Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Can you help me with number 2? I prefer equations and such rather than excel work. CASE PROBLEM Wal-Mart Cost of Capital WalMart, with 535
Can you help me with number 2? I prefer equations and such rather than excel work. 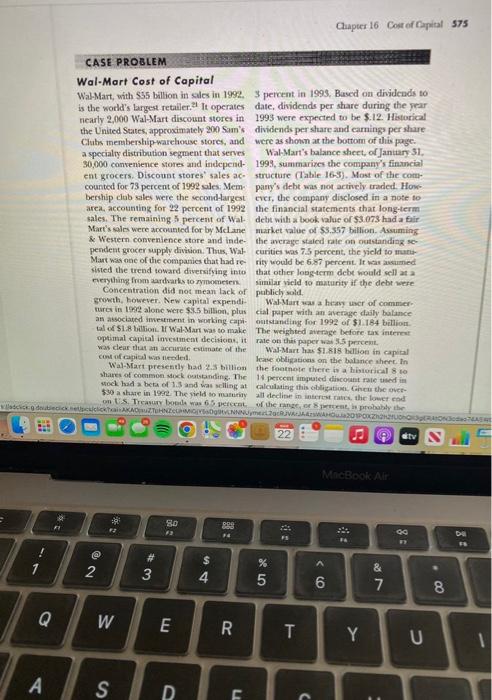
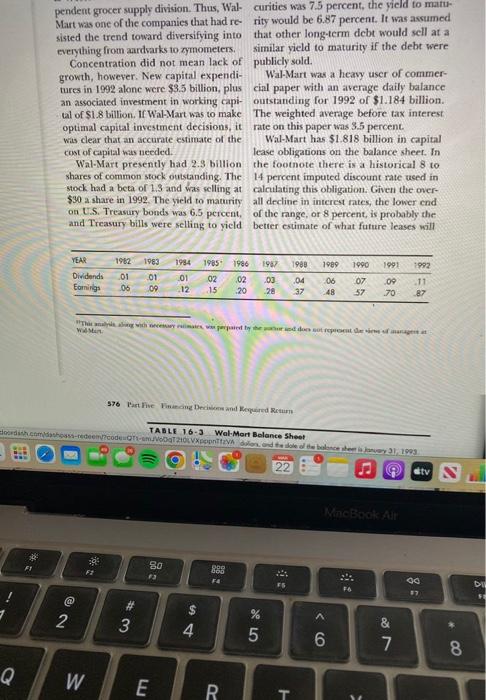
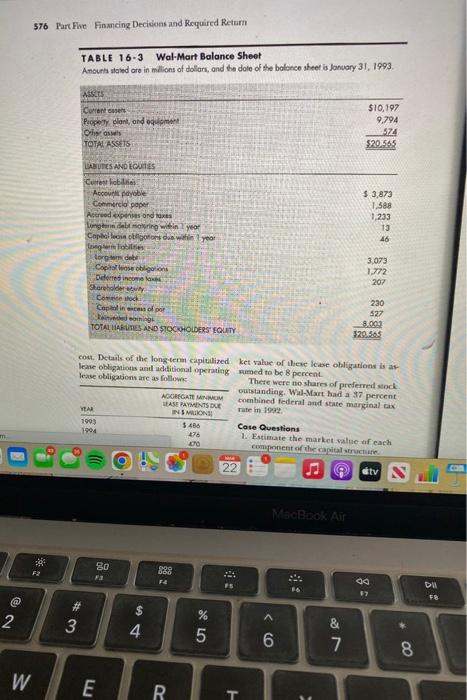
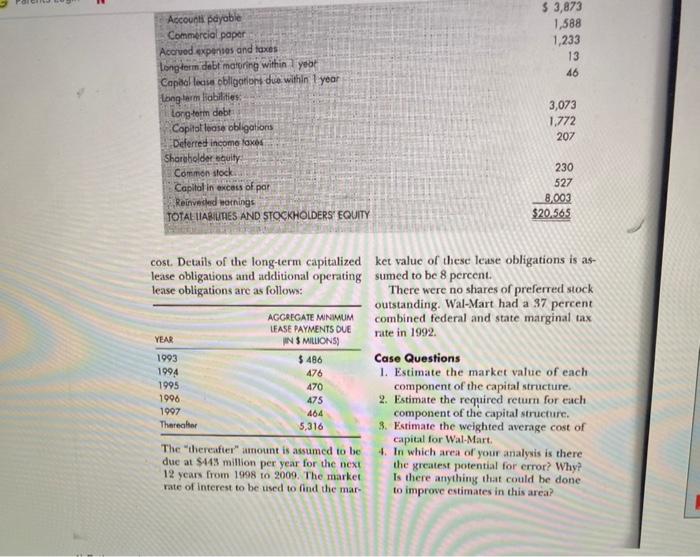
CASE PROBLEM Wal-Mart Cost of Capital WalMart, with 535 bilion in sales in 1992. 3 pereent in 1993, Based on dividends to is the woold's brgest retilere? It operates date, dividends per share during the pear nearly 2,000 Wai-Mart discount stores in 1995 were expected to be $. 12. Historical the United Sates, approximately 200 Sam's dividends per share and earnings per share Cluts mermbership-warehouse stores, and were as shonn at the bottom of this page. a specialy distribution segment that serves Wal-Mart's balance sheet, of Jantary 51 , 30,000 convenience stores and independ-1999, summarizes the company's finumcial ent grocers. Discoubt stores' sales ac- structure (Table 16-3). Most of the com:counted for 73 percent of 1992 sales: Mem pany's debe was not artively traded. Howberthip clab sales were the secondlargest cers, the company disclosed in a note to area accounting for 22 percent of 1992 the finaneial statements that longterm sales. The remaining 5 percent of Wal debe nith a book value or $3.073 had a fir Mart's sales were accounted for by Mclane market value of $3.357 billion. Assumings \& Wertern convenience store and inde- the avcrage staied rate on outstandiag sependent grocer supply divition. Thus, Wat curitie was 7.5 percent, the yield to martMart nas one of tie companics that had re rity would be 6.87 percent. It was avamed sisted the trend toward diversifving into that other loogterm debe nould sell at a negything from ardharks to symoneten. sinilar vield to maturity if the debt were Concentration did not mean tack of publich sold growth, boweren. New capital expendl- WalMart was a hras uce of commerturc in 1992 alone were $55 billion, plus cial paper with an aterege datly bulance. as associased imestitrnt in working capi- outsameling for 1992 of 51.184 bitlion. Wl of 518 litition. If Wal Mart was wo make. The weighted murage before tax intereet was clear that an accourate chumate of the Wal-Mart has $1.818 bellioe in capital com of capiat wis necderi. lase obligaticess on the butance shere. in Wal-Mart presently had 2.5 bilion the foemele there is a hiblorical 8 to sock had a bet of 1.3 and was sclilisg at calculating thib obligation Ghew the over- pendent grocer supply division. Thus, Wal- curities was 7.5 pereent, the yield to matuMart was one of the companies that had re- rity would be 6.87 percent. It was assumed sisted the trend toward diversifying into that other long-term debt would sell at a everything from aardvarks to zymometers. similar yield to maturity if the debt were Concentration did not mean lack of publicly sold. growth, however. New capital expendi- Wal-Mart was a heawy user of commertures in 1992 alone were $3.5 billion, plus cial paper with an arenge daily balance an associated investment in working capi- outstanding for 1992 of $1.184 billion. tal of \$1.8 billion. If Wal-Mart was to make The weighted average before tax interest optimal capital investment decisions, it rate on this paper was 3.5 percent. was clear that an accurate estimate of the Wal-Mart has $1.818 billion in capital cost of capial was needed. lease obligations on the balance sheet. In Wal-Mart presently bad 2.9 bilion the footnote there is a historical 8 to shares of common stock outstanding. The 14 percent imputed discotant rate used in stock had a beta of 1.3 and was selling at calculating this obligation. Given the over$90 a share in 1992 . The yield to maturity all decline in interest rates, the lower end on U.S. Treasury bonds was 6.5 percent, of the range, or 8 percent, is probably the and Treasury bills were selling to yield better extimate of what future leases will 576 Part Fhe Finmeing Decisions and Requaired Retura TABLE 16-3 Wal-Mart Balance Sheet Anourt staled are in millons of dolon, and the dole of the bolonce sheet is Jonuary 31, 1993. cost. Details of the long-term capitalized ket value of these lease obligations is aslease obligations and additional operating sumed to be 8 percent. lease obligations are as follows: There were no shares of preferted stock outstanding. Wal-Mart had a 37 percent combined federal and state marginal tax rate in 1992. Case Questions 1. Estimate the market value of each component of the capital structure. 2. Estimate the required return for each component of the capital structure. 3. Estimate the weighted average cost of eapital for Wal-Mart. The "thereafter" umount is assumed to be 4. In which areia of your analysis is there due at $443 million per year for the next the greatest potential for error? Why? 12 years from 1998 to 2009 . The market Is there anything that could be done rate of interest to be used to find the mar- to improve estimates in this area? CASE PROBLEM Wal-Mart Cost of Capital WalMart, with 535 bilion in sales in 1992. 3 pereent in 1993, Based on dividends to is the woold's brgest retilere? It operates date, dividends per share during the pear nearly 2,000 Wai-Mart discount stores in 1995 were expected to be $. 12. Historical the United Sates, approximately 200 Sam's dividends per share and earnings per share Cluts mermbership-warehouse stores, and were as shonn at the bottom of this page. a specialy distribution segment that serves Wal-Mart's balance sheet, of Jantary 51 , 30,000 convenience stores and independ-1999, summarizes the company's finumcial ent grocers. Discoubt stores' sales ac- structure (Table 16-3). Most of the com:counted for 73 percent of 1992 sales: Mem pany's debe was not artively traded. Howberthip clab sales were the secondlargest cers, the company disclosed in a note to area accounting for 22 percent of 1992 the finaneial statements that longterm sales. The remaining 5 percent of Wal debe nith a book value or $3.073 had a fir Mart's sales were accounted for by Mclane market value of $3.357 billion. Assumings \& Wertern convenience store and inde- the avcrage staied rate on outstandiag sependent grocer supply divition. Thus, Wat curitie was 7.5 percent, the yield to martMart nas one of tie companics that had re rity would be 6.87 percent. It was avamed sisted the trend toward diversifving into that other loogterm debe nould sell at a negything from ardharks to symoneten. sinilar vield to maturity if the debt were Concentration did not mean tack of publich sold growth, boweren. New capital expendl- WalMart was a hras uce of commerturc in 1992 alone were $55 billion, plus cial paper with an aterege datly bulance. as associased imestitrnt in working capi- outsameling for 1992 of 51.184 bitlion. Wl of 518 litition. If Wal Mart was wo make. The weighted murage before tax intereet was clear that an accourate chumate of the Wal-Mart has $1.818 bellioe in capital com of capiat wis necderi. lase obligaticess on the butance shere. in Wal-Mart presently had 2.5 bilion the foemele there is a hiblorical 8 to sock had a bet of 1.3 and was sclilisg at calculating thib obligation Ghew the over- pendent grocer supply division. Thus, Wal- curities was 7.5 pereent, the yield to matuMart was one of the companies that had re- rity would be 6.87 percent. It was assumed sisted the trend toward diversifying into that other long-term debt would sell at a everything from aardvarks to zymometers. similar yield to maturity if the debt were Concentration did not mean lack of publicly sold. growth, however. New capital expendi- Wal-Mart was a heawy user of commertures in 1992 alone were $3.5 billion, plus cial paper with an arenge daily balance an associated investment in working capi- outstanding for 1992 of $1.184 billion. tal of \$1.8 billion. If Wal-Mart was to make The weighted average before tax interest optimal capital investment decisions, it rate on this paper was 3.5 percent. was clear that an accurate estimate of the Wal-Mart has $1.818 billion in capital cost of capial was needed. lease obligations on the balance sheet. In Wal-Mart presently bad 2.9 bilion the footnote there is a historical 8 to shares of common stock outstanding. The 14 percent imputed discotant rate used in stock had a beta of 1.3 and was selling at calculating this obligation. Given the over$90 a share in 1992 . The yield to maturity all decline in interest rates, the lower end on U.S. Treasury bonds was 6.5 percent, of the range, or 8 percent, is probably the and Treasury bills were selling to yield better extimate of what future leases will 576 Part Fhe Finmeing Decisions and Requaired Retura TABLE 16-3 Wal-Mart Balance Sheet Anourt staled are in millons of dolon, and the dole of the bolonce sheet is Jonuary 31, 1993. cost. Details of the long-term capitalized ket value of these lease obligations is aslease obligations and additional operating sumed to be 8 percent. lease obligations are as follows: There were no shares of preferted stock outstanding. Wal-Mart had a 37 percent combined federal and state marginal tax rate in 1992. Case Questions 1. Estimate the market value of each component of the capital structure. 2. Estimate the required return for each component of the capital structure. 3. Estimate the weighted average cost of eapital for Wal-Mart. The "thereafter" umount is assumed to be 4. In which areia of your analysis is there due at $443 million per year for the next the greatest potential for error? Why? 12 years from 1998 to 2009 . The market Is there anything that could be done rate of interest to be used to find the mar- to improve estimates in this area 



Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


