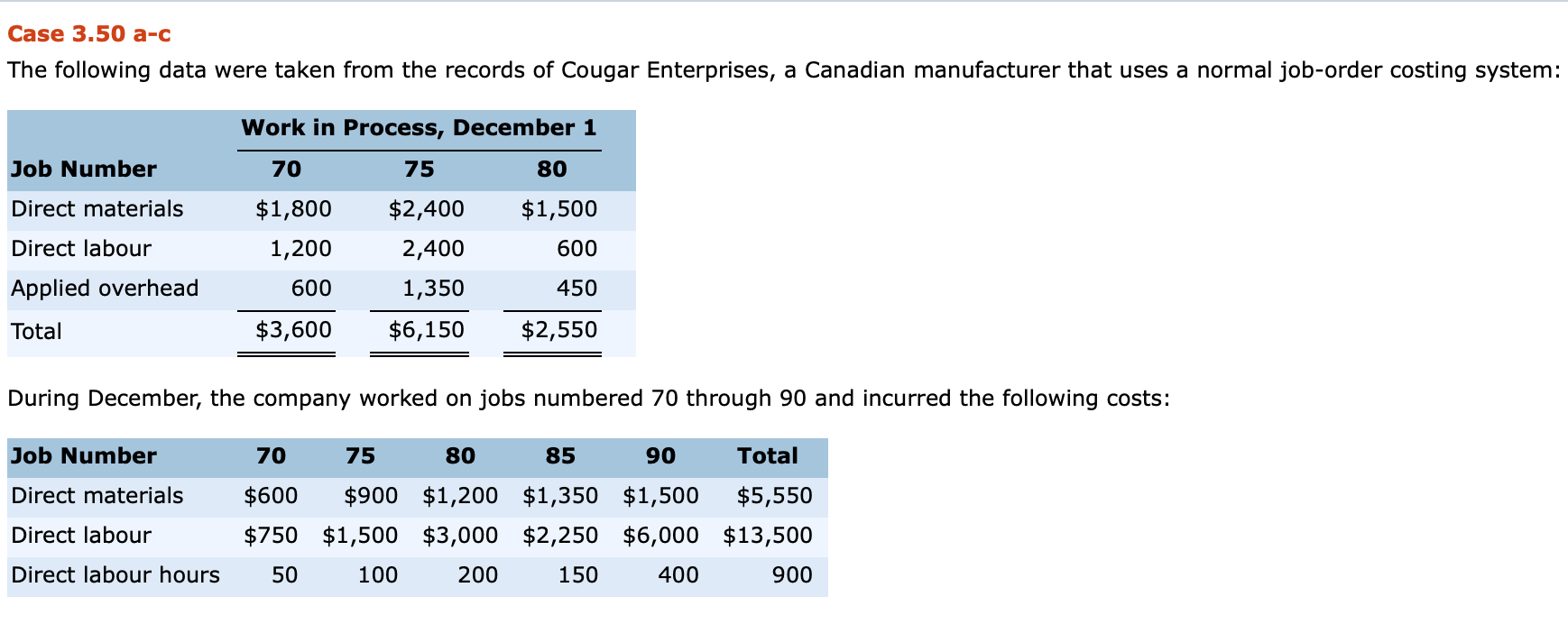
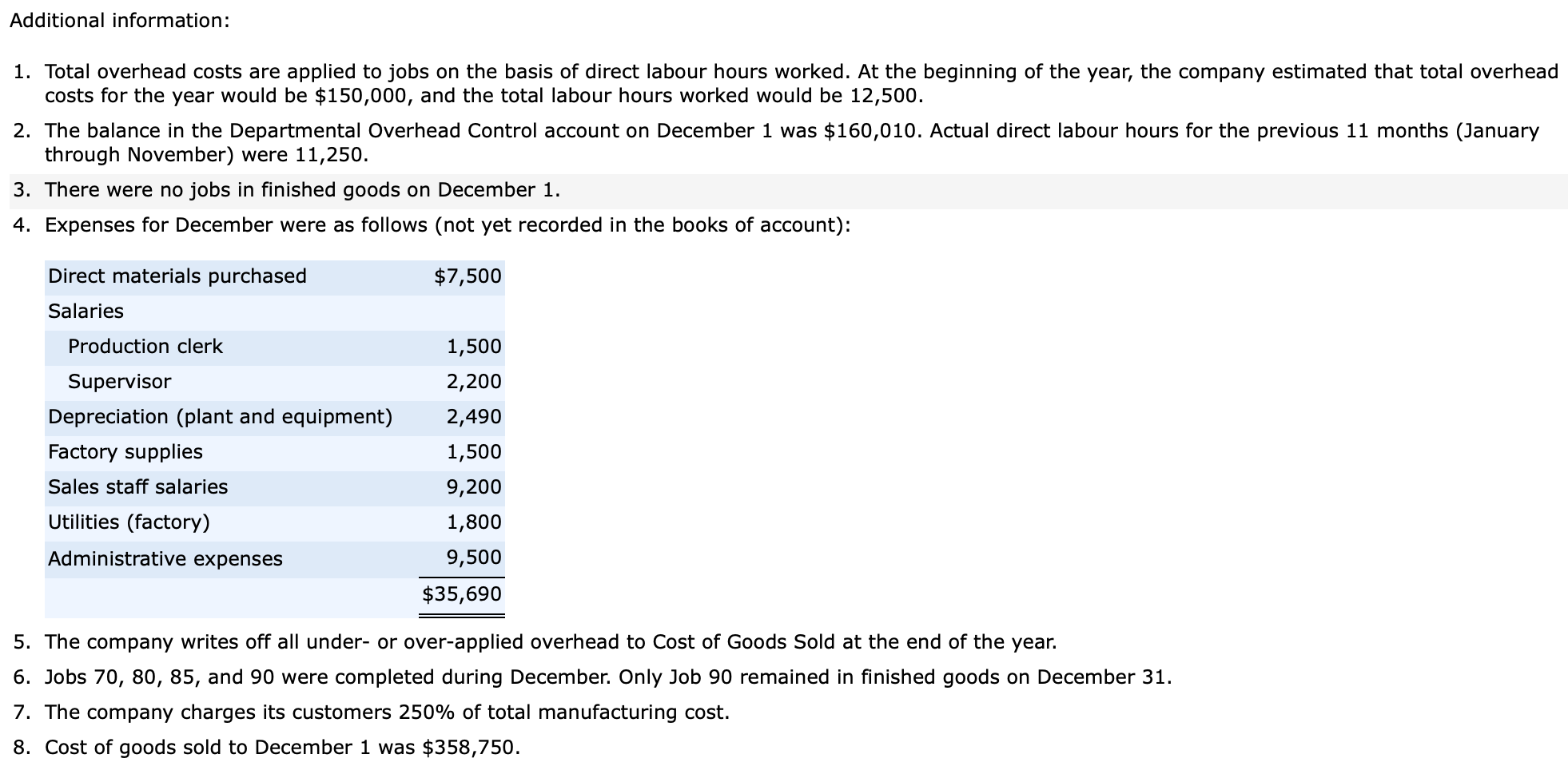
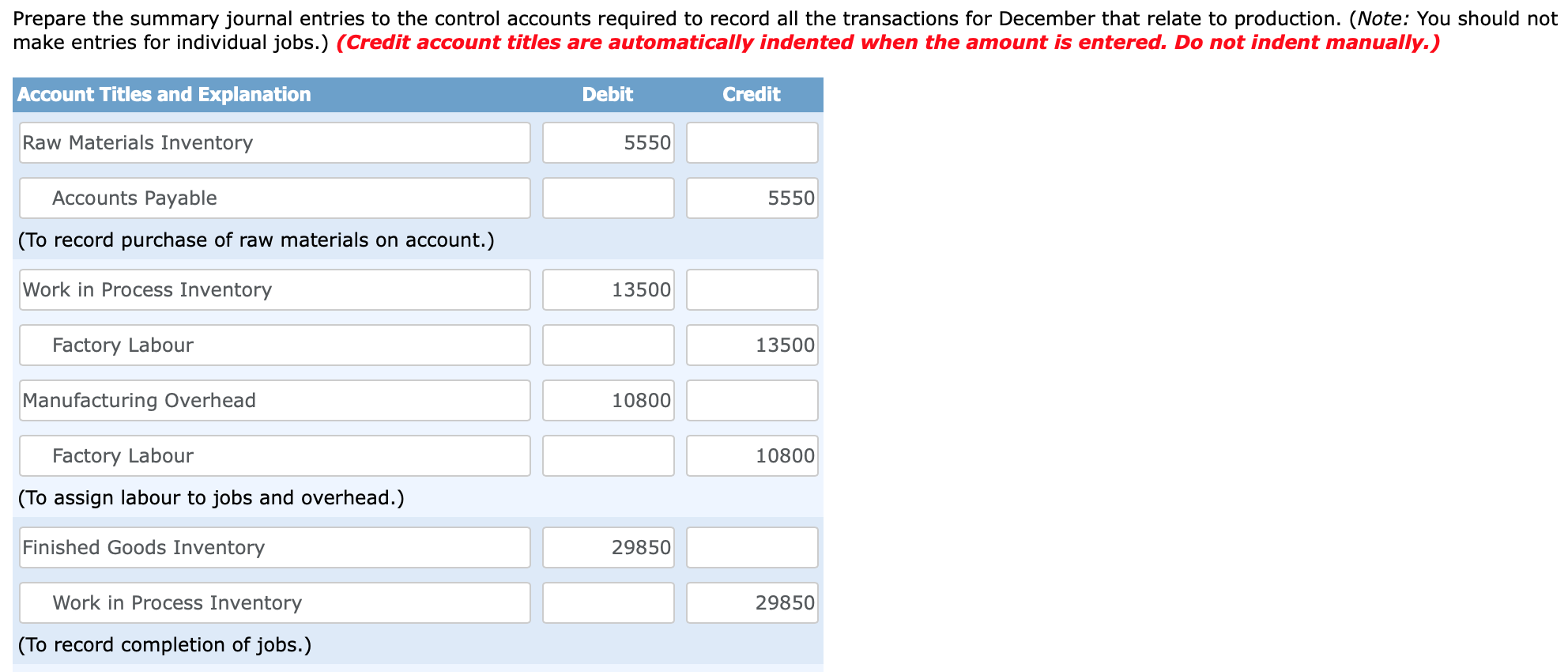
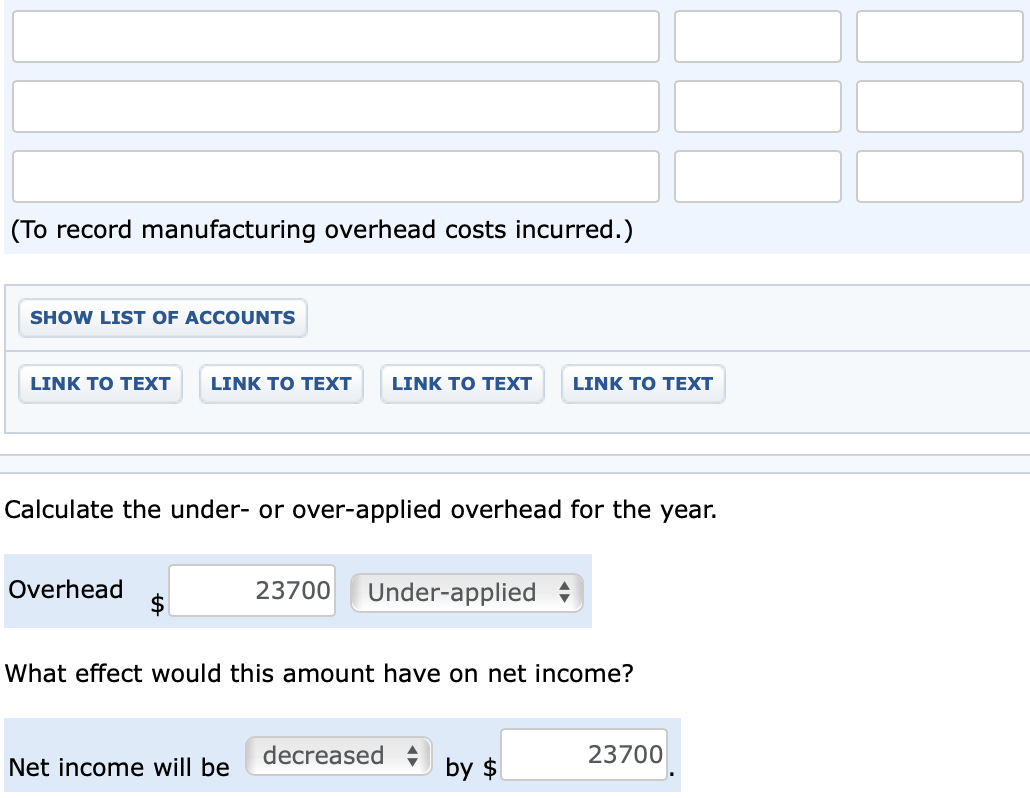
Case 3.50 a-c The following data were taken from the records of Cougar Enterprises, a Canadian manufacturer that uses a normal job-order costing system: Job Number Direct materials Direct labour Work in Process, December 1 70 75 80 $1,800 $2,400 $1,500 1,200 2,400 600 600 1,350 450 $3,600 $6,150 $2,550 Applied overhead Total During December, the company worked on jobs numbered 70 through 90 and incurred the following costs: Job Number Direct materials Direct labour Direct labour hours 70 75 80 85 90 Total $600 $900 $1,200 $1,350 $1,500 $5,550 $750 $1,500 $3,000 $2,250 $6,000 $13,500 50 100 200 150 400 900 Additional information: 1. Total overhead costs are applied to jobs on the basis of direct labour hours worked. At the beginning of the year, the company estimated that total overhead costs for the year would be $150,000, and the total labour hours worked would be 12,500. 2. The balance in the Departmental Overhead Control account on December 1 was $160,010. Actual direct labour hours for the previous 11 months (January through November) were 11,250. 3. There were no jobs in finished goods on December 1. 4. Expenses for December were as follows (not yet recorded in the books of account): $7,500 1,500 2,200 Direct materials purchased Salaries Production clerk Supervisor Depreciation (plant and equipment) Factory supplies Sales staff salaries Utilities (factory) 2,490 1,500 9,200 1,800 9,500 $35,690 Administrative expenses 5. The company writes off all under- or over-applied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold at the end of the year. 6. Jobs 70, 80, 85, and 90 were completed during December. Only Job 90 remained in finished goods on December 31. 7. The company charges its customers 250% of total manufacturing cost. 8. Cost of goods sold to December 1 was $358,750. Prepare the summary journal entries to the control accounts required to record all the transactions for December that relate to production. (Note: You should not make entries for individual jobs.) (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Raw Materials Inventory 5550 5550 Accounts Payable (To record purchase of raw materials on account.) Work in Process Inventory 13500 Factory Labour 13500 Manufacturing Overhead 10800 Factory Labour 10800 (To assign labour to jobs and overhead.) Finished Goods Inventory 29850 29850 Work in Process Inventory (To record completion of jobs.) (To record manufacturing overhead costs incurred.) SHOW LIST OF ACCOUNTS LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT Calculate the under- or over-applied overhead for the year. Overhead $ 23700 Under-applied What effect would this amount have on net income? Net income will be decreased by $ 23700 Case 3.50 a-c The following data were taken from the records of Cougar Enterprises, a Canadian manufacturer that uses a normal job-order costing system: Job Number Direct materials Direct labour Work in Process, December 1 70 75 80 $1,800 $2,400 $1,500 1,200 2,400 600 600 1,350 450 $3,600 $6,150 $2,550 Applied overhead Total During December, the company worked on jobs numbered 70 through 90 and incurred the following costs: Job Number Direct materials Direct labour Direct labour hours 70 75 80 85 90 Total $600 $900 $1,200 $1,350 $1,500 $5,550 $750 $1,500 $3,000 $2,250 $6,000 $13,500 50 100 200 150 400 900 Additional information: 1. Total overhead costs are applied to jobs on the basis of direct labour hours worked. At the beginning of the year, the company estimated that total overhead costs for the year would be $150,000, and the total labour hours worked would be 12,500. 2. The balance in the Departmental Overhead Control account on December 1 was $160,010. Actual direct labour hours for the previous 11 months (January through November) were 11,250. 3. There were no jobs in finished goods on December 1. 4. Expenses for December were as follows (not yet recorded in the books of account): $7,500 1,500 2,200 Direct materials purchased Salaries Production clerk Supervisor Depreciation (plant and equipment) Factory supplies Sales staff salaries Utilities (factory) 2,490 1,500 9,200 1,800 9,500 $35,690 Administrative expenses 5. The company writes off all under- or over-applied overhead to Cost of Goods Sold at the end of the year. 6. Jobs 70, 80, 85, and 90 were completed during December. Only Job 90 remained in finished goods on December 31. 7. The company charges its customers 250% of total manufacturing cost. 8. Cost of goods sold to December 1 was $358,750. Prepare the summary journal entries to the control accounts required to record all the transactions for December that relate to production. (Note: You should not make entries for individual jobs.) (Credit account titles are automatically indented when the amount is entered. Do not indent manually.) Account Titles and Explanation Debit Credit Raw Materials Inventory 5550 5550 Accounts Payable (To record purchase of raw materials on account.) Work in Process Inventory 13500 Factory Labour 13500 Manufacturing Overhead 10800 Factory Labour 10800 (To assign labour to jobs and overhead.) Finished Goods Inventory 29850 29850 Work in Process Inventory (To record completion of jobs.) (To record manufacturing overhead costs incurred.) SHOW LIST OF ACCOUNTS LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT LINK TO TEXT Calculate the under- or over-applied overhead for the year. Overhead $ 23700 Under-applied What effect would this amount have on net income? Net income will be decreased by $ 23700










