=101325Nmm21mmHg001934ltm21Iorr Selected Dimensional Equivalents Force 1 slug 1lbfs2/ft=32.174lbm 1N1kgm/s2 1dyn1gcm/s2 1lbf=4.448105dyn=4.448N Energy 1J1kgm2/s2 1Btu778.16ftlbf=1.0551010ergs=252cal=1055.0J 1cal4.186J 1kcal4186J=1000cal 1erg1gcm2/s2=107J 1eV1.6021019J 1Q1018Btu=1.0556021J 1Quad=1015Btu 1kJ=0.947813Btu=0.23884kcal Power 1W1kgm2/s3=1J/s 1hp550ftlbf/s 1hp=2545Btu/h=746W 1kW1000W=3412Btu/h Pressure 1atm14.696lbf/in2=760 torr =101325N/m2 1mmHg=0.01934lbf/in21 torr 1dyn/cm2=145.04107lbf/in2 1 bar 105N/m2=14.504lbf/in2=106dyn/cm2 1106mHg=103mmHg 1Pa1N/m2=1.4504104lbf/in2 1 in Hg3376.8N/m2 1 in H2O248.8N/m2 Power per unit area i W/m2=0.3170Btu/(hft2)=0.85984kcal/(hm2) Heat-transfer coefficient 1W/(m2C)=0.1761Btu/(hft2F)=0.85984kcal/(hm2C) 1 bar 10N/m2=14.504101/m10ayn/cm 1106mHg=103mmHg 1Pa1N/m2=1.4504104lbf/in2 1 in Hg3376.8N/m2 1 in H2O248.8N/m2 1W/m2=0.3170Btu/(hft2)=0.85984kcal/(hm2) 1W/(m2C)=0.1761Btu/(hft2F)=0.85984kcal/(hm2C) 1kJ/kg=0.4299Btu/lbm=0.23884kcal/kg 1kJ/(kgC)=0.23884Btu/(lbmF)=0.23884kcal/(kgC) 1W/(mC)=0.5778Btu(hftF)=0.85984kcal/(hmC) 1kg/(ms)=1Ns/m2=0.6720lbm/(fts)=10 Poise C=1.8F 0C corresponds to 32F,273.16K, and 491.69R 1G1g1/2/(cm1/2s) 1G=103C/(ms) for M 1G=(1/4)103C/(ms) for H 1G=104T for B 1T1kg/(Cs) 1. A 1-ton (2000lbm) spacecraft is in a circular orbit around the Earth. Its velocity relative to the center of the Earth is 17,000MPH (miles per hour). a) What is its velocity, v, in m/s (meters /sec) ? Ans: 7,600 b) What is the kinetic energy, Ek, of the spacecraft relative to the center of the Earth in units of: (i) ftlbf ? Ans: 1.931010 (ii) Btu? Ans: 24.8106 (iii) kW-hrs? Ans: 7.27103 (iv) HP-hr? Ans: 9.75103 c) The centrifugal force, Fc=Msv2/r, is equal to the gravitational force, Fg=kgMsMd/r2, acting on the orbiting spacecraft, where: Ms= mass of the spacecraft (1 ton) Me= mass of the Earth (5.981024kg) kg= universal gravitational constant (6.671011m3/kgs2) r= separation distance between center of mass of the Earth and center of mass of the spacecraft If the mean diameter of the Earth, dc, is 12,742km, find the height, h, of the spacecraft above the surface of the Earth in units of: (i) km (ii) miles Ans: 332 Selected Dimensional Equivalents Length1m=3.2808ft39.37inFrom:1cm=102m=0.394in=0.0328ftThermodynamics1mm=103m1m=106m1A=1010mMcGrawHill1km=0.621mi1mi=5280ftArea1m210.76m21cm2=106m2=0.155in2Volume1gal=0.13368f3=3.785liters1liter=10xm3Time1h=3600s60min1ms=103sI1is=106s1as=104sMass1kg=1000g=22046lbm=6.8521107,slug1slug=1lbfs2ft32.174lbm1N=1kgm/s21dyn=1gcm/s31bbt=4.448103dyn=4.448NjJ=1kgm2/s21Btu=778.16ftbbr=10ss1010ergs=252cal=1055JJ1cal=4.186J1kcal=4186J1000cal1crg=1gcm2/s2=107}1cV=1.6021019J1Q=1018B14=1.0551021J1Quad-1013Btu1kJ0.947813Btu=0.23884kcal1w=1kgm2/s31js1thp=s50fe-lofisithp=2545Bru/h=746W1kw=1000w3412BB/h1atm+34.696lb/cm2=760larr=101325Nmm21mmHg001934ltm21Iorr Selected Dimensional Equivalents Force 1 slug 1lbfs2/ft=32.174lbm 1N1kgm/s2 1dyn1gcm/s2 1lbf=4.448105dyn=4.448N Energy 1J1kgm2/s2 1Btu778.16ftlbf=1.0551010ergs=252cal=1055.0J 1cal4.186J 1kcal4186J=1000cal 1erg1gcm2/s2=107J 1eV1.6021019J 1Q1018Btu=1.0556021J 1Quad=1015Btu 1kJ=0.947813Btu=0.23884kcal Power 1W1kgm2/s3=1J/s 1hp550ftlbf/s 1hp=2545Btu/h=746W 1kW1000W=3412Btu/h Pressure 1atm14.696lbf/in2=760 torr =101325N/m2 1mmHg=0.01934lbf/in21 torr 1dyn/cm2=145.04107lbf/in2 1 bar 105N/m2=14.504lbf/in2=106dyn/cm2 1106mHg=103mmHg 1Pa1N/m2=1.4504104lbf/in2 1 in Hg3376.8N/m2 1 in H2O248.8N/m2 Power per unit area i W/m2=0.3170Btu/(hft2)=0.85984kcal/(hm2) Heat-transfer coefficient 1W/(m2C)=0.1761Btu/(hft2F)=0.85984kcal/(hm2C) 1 bar 10N/m2=14.504101/m10ayn/cm 1106mHg=103mmHg 1Pa1N/m2=1.4504104lbf/in2 1 in Hg3376.8N/m2 1 in H2O248.8N/m2 1W/m2=0.3170Btu/(hft2)=0.85984kcal/(hm2) 1W/(m2C)=0.1761Btu/(hft2F)=0.85984kcal/(hm2C) 1kJ/kg=0.4299Btu/lbm=0.23884kcal/kg 1kJ/(kgC)=0.23884Btu/(lbmF)=0.23884kcal/(kgC) 1W/(mC)=0.5778Btu(hftF)=0.85984kcal/(hmC) 1kg/(ms)=1Ns/m2=0.6720lbm/(fts)=10 Poise C=1.8F 0C corresponds to 32F,273.16K, and 491.69R 1G1g1/2/(cm1/2s) 1G=103C/(ms) for M 1G=(1/4)103C/(ms) for H 1G=104T for B 1T1kg/(Cs)Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


