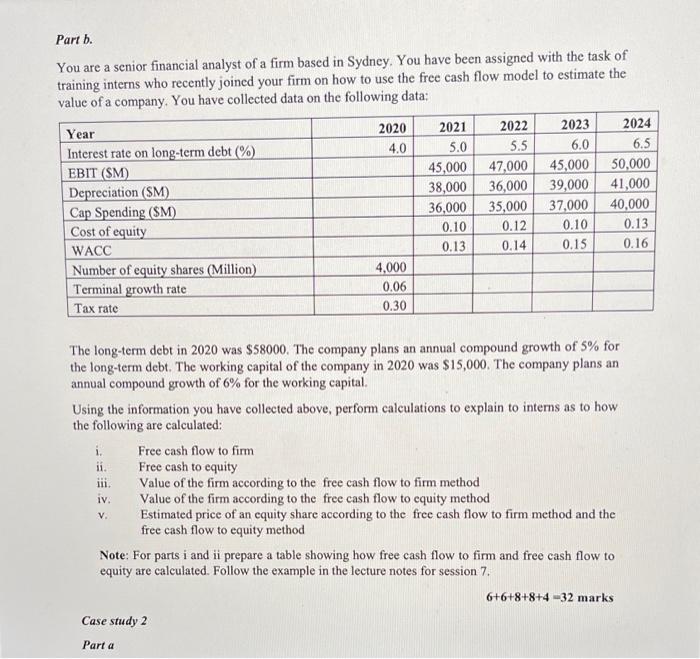
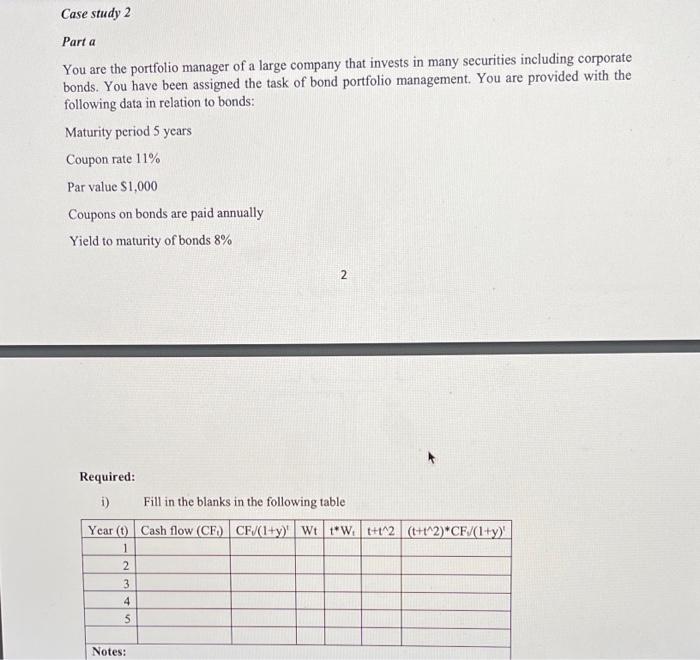
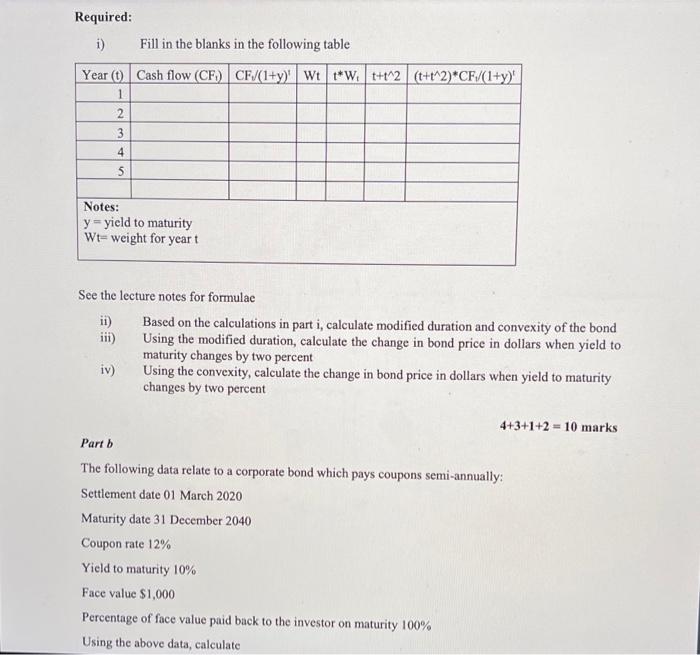
Case study 1 Part a. You are an investment adviser. One of your clients approaches you for your advice on investing in equity shares of Theta Company. You have collected the following data: Earnings per share at the end of this year $15.00 Retention ratio 0.60 Return on equity 0.30 Cost of equity capital 0.20 The company plans to decrease the retention ratio to 40% from year 6. Required: i) Estimate the price of an equity share of this company using two-period dividend discount model and advise your client whether they should buy a share of the company. ii) Your client is keen to know whether there are any positive growth opportunities from their investment. Explain to your client the meaning of this concept using appropriate calculations. iii) If there are positive or negative growth opportunities, explain the reason for such opportunities. 17+2+1 - 20 marks Part b. a You are a senior financial analyst of a firm based in Sydney. You have been assigned with the task of training interns who recently joined your firm on how to use the free cash flow model to estimate the value of a company. You have collected data on the following data: 2020 4.0 Year Interest rate on long-term debt (%) EBIT (SM) Depreciation (SM) Cap Spending (SM) Cost of equity WACC Number of equity shares (Million) Terminal growth rate Tax rate 2021 5.0 45,000 38,000 36,000 0.10 0.13 2022 5.5 47,000 36,000 35,000 0.12 0.14 2023 2024 6.0 6.5 45,000 50,000 39,000 41,000 37,000 40,000 0.10 0.13 0.15 0.16 4,000 0.06 0.30 The long-term debt in 2020 was $58000. The company plans an annual compound growth of 5% for the long-term debt. The working capital of the company in 2020 was $15,000. The company plans an annual compound growth of 6% for the working capital. Using the information you have collected above, perform calculations to explain to interns as to how the following are calculated: i. Free cash flow to firm ii. Free cash to equity Value of the firm according to the free cash flow to firm method Value of the firm according to the free cash flow to cquity method Estimated price of an equity share according to the free cash flow to firm method and the free cash flow to equity method Note: For parts i and ii prepare a table showing how free cash flow to firm and free cash flow to equity are calculated. Follow the example in the lecture notes for session 7. 6+6+8+8+4-32 marks Case study 2 ili iv. V. Parta Case study 2 Part a You are the portfolio manager of a large company that invests in many securities including corporate bonds. You have been assigned the task of bond portfolio management. You are provided with the following data in relation to bonds: Maturity period 5 years Coupon rate 11% Par value $1,000 Coupons on bonds are paid annually Yield to maturity of bonds 8% N Required: 1) Fill in the blanks in the following table Year (0) Cash flow (CF) CF/(1+y)' Wt 1* Wt+t2 (t+1^2) *CF/(1+y) 1 2 3 4 5 Notes: Required: i) Fill in the blanks in the following table Year (0) Cash flow (CF) CF/(1+y) Wt 1*W t+t2(t+t^2) *CF/(1+y) 1 2 3 4 5 Notes: y = yield to maturity Wt-weight for yeart See the lecture notes for formulae ii) Based on the calculations in part i, calculate modified duration and convexity of the bond iii) Using the modified duration, calculate the change in bond price in dollars when yield to maturity changes by two percent iv) Using the convexity, calculate the change in bond price in dollars when yield to maturity changes by two percent 4+3+1+2 = 10 marks Part 5 The following data relate to a corporate bond which pays coupons semi-annually: Settlement date 01 March 2020 Maturity date 31 December 2040 Coupon rate 12% Yield to maturity 10% Face value $1,000 Percentage of face value paid back to the investor on maturity 100% Using the above data, calculate Part b The following data relate to a corporate bond which pays coupons semi-annually: Settlement date 01 March 2020 Maturity date 31 December 2040 Coupon rate 12% Yield to maturity 10% Face value $1,000 Percentage of face value paid back to the investor on maturity 100% Using the above data, calculate i. The flat price of the bond ii. Accrued interest iii. Invoice price of the bond Note: Show the assumptions, if any, you made in your calculations. 3+2+1 - 6 marks 3 Parte A company must make a payment of $18,983 in 11 years. The market interest rate is 6%. The company's portfolio manager wishes to fund the obligation using four-year zero-coupon bonds and perpetuities paying annual coupons. How can the manager immunize the obligation? Suppose that three years have passed, and the interest rate remains at 6%. Is the position still fully funded? Is it still immunized? If not, what actions are required? 8 marks Total = 76 marks