Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
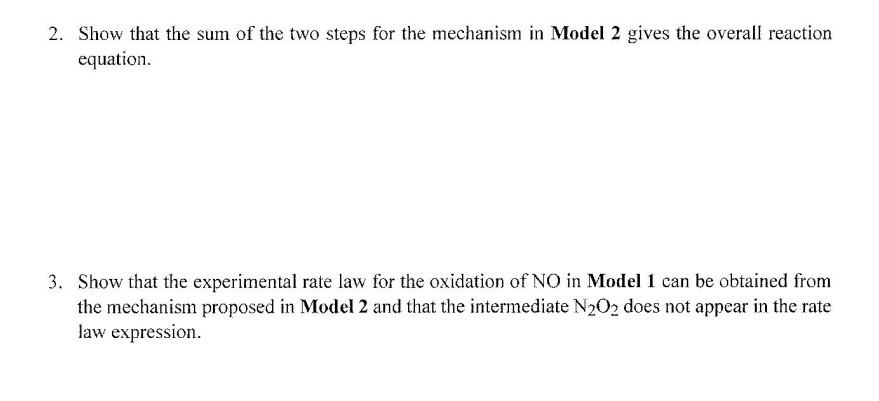
Question
1 Approved Answer
Can you guys help me with these problems? Thank you so much! A reaction mechanism is a sequence of elementary reactions that describe what we


Can you guys help me with these problems?
Thank you so much!
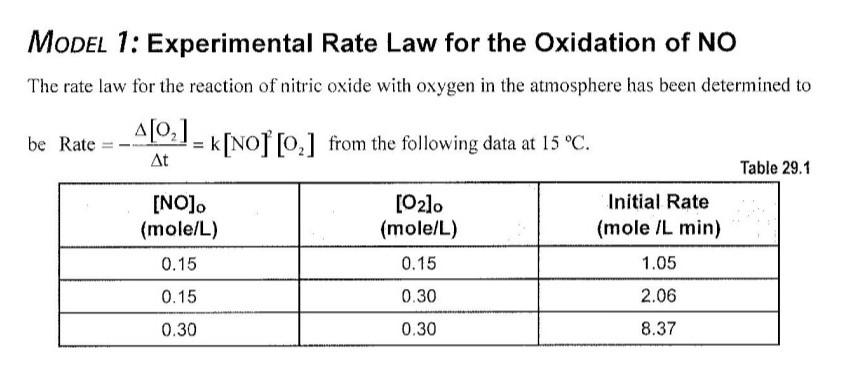
A reaction mechanism is a sequence of elementary reactions that describe what we believe takes place as the reactant molecules are transformed into product molecules. A rate law can be predicted from a proposed reaction mechanism, and you can compare predicted and experimental rate laws to determine whether a proposed reaction mechanism is consistent with the experimental rate law In order for the mechanism to be correct, the predicted rate law must match the rate law that is determined experimentally. LEARNING OBJECTIVES - Understand how a chemical reaction proceeds by a series of elementary reactions - Develop the ability to produce a rate law from experimental data - Develop the ability to produce a rate law from a proposed reaction mechanism SUCCESS CRITERIA - Determine the rate law for a reaction from experimental rate data - Design a reaction mechanism that produces the experimentally determined rate law and the overall balanced chemical reaction equation PREREQUISITE - Activity 28: Rates of Chemical Reactions INFORMATION A chemical reaction mechanism is a sequence of reactions that depict what is happening at the molecular level. These molecular-level reactions are called elementary reactions. The sum of the elementary reactions in a mechanism gives the overall balanced reaction equation. A rate law can be predicted from a proposed reaction mechanism. If the predicted rate law does not match the experimental rate law, then the proposed mechanism cannot be correct. If the predicted rate law matches the experimental rate law, then it is possible that the proposed mechanism is correct. It also is possible for an incorrect mechanism to produce the correct rate law so a match is not definitive! Activity 29 -Reaction Mechanisms 199 An elementary reaction usually involves one or two molecules as reactants. Rarely are more than two molecules involved in an elementary reaction. A unimolecular reaction involves only one molecule. A bimolecular reaction involves two molecules. 1. Given the data in the table for Model 1, determine the value and units for the rate constant for the oxidation of nitrogen monoxide. Activity 29 -Reaction Mechanisms 203 2. Show that the sum of the two steps for the mechanism in Model 2 gives the overall reaction equation. 3. Show that the experimental rate law for the oxidation of NO in Model 1 can be obtained from the mechanism proposed in Model 2 and that the intermediate N2O2 does not appear in the rate law expression. MODEL 1: Experimental Rate Law for the Oxidation of NO The rate law for the reaction of nitric oxide with oxygen in the atmosphere has been determined to be Rate =t[O2]=k[NO]2[O2] from the following data at 15C. Table 29.1
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


