Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Can you please help me finish this whole problem. I am having trouble finding the conversion costs incurred for the period. Major League Bat Company


Can you please help me finish this whole problem. I am having trouble finding the conversion costs incurred for the period.
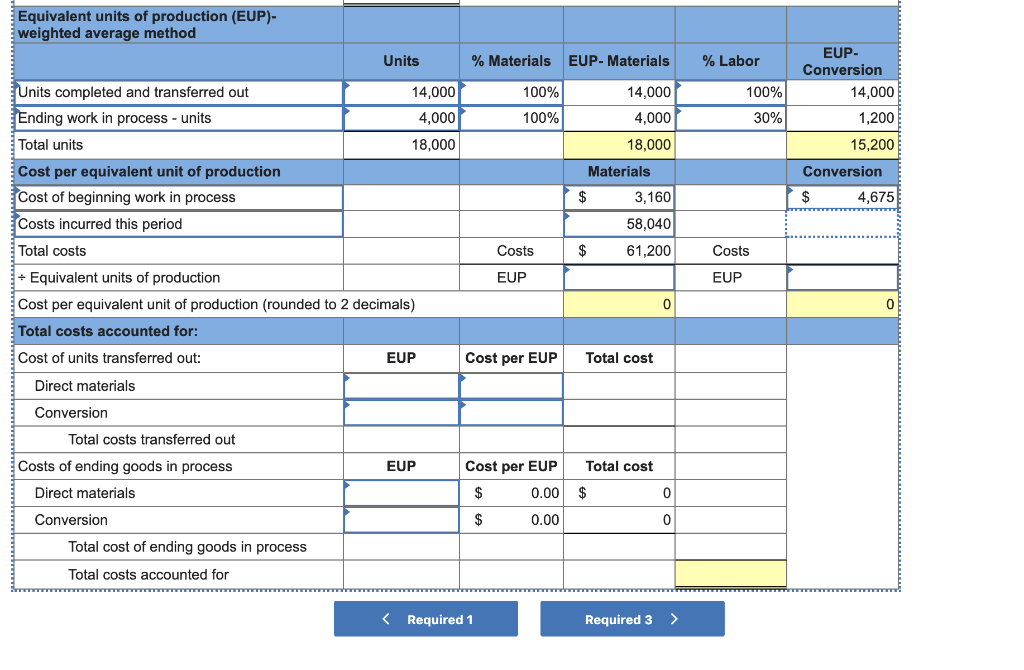
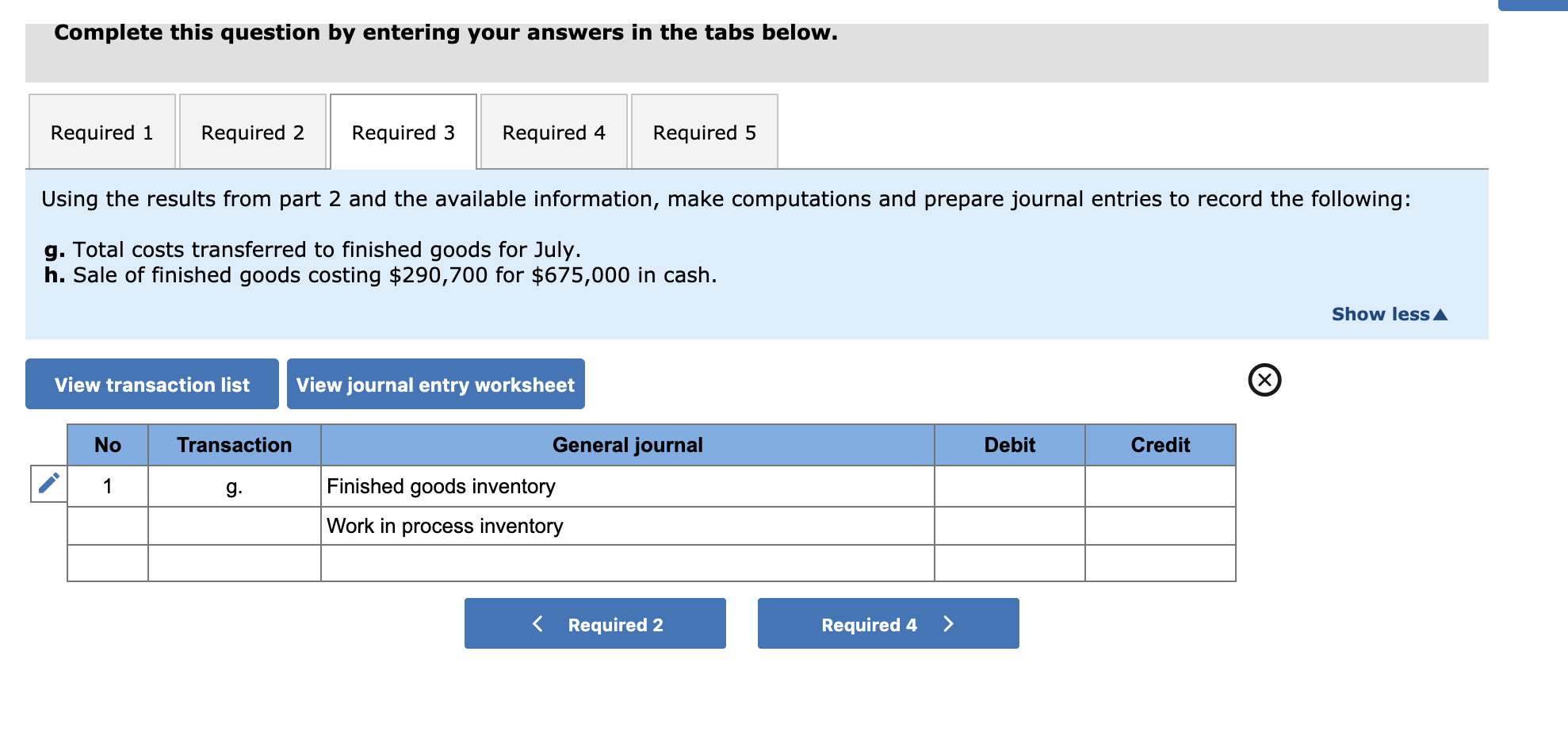
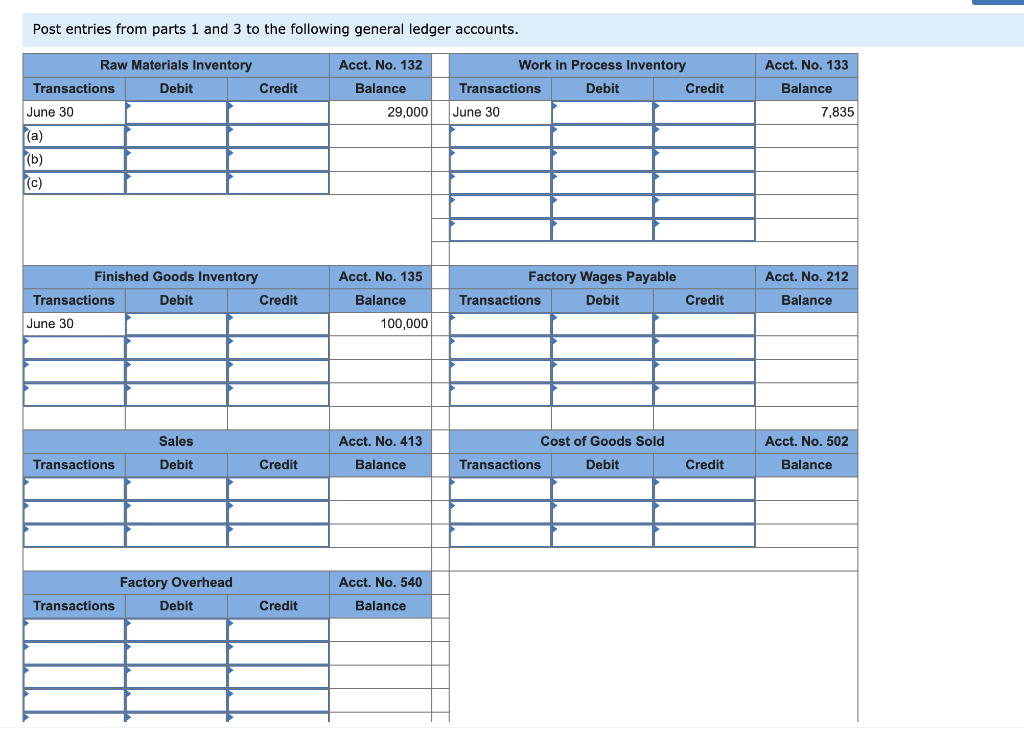
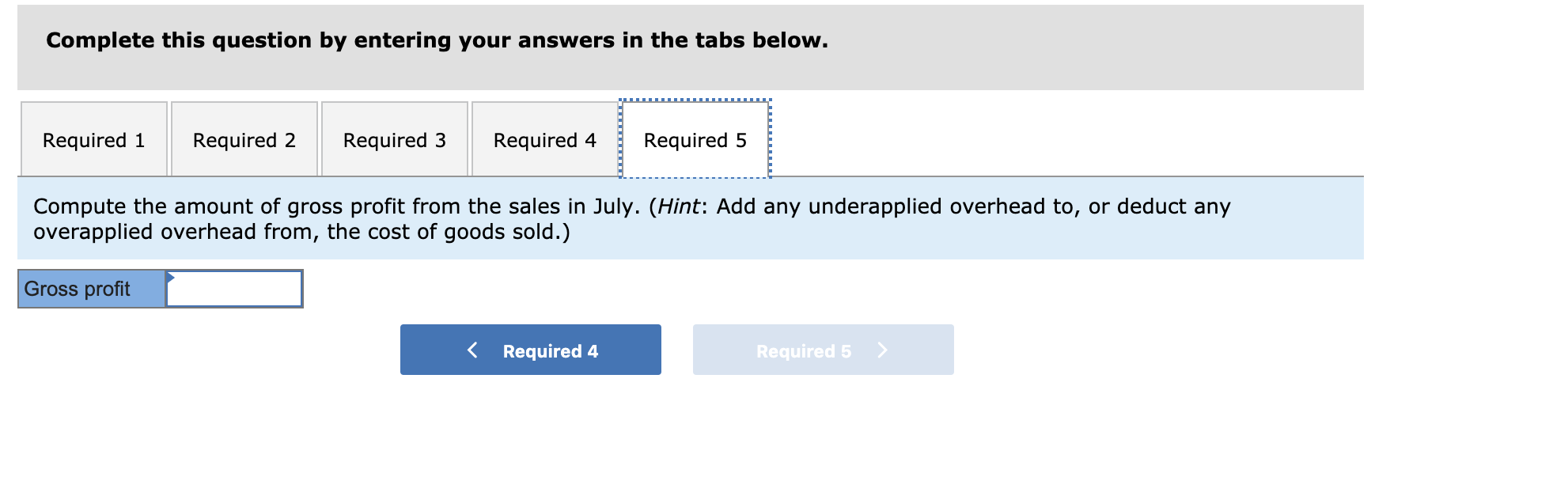
Major League Bat Company manufactures baseball bats. In addition to its work in process inventories, the company maintains inventories of raw materials and finished goods. It uses raw materials as direct materials in production and as indirect materials. Its factory payroll costs include direct labor for production and indirect labor. All materials are added at the beginning of the process, and conversion costs are applied uniformly throughout the production process. Required: You are to maintain records and produce measures of inventories to reflect the July events of this company. The June 30 balances: Raw Materials Inventory, $29,000; Work in Process Inventory, $7,835 ($3,160 of direct materials and $4,675 of conversion); Finished Goods Inventory, $100,000; Sales, $0; Cost of Goods Sold, $0; Factory Wages Payable, $0; and Factory Overhead, $0. 1. Prepare journal entries to record the following July transactions and events. a. Purchased raw materials for $165,000 cash (the company uses a perpetual inventory system). b. Used raw materials as follows: direct materials, $58,040; and indirect materials, $15,000. c. Recorded factory wages payable costs as follows: direct labor, $214,750; and indirect labor, $30,000. d. Paid factory payroll cost of $244,750 with cash (ignore taxes). e. Incurred additional factory overhead costs of $90,000 paid in cash. f. Applied factory overhead to production at 50% of direct labor costs. 2. Information about the July inventories follows. Use this information with that from part 1 to prepare a process cost summary, assuming the weighted average method is used. (Round "Cost per EUP" to 2 decimal places.) 8,000 units 10,000 units 4,000 units Units Beginning inventory Started Ending inventory Beginning inventory Materials-Percent complete Conversion-Percent complete Ending inventory Materials,Percent complete Conversion-Percent complete 1008 70% 100% 30% Check my work 2. Information about the July inventories follows. Use this information with that from part 1 to prepare a process cost summary, assuming the weighted-average method is used. (Round "Cost per EUP" to 2 decimal places.) 8,000 units 10,000 units 4,000 units Units Beginning inventory Started Ending inventory Beginning inventory Materials-Percent complete Conversion-Percent complete Ending inventory Materials-Percent complete Conversion-Percent complete 100% 70% 100% 30% 3. Using the results from part 2 and the available information, make computations and prepare journal entries to record the following: g. Total costs transferred to finished goods for July. h. Sale of finished goods costing $290,700 for $675,000 in cash. 4. Post entries from parts 1 and 3 to the following general ledger accounts. 5. Compute the amount of gross profit from the sales in July. (Hint. Add any underapplied overhead to, or deduct any overapplied overhead from, the cost of goods sold.) % Labor 100% 30% EUP- Conversion 14,000 1,200 15,200 Conversion $ 4,675 % Materials EUP- Materials 100% 14,000 100% 4,000 18,000 Materials 3,160 58,040 Costs $ 61,200 EUP 0 Equivalent units of production (EUP)- weighted average method Units Units completed and transferred out 14,000 Ending work in process - units 4,000 Total units 18,000 Cost per equivalent unit of production Cost of beginning work in process Costs incurred this period Total costs 1Equivalent units of production Cost per equivalent unit of production (rounded to 2 decimals) Total costs accounted for: Cost of units transferred out: EUP Direct materials Conversion Total costs transferred out Costs of ending goods in process Direct materials Conversion Total cost of ending goods in process Total costs accounted for Costs EUP 0 Cost per EUP Total cost EUP Cost per EUP 0.00 $ 0.00 Total cost $ 0 0 Required 1 Required 3 > Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Required 5 Using the results from part 2 and the available information, make computations and prepare journal entries to record the following: g. Total costs transferred to finished goods for July. h. Sale of finished goods costing $290,700 for $675,000 in cash. Show less A View transaction list View journal entry worksheet No Transaction Debit Credit General journal Finished goods inventory Work in process inventory Post entries from parts 1 and 3 to the following general ledger accounts. Raw Materials Inventory Transactions Debit June 30 Credit Acct. No. 132 Balance 29,000 Work in Process Inventory Transactions Debit Credit June 30 Acct. No. 133 Balance 7,835 (a) (b) Finished Goods Inventory Transactions Debit Credit June 30 Acct. No. 135 Balance 100,000 Factory Wages Payable Transactions Debit Acct. No. 212 Balance Credit Sales Debit Acct. No. 413 Balance Cost of Goods Sold Transactions Debit Acct. No. 502 Balance Transactions Credit Credit Factory Overhead Transactions Debit Acct. No. 540 Balance Credit Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Required 3 Required 4 Required 5 -------- Compute the amount of gross profit from the sales in July. (Hint: Add any underapplied overhead to, or deduct any overapplied overhead from, the cost of goods sold.) Gross profitStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


