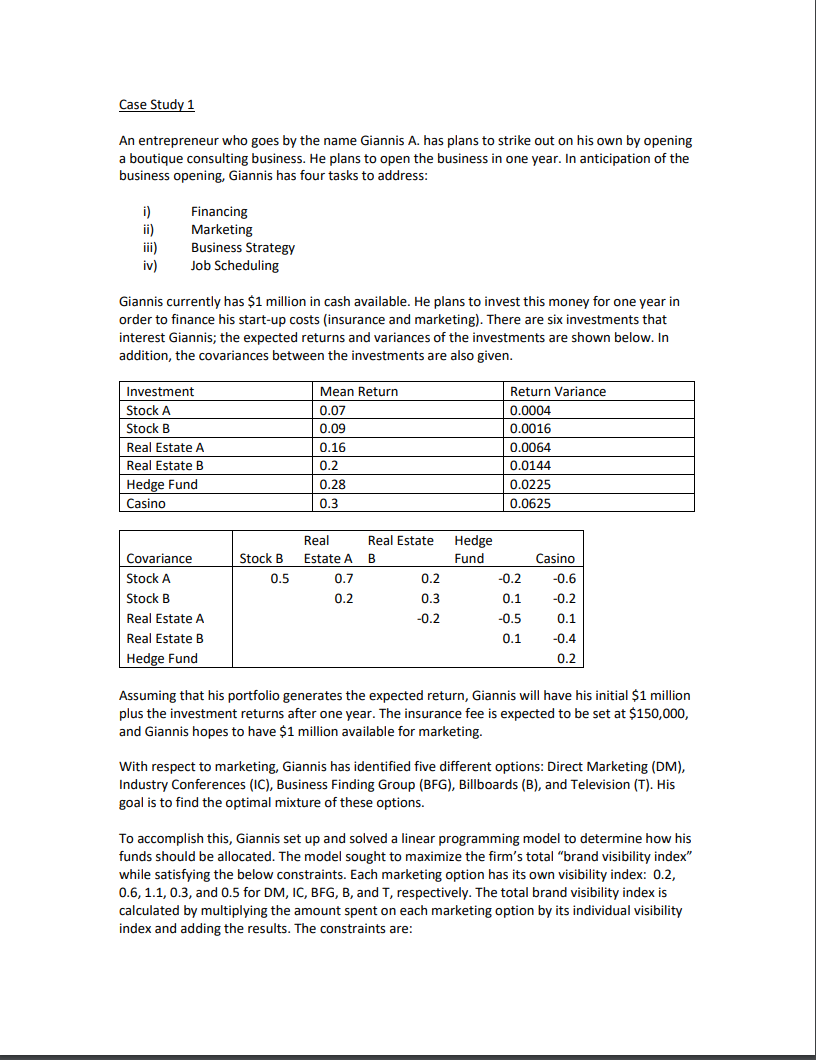
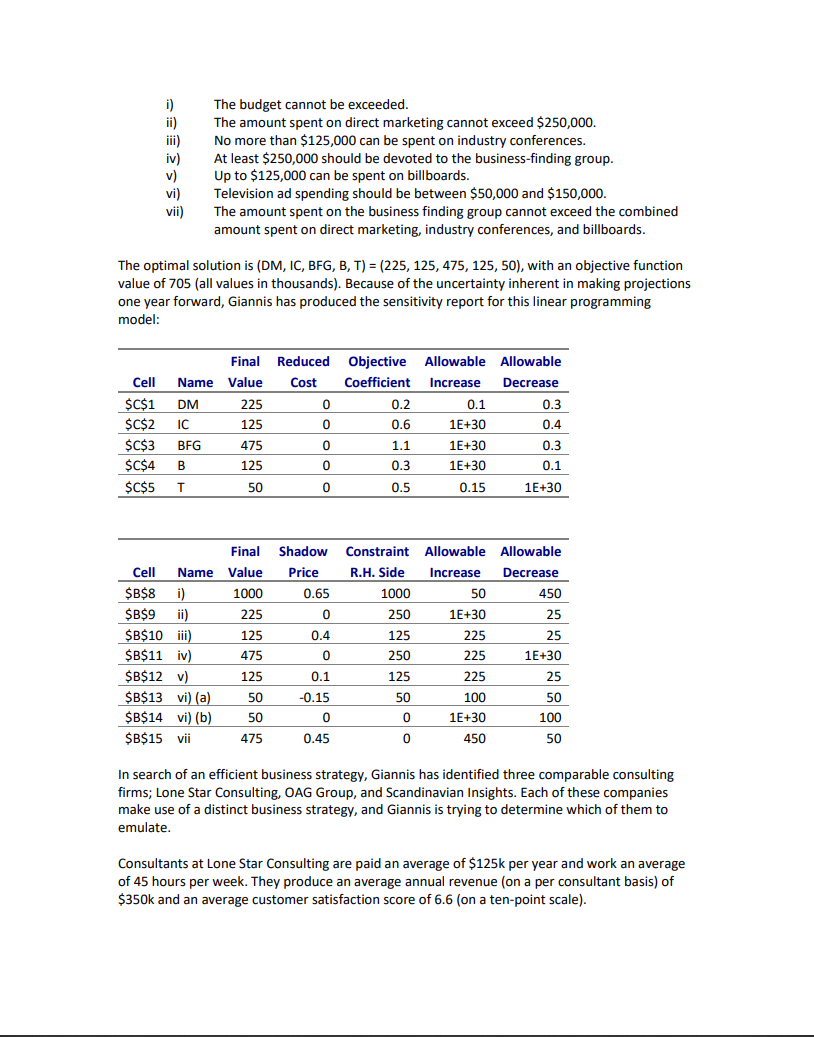


Case Study 1 An entrepreneur who goes by the name Giannis A. has plans to strike out on his own by opening a boutique consulting business. He plans to open the business in one year. In anticipation of the business opening, Giannis has four tasks to address: i) ii) iii) iv) Financing Marketing Business Strategy Job Scheduling Giannis currently has $1 million in cash available. He plans to invest this money for one year in order to finance his start-up costs (insurance and marketing). There are six investments that interest Giannis; the expected returns and variances of the investments are shown below. In addition, the covariances between the investments are also given. Investment Stock A Stock B Real Estate A Real Estate B Hedge Fund Casino Mean Return 0.07 0.09 0.16 0.2 0.28 0.3 Return Variance 0.0004 0.0016 0.0064 0.0144 0.0225 0.0625 Real Estate A 0.7 Hedge Fund Stock B 0.5 Casino Real Estate B 0.2 0.3 -0.2 -0.2 -0.6 -0.2 0.2 Covariance Stock A Stock B Real Estate A Real Estate B Hedge Fund 0.1 0.1 -0.5 0.1 -0.4 0.2 Assuming that his portfolio generates the expected return, Giannis will have his initial $1 million plus the investment returns after one year. The insurance fee is expected to be set at $150,000, and Giannis hopes to have $1 million available for marketing. With respect to marketing, Giannis has identified five different options: Direct Marketing (DM), Industry Conferences (IC), Business Finding Group (BFG), Billboards (B), and Television (T). His goal is to find the optimal mixture of these options. To accomplish this, Giannis set up and solved a linear programming model to determine how his funds should be allocated. The model sought to maximize the firm's total "brand visibility index" while satisfying the below constraints. Each marketing option has its own visibility index: 0.2, 0.6, 1.1, 0.3, and 0.5 for DM, IC, BFG, B, and T, respectively. The total brand visibility index is calculated by multiplying the amount spent on each marketing option by its individual visibility index and adding the results. The constraints are: i) ii) iii) iv) The budget cannot be exceeded. The amount spent on direct marketing cannot exceed $250,000. No more than $125,000 can be spent on industry conferences. At least $250,000 should be devoted to the business-finding group. Up to $125,000 can be spent on billboards. Television ad spending should be between $50,000 and $150,000. The amount spent on the business finding group cannot exceed the combined amount spent on direct marketing, industry conferences, and billboards. vi) vii) The optimal solution is (DM, IC, BFG, B, T) = (225, 125, 475, 125, 50), with an objective function value of 705 (all values in thousands). Because of the uncertainty inherent in making projections one year forward, Giannis has produced the sensitivity report for this linear programming model: Cell $C$1 $C$2 $C$3 $C$4 $C$5 Final Reduced Objective Allowable Allowable Name Value Cost Coefficient Increase Decrease DM 225 0 0.2 0.1 0.3 IC 125 0 0.6 1E+30 0.4 BFG 475 0 1.1 1E+30 0.3 B 125 0 0.3 1E+30 0.1 T 50 0 0.5 0.15 1E+30 Final Shadow Constraint Allowable Allowable Cell Name Value Price R.H. Side Increase Decrease $B$8 i) 1000 0.65 1000 50 450 $B$9 ii) 225 0 250 1E+30 25 $B$10 iii) 125 0.4 125 225 25 $B$11 iv) 475 0 250 225 1E+30 $B$12 v) 125 0.1 125 225 25 $B$13 vi) (a) 50 -0.15 50 100 50 $B$14 vi) (b) 50 0 0 1E+30 100 $B$15 vii 475 0.45 0 450 50 In search of an efficient business strategy, Giannis has identified three comparable consulting firms; Lone Star Consulting, OAG Group, and Scandinavian Insights. Each of these companies make use of a distinct business strategy, and Giannis is trying to determine which of them to emulate. Consultants at Lone Star Consulting are paid an average of $125k per year and work an average of 45 hours per week. They produce an average annual revenue (on a per consultant basis) of $350k and an average customer satisfaction score of 6.6 (on a ten-point scale). Questions 1) a) Determine the proportion of Giannis' capital to be placed in each investment that will maximize his expected return. As a risk control, he would like the variance of his portfolio to be no more than 0.001. In addition, various regulations require that no more than 21% of the portfolio can come from the hedge fund and casino, the two stocks must be at least 50% of the portfolio, and the combined amount of Stock B and Real Estate B cannot exceed 25% of the portfolio. b) Because the insurance fee is $150,000, Giannis is concerned that the solution to the previous question may not be adequate. Keeping the regulatory constraints mentioned above, determine the variance minimizing portfolio that will generate an expected return that is large enough to cover the insurance fee. 2) Using only the sensitivity report given above, answer the following questions. Give as much information as possible regarding changes to the objective function value and/or changes to the optimal variable values. a) Suppose that the brand visibility index for direct marketing is questioned. What would happen if its index was actually 0.4 b) Suppose that the brand visibility index for industry conferences is questioned. What would happen if its index was actually 0.75? c) Suppose that the brand visibility index for business finding group is questioned. What would happen if its index was actually 1.0? d) Because the budget is dependent on the results of the above investments, Aristotle is interested to understand how things might change under two scenarios: i) if the budget turned out to be $100,000 larger than expected and ii) if the budget turned out to be $100,000 less than expected. What would happen if either of these scenarios occurred? e) What would happen if the amount that can be spent on direct marketing increased to $300,000? f) What would happen if the minimum television ad spending was decreased to 25,000? g) What would happen if the maximum amount of industry conference spending were to increase to $150,000? 3) a) of the three consulting companies identified by Giannis (Loan Star Consulting, OAG Group, and Scandinavian Insights), which would you suggest that Giannis try to emulate? Base your answer on the relative efficiency that each company displays in utilizing their labor to produce revenue and positive customer satisfaction scores. Support your answer with the appropriate analysis. b) An outside analyst has predicted that, after its first year of business, Giannis' company will have paid consultants an average salary of $140k for an average of 50 hours of work per week. The analyst predicts that the average profit per analyst will be $300,000 and that the average customer satisfaction score will be 5.0. Relative to the other three consulting companies, how is Giannis' company expected to perform with respect to efficient usage of labor to produce revenue and positive customer satisfaction scores? Support your answer with the appropriate analysis. 4) Develop a linear programming model that will determine how many jobs to complete in each category each month. Do not force the optimal variable values to be integers. (Because the problem is done on a "per month" basis, non-integer solutions are ok, for instance, if the optimal solution is to complete 5.5 transportation jobs, Giannis could fully complete 5 transportation jobs in a month and do half of the work on another transportation job. The job that was not completed would then be finished in the next month.) a) How many jobs should be completed in each category? b) An advisor has suggested that an increase to the amount of available labor would be a good idea. All else being the same, is this suggestion good? Why or why not? c) The advisor also suggested that, since Pharma has the highest profit per job, it would be in our interest to find more Pharma jobs (i.e., to increase the number of available Pharma jobs from 6 to something higher). All else being the same, is this suggestion good? Why or why not? Case Study 1 An entrepreneur who goes by the name Giannis A. has plans to strike out on his own by opening a boutique consulting business. He plans to open the business in one year. In anticipation of the business opening, Giannis has four tasks to address: i) ii) iii) iv) Financing Marketing Business Strategy Job Scheduling Giannis currently has $1 million in cash available. He plans to invest this money for one year in order to finance his start-up costs (insurance and marketing). There are six investments that interest Giannis; the expected returns and variances of the investments are shown below. In addition, the covariances between the investments are also given. Investment Stock A Stock B Real Estate A Real Estate B Hedge Fund Casino Mean Return 0.07 0.09 0.16 0.2 0.28 0.3 Return Variance 0.0004 0.0016 0.0064 0.0144 0.0225 0.0625 Real Estate A 0.7 Hedge Fund Stock B 0.5 Casino Real Estate B 0.2 0.3 -0.2 -0.2 -0.6 -0.2 0.2 Covariance Stock A Stock B Real Estate A Real Estate B Hedge Fund 0.1 0.1 -0.5 0.1 -0.4 0.2 Assuming that his portfolio generates the expected return, Giannis will have his initial $1 million plus the investment returns after one year. The insurance fee is expected to be set at $150,000, and Giannis hopes to have $1 million available for marketing. With respect to marketing, Giannis has identified five different options: Direct Marketing (DM), Industry Conferences (IC), Business Finding Group (BFG), Billboards (B), and Television (T). His goal is to find the optimal mixture of these options. To accomplish this, Giannis set up and solved a linear programming model to determine how his funds should be allocated. The model sought to maximize the firm's total "brand visibility index" while satisfying the below constraints. Each marketing option has its own visibility index: 0.2, 0.6, 1.1, 0.3, and 0.5 for DM, IC, BFG, B, and T, respectively. The total brand visibility index is calculated by multiplying the amount spent on each marketing option by its individual visibility index and adding the results. The constraints are: i) ii) iii) iv) The budget cannot be exceeded. The amount spent on direct marketing cannot exceed $250,000. No more than $125,000 can be spent on industry conferences. At least $250,000 should be devoted to the business-finding group. Up to $125,000 can be spent on billboards. Television ad spending should be between $50,000 and $150,000. The amount spent on the business finding group cannot exceed the combined amount spent on direct marketing, industry conferences, and billboards. vi) vii) The optimal solution is (DM, IC, BFG, B, T) = (225, 125, 475, 125, 50), with an objective function value of 705 (all values in thousands). Because of the uncertainty inherent in making projections one year forward, Giannis has produced the sensitivity report for this linear programming model: Cell $C$1 $C$2 $C$3 $C$4 $C$5 Final Reduced Objective Allowable Allowable Name Value Cost Coefficient Increase Decrease DM 225 0 0.2 0.1 0.3 IC 125 0 0.6 1E+30 0.4 BFG 475 0 1.1 1E+30 0.3 B 125 0 0.3 1E+30 0.1 T 50 0 0.5 0.15 1E+30 Final Shadow Constraint Allowable Allowable Cell Name Value Price R.H. Side Increase Decrease $B$8 i) 1000 0.65 1000 50 450 $B$9 ii) 225 0 250 1E+30 25 $B$10 iii) 125 0.4 125 225 25 $B$11 iv) 475 0 250 225 1E+30 $B$12 v) 125 0.1 125 225 25 $B$13 vi) (a) 50 -0.15 50 100 50 $B$14 vi) (b) 50 0 0 1E+30 100 $B$15 vii 475 0.45 0 450 50 In search of an efficient business strategy, Giannis has identified three comparable consulting firms; Lone Star Consulting, OAG Group, and Scandinavian Insights. Each of these companies make use of a distinct business strategy, and Giannis is trying to determine which of them to emulate. Consultants at Lone Star Consulting are paid an average of $125k per year and work an average of 45 hours per week. They produce an average annual revenue (on a per consultant basis) of $350k and an average customer satisfaction score of 6.6 (on a ten-point scale). Questions 1) a) Determine the proportion of Giannis' capital to be placed in each investment that will maximize his expected return. As a risk control, he would like the variance of his portfolio to be no more than 0.001. In addition, various regulations require that no more than 21% of the portfolio can come from the hedge fund and casino, the two stocks must be at least 50% of the portfolio, and the combined amount of Stock B and Real Estate B cannot exceed 25% of the portfolio. b) Because the insurance fee is $150,000, Giannis is concerned that the solution to the previous question may not be adequate. Keeping the regulatory constraints mentioned above, determine the variance minimizing portfolio that will generate an expected return that is large enough to cover the insurance fee. 2) Using only the sensitivity report given above, answer the following questions. Give as much information as possible regarding changes to the objective function value and/or changes to the optimal variable values. a) Suppose that the brand visibility index for direct marketing is questioned. What would happen if its index was actually 0.4 b) Suppose that the brand visibility index for industry conferences is questioned. What would happen if its index was actually 0.75? c) Suppose that the brand visibility index for business finding group is questioned. What would happen if its index was actually 1.0? d) Because the budget is dependent on the results of the above investments, Aristotle is interested to understand how things might change under two scenarios: i) if the budget turned out to be $100,000 larger than expected and ii) if the budget turned out to be $100,000 less than expected. What would happen if either of these scenarios occurred? e) What would happen if the amount that can be spent on direct marketing increased to $300,000? f) What would happen if the minimum television ad spending was decreased to 25,000? g) What would happen if the maximum amount of industry conference spending were to increase to $150,000? 3) a) of the three consulting companies identified by Giannis (Loan Star Consulting, OAG Group, and Scandinavian Insights), which would you suggest that Giannis try to emulate? Base your answer on the relative efficiency that each company displays in utilizing their labor to produce revenue and positive customer satisfaction scores. Support your answer with the appropriate analysis. b) An outside analyst has predicted that, after its first year of business, Giannis' company will have paid consultants an average salary of $140k for an average of 50 hours of work per week. The analyst predicts that the average profit per analyst will be $300,000 and that the average customer satisfaction score will be 5.0. Relative to the other three consulting companies, how is Giannis' company expected to perform with respect to efficient usage of labor to produce revenue and positive customer satisfaction scores? Support your answer with the appropriate analysis. 4) Develop a linear programming model that will determine how many jobs to complete in each category each month. Do not force the optimal variable values to be integers. (Because the problem is done on a "per month" basis, non-integer solutions are ok, for instance, if the optimal solution is to complete 5.5 transportation jobs, Giannis could fully complete 5 transportation jobs in a month and do half of the work on another transportation job. The job that was not completed would then be finished in the next month.) a) How many jobs should be completed in each category? b) An advisor has suggested that an increase to the amount of available labor would be a good idea. All else being the same, is this suggestion good? Why or why not? c) The advisor also suggested that, since Pharma has the highest profit per job, it would be in our interest to find more Pharma jobs (i.e., to increase the number of available Pharma jobs from 6 to something higher). All else being the same, is this suggestion good? Why or why not










