Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Can you give reasons/calculations for all the answers Try 4b Data entry in colored cells only. If colour formatting error, scroll up and down to
Can you give reasons/calculations for all the answers
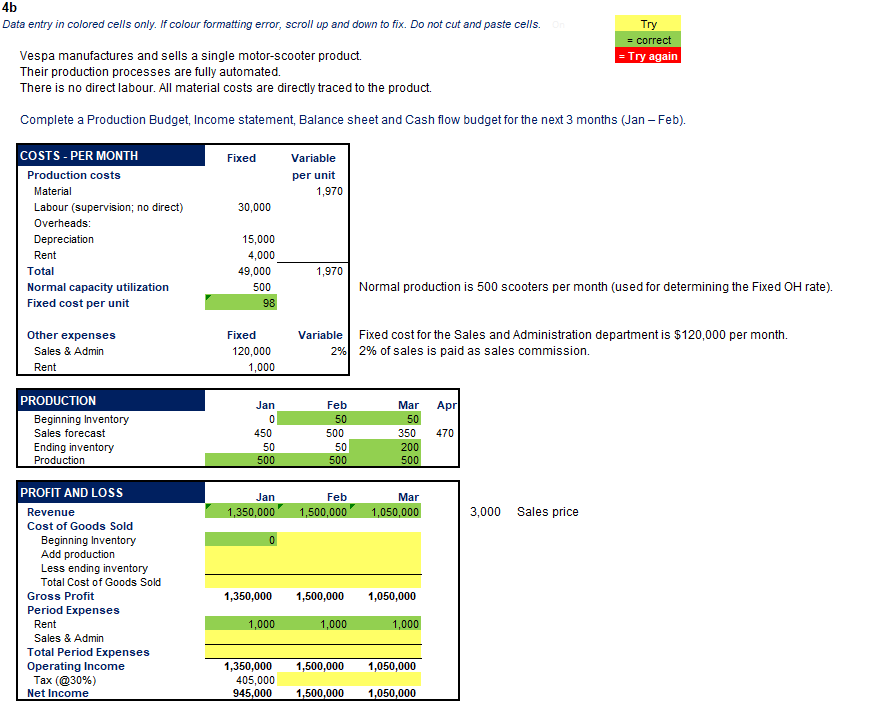
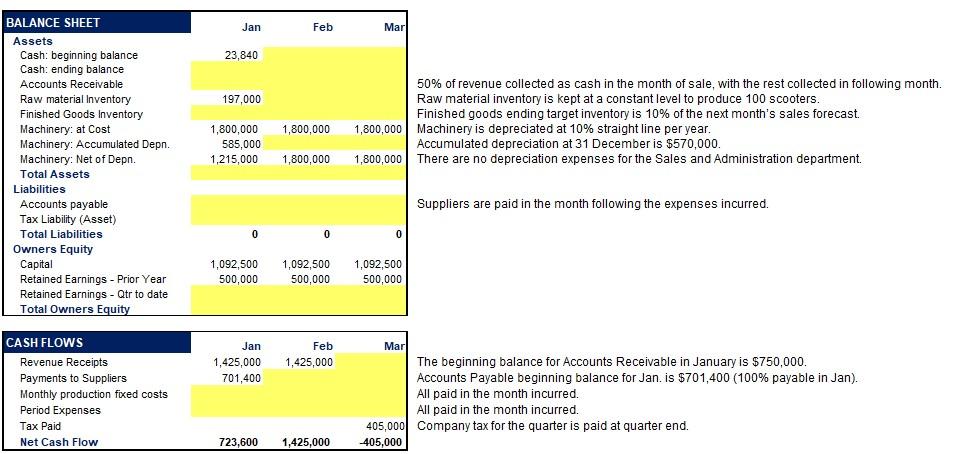
Try 4b Data entry in colored cells only. If colour formatting error, scroll up and down to fix. Do not cut and paste cells. Vespa manufactures and sells a single motor-scooter product. Their production processes are fully automated. There is no direct labour. All material costs are directly traced to the product. = correct =Try again Complete a Production Budget, Income statement, Balance sheet and Cash flow budget for the next 3 months (Jan-Feb). Fixed Variable per unit 1,970 30,000 COSTS - PER MONTH Production costs Material Labour (supervision; no direct) Overheads: Depreciation Rent Total Normal capacity utilization Fixed cost per unit 15,000 4,000 49,000 500 98 1,970 Normal production is 500 scooters per month (used for determining the Fixed OH rate). Other expenses Sales & Admin Fixed 120,000 1,000 Variable Fixed cost for the Sales and Administration department is $120,000 per month. 2% 2% of sales is paid as sales commission. Rent Apr PRODUCTION Beginning Inventory Sales forecast Ending inventory Production Jan 0 450 50 500 Feb 50 500 50 500 Mar 50 350 200 500 470 Jan 1,350,000 Feb 1,500,000 Mar 1,050,000 3,000 Sales price 0 PROFIT AND LOSS Revenue Cost of Goods Sold Beginning Inventory Add production Less ending inventory Total Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Period Expenses Rent Sales & Admin Total Period Expenses Operating Income Tax (@30%) Net Income 1,350,000 1,500,000 1,050,000 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,500,000 1,050,000 1,350,000 405,000 945,000 1,500,000 1,050,000 Jan Feb Mar 23,840 197,000 50% of revenue collected as cash in the month of sale, with the rest collected in following month. Raw material inventory is kept at a constant level to produce 100 scooters. Finished goods ending target inventory is 10% of the next month's sales forecast 1,800,000 Machinery is depreciated at 10% straight line per year. Accumulated depreciation at 31 December is $570,000. 1,800,000 There are no depreciation expenses for the Sales and Administration department. 1,800,000 585,000 1,215,000 1,800,000 1,800,000 BALANCE SHEET Assets Cash: beginning balance Cash: ending balance Accounts Receivable Raw material Inventory Finished Goods Inventory Machinery: at Cost Machinery: Accumulated Depn. Machinery: Net of Depn. Total Assets Liabilities Accounts payable Tax Liability (Asset) Total Liabilities Owners Equity Capital Retained Earnings - Prior Year Retained Earnings - Qtr to date Total Owners Equity Suppliers are paid in the month following the expenses incurred. 0 0 0 1,092,500 500,000 1,092,500 500,000 1,092,500 500,000 Jan 1,425,000 701,400 Feb 1,425,000 CASH FLOWS Revenue Receipts Payments to Suppliers Monthly production fixed costs Period Expenses Tax Paid Net Cash Flow Mar The beginning balance for Accounts Receivable in January is $750,000. Accounts Payable beginning balance for Jan. is $701,400 (100% payable in Jan). All paid in the month incurred. All paid in the month incurred. 405,000 Company tax for the quarter is paid at quarter end. -405,000 723,600 1,425,000 Try 4b Data entry in colored cells only. If colour formatting error, scroll up and down to fix. Do not cut and paste cells. Vespa manufactures and sells a single motor-scooter product. Their production processes are fully automated. There is no direct labour. All material costs are directly traced to the product. = correct =Try again Complete a Production Budget, Income statement, Balance sheet and Cash flow budget for the next 3 months (Jan-Feb). Fixed Variable per unit 1,970 30,000 COSTS - PER MONTH Production costs Material Labour (supervision; no direct) Overheads: Depreciation Rent Total Normal capacity utilization Fixed cost per unit 15,000 4,000 49,000 500 98 1,970 Normal production is 500 scooters per month (used for determining the Fixed OH rate). Other expenses Sales & Admin Fixed 120,000 1,000 Variable Fixed cost for the Sales and Administration department is $120,000 per month. 2% 2% of sales is paid as sales commission. Rent Apr PRODUCTION Beginning Inventory Sales forecast Ending inventory Production Jan 0 450 50 500 Feb 50 500 50 500 Mar 50 350 200 500 470 Jan 1,350,000 Feb 1,500,000 Mar 1,050,000 3,000 Sales price 0 PROFIT AND LOSS Revenue Cost of Goods Sold Beginning Inventory Add production Less ending inventory Total Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Period Expenses Rent Sales & Admin Total Period Expenses Operating Income Tax (@30%) Net Income 1,350,000 1,500,000 1,050,000 1,000 1,000 1,000 1,500,000 1,050,000 1,350,000 405,000 945,000 1,500,000 1,050,000 Jan Feb Mar 23,840 197,000 50% of revenue collected as cash in the month of sale, with the rest collected in following month. Raw material inventory is kept at a constant level to produce 100 scooters. Finished goods ending target inventory is 10% of the next month's sales forecast 1,800,000 Machinery is depreciated at 10% straight line per year. Accumulated depreciation at 31 December is $570,000. 1,800,000 There are no depreciation expenses for the Sales and Administration department. 1,800,000 585,000 1,215,000 1,800,000 1,800,000 BALANCE SHEET Assets Cash: beginning balance Cash: ending balance Accounts Receivable Raw material Inventory Finished Goods Inventory Machinery: at Cost Machinery: Accumulated Depn. Machinery: Net of Depn. Total Assets Liabilities Accounts payable Tax Liability (Asset) Total Liabilities Owners Equity Capital Retained Earnings - Prior Year Retained Earnings - Qtr to date Total Owners Equity Suppliers are paid in the month following the expenses incurred. 0 0 0 1,092,500 500,000 1,092,500 500,000 1,092,500 500,000 Jan 1,425,000 701,400 Feb 1,425,000 CASH FLOWS Revenue Receipts Payments to Suppliers Monthly production fixed costs Period Expenses Tax Paid Net Cash Flow Mar The beginning balance for Accounts Receivable in January is $750,000. Accounts Payable beginning balance for Jan. is $701,400 (100% payable in Jan). All paid in the month incurred. All paid in the month incurred. 405,000 Company tax for the quarter is paid at quarter end. -405,000 723,600 1,425,000Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


