Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
cant use the same answer from previous posted question, can you rephrase the answer or give a different one ? i need for all 1.




cant use the same answer from previous posted question, can you rephrase the answer or give a different one ?
i need for all
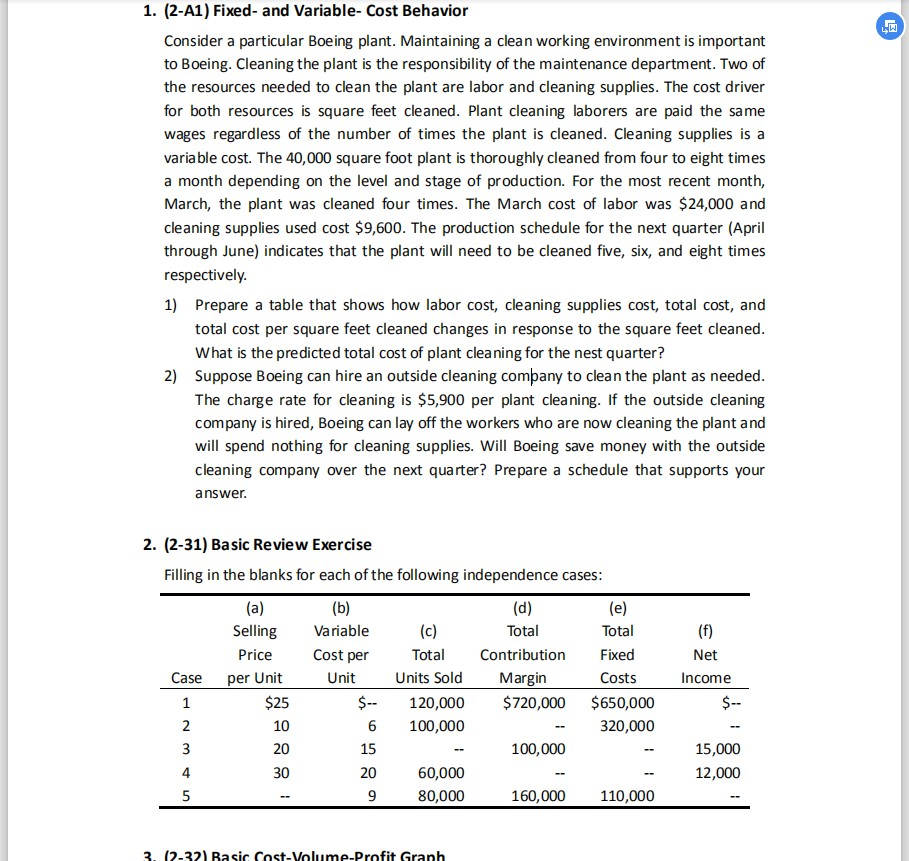
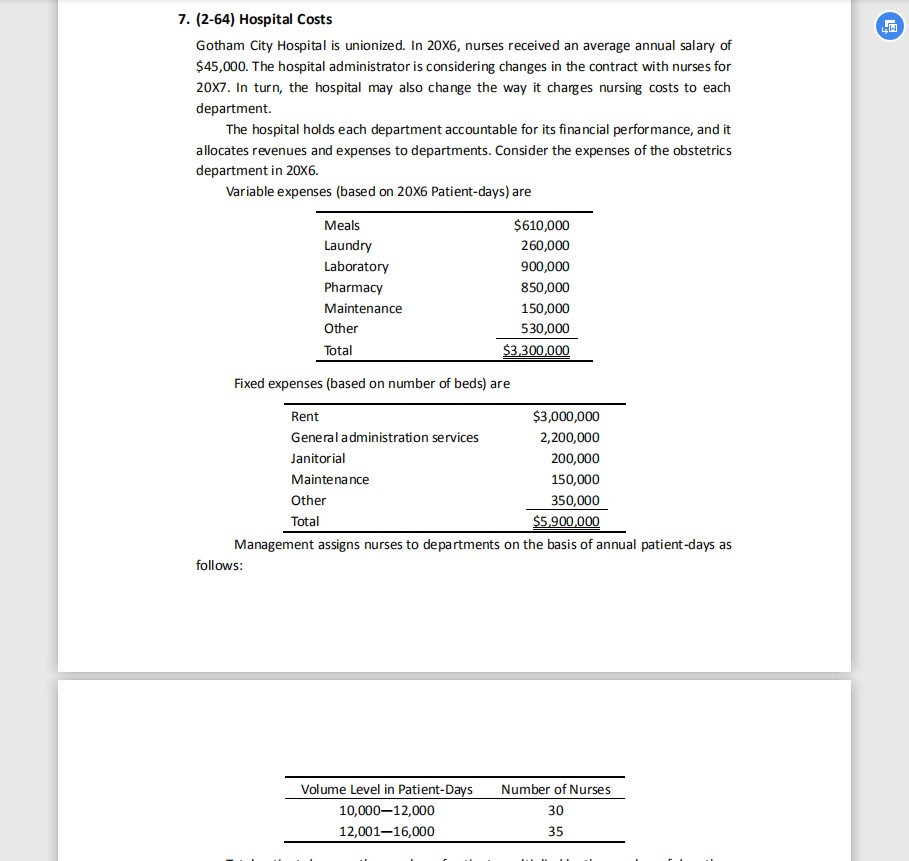
1. (2-A1) Fixed- and Variable- Cost Behavior Consider a particular Boeing plant. Maintaining a clean working environment is important to Boeing. Cleaning the plant is the responsibility of the maintenance department. Two of the resources needed to clean the plant are labor and cleaning supplies. The cost driver for both resources is square feet cleaned. Plant cleaning laborers are paid the same wages regardless of the number of times the plant is cleaned. Cleaning supplies is a variable cost. The 40,000 square foot plant is thoroughly cleaned from four to eight times a month depending on the level and stage of production. For the most recent month, March, the plant was cleaned four times. The March cost of labor was $24,000 and cleaning supplies used cost $9,600. The production schedule for the next quarter (April through June) indicates that the plant will need to be cleaned five, six, and eight times respectively. 1) Prepare a table that shows how labor cost, cleaning supplies cost, total cost, and total cost per square feet cleaned changes in response to the square feet cleaned. What is the predicted total cost of plant cleaning for the nest quarter? Suppose Boeing can hire an outside cleaning company to clean the plant as needed. The charge rate for cleaning is $5,900 per plant cleaning. If the outside cleaning company is hired, Boeing can lay off the workers who are now cleaning the plant and will spend nothing for cleaning supplies. Will Boeing save money with the outside cleaning company over the next quarter? Prepare a schedule that supports your answer. 2) (e) 2. (2-31) Basic Review Exercise Filling in the blanks for each of the following independence cases: (a) (b) (d) Selling Variable (c) Total Total Price Cost per Total Contribution Fixed Case per Unit Unit Units Sold Margin Costs $25 120,000 $720,000 $650,000 100,000 320,000 100,000 20 60,000 80,000 160,000 110,000 Net Income 15,000 12,000 3. 12-32) Basic Cost-Volume-Profit Granh 3. (2-32) Basic Cost-Volume-Profit Graph Refer to Exercise 2. Construct a cost-volume-profit graph for Case 2 that depicts the total revenue, total variable cost, total fixed cost, and total cost lines. Estimate the break-even point in total units sold and the next income for 100,000 units sold. 4. (2-45) Fixed Costs and Relevant Range Bridger Canyon Systems Group (BCSG) has a substantial year-to-year fluctuation in billings to clients. Top management has the following policy regarding the employment of key professional personnel: If Gross annual Billings Are $2,000,000 or less $2,000,0012,400,000 $2,400,0012,800,000 Number of Persons to Be Employed 10 11 12 Key Professional Annual Salaries $1,000,000 $1,100,000 $1,200,000 Top management believes that the group should maintain a minimum of 10 individuals for a year or more even if billings drop drastically below $2 million. For the past 5 years, gross annual billings for BCSG have fluctuated between $2,020,000 and $2,380,000. Expectations for next year are that gross billings will be between $2,100,000 and $2,300,000. What amount should the group budget for key professional personnel salaries? Graph the relationship on an annual basis, using the two approaches illustrated in Exhibit 2-6 on page 61. Indicate the relevant range on each graph. You need not use graph paper; simply approximate the graphical relationships. 5. (2-48) Promotion of a Rock Concert 5. (2-48) Promotion of a Rock Concert BBT Productions, Ltd., is promoting a rock concert in London. The bands will receive a flat fee of 7 million in cash. The concert will be shown worldwide on closed-circuit television. BBT will collect 100% of the receipts and will return 30% to the individual local closed-circuit theater managers. BBT expects to sell 1.1 million seats at a net average price of 13 each. BBT will also receive 300,000 from the London arena (which has sold out its 19,500 seats, ranging from 150 for box seats to 20 for general admission, for a gross revenue of 1.25 million); BBT will not share the 300,000 with the local promoters. 1) The general manager of BBT Productions is trying to decide what amount to spend for advertising. What is the most BBT could spend and still break even on overall operations, assuming sales of 1.1 million tickets? 2) If BBT desires an operating income of 500,000, how many seats would it have to sell? Assume that the average price is 13 and the total fixed costs (including 2,000,000 in advertising) are 9 million. 6. (2-57) Cross Margin and Contribution Margin Eastman Kodak Company is a provider of imaging technology products and services to the photographic, graphic communications, and health-care markets. A condensed 2008 income statement follows (in millions): Sales Cost of goods sold $9,416 7,247 6. (2-57) Cross Margin and Contribution Margin Eastman Kodak Company is a provider of imaging technology products and services to the photographic, graphic communications, and health-care markets. A condensed 2008 income statement follows (in millions): Sales Cost of goods sold Gross margin Other operating expenses Loss from continuing operations $9,416 7,247 2,169 2,896 $(727) Assume that $1,400 million of the cost of goods sold is a fixed cost representing depreciation and other production costs that do not change with the volume of production. In addition, $2,000 million of the other operating expenses is fixed. 1) Compute the total contribution margin for 2008 and the contribution margin percentage. Explain why the contribution margin differs from the gross margin. 2) Suppose that sales for Eastman Kodak were predicted to increase by 10% in 2009 and that the cost behavior was expected to continue in 2009 as it did in 2008. Compute the predicted operating income (loss) for 2009. 3) What assumptions were necessary to compute the predicted 2009 operating income in requirement 2? 7. (2-64) Hospital Costs Gotham City Hospital is unionized. In 20X6, nurses received an average annual salary of 7. (2-64) Hospital Costs Gotham City Hospital is unionized. In 20X6, nurses received an average annual salary of $ 45,000. The hospital administrator is considering changes in the contract with nurses for 20x7. In turn, the hospital may also change the way it charges nursing costs to each department. The hospital holds each department accountable for its financial performance, and it allocates revenues and expenses to departments. Consider the expenses of the obstetrics department in 20X6. Variable expenses (based on 20x6 Patient-days) are Meals Laundry Laboratory Pharmacy Maintenance Other Total $610,000 260,000 900,000 850,000 150,000 530,000 $3,300,000 Fixed expenses (based on number of beds) are Rent $3,000,000 General administration services 2,200,000 Janitorial 200,000 Maintenance 150,000 Other 350,000 Total $5,900,000 Management assigns nurses to departments on the basis of annual patient-days as follows: Number of Nurses Volume Level in Patient-Days 10,00012,000 12,00116,000 30 35 Volume Level in Patient-Days 10,00012,000 12,00116,000 Number of Nurses 30 35 Total patient-days are the number of patients multiplied by the number of days they are hospitalized. The hospital charges each department for the salaries of the nurse assigned to it. During 20x6, the obstetrics department had a capacity of 60 beds, billed each patient an average of $810 per day, and had revenues of $12.15 million. 1) Compute the 20x6 volume of activity in patient-days. 2) Compute the 20x6 patient-days that would have been necessary for the obstetrics department to recoup all fixed expenses except nursing expenses. 3) Compute the 20x6 patient-days that would have been necessary for the obstetrics department to break even including nurses' salaries as a fixed cost. 4) Suppose obstetrics must pay $200 per patient-day for nursing services. This plan would replace the two-level, fixed-cost system employed in 20X6. Compute what the break-even point in patient-days would have been in 20x6 under this planStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


