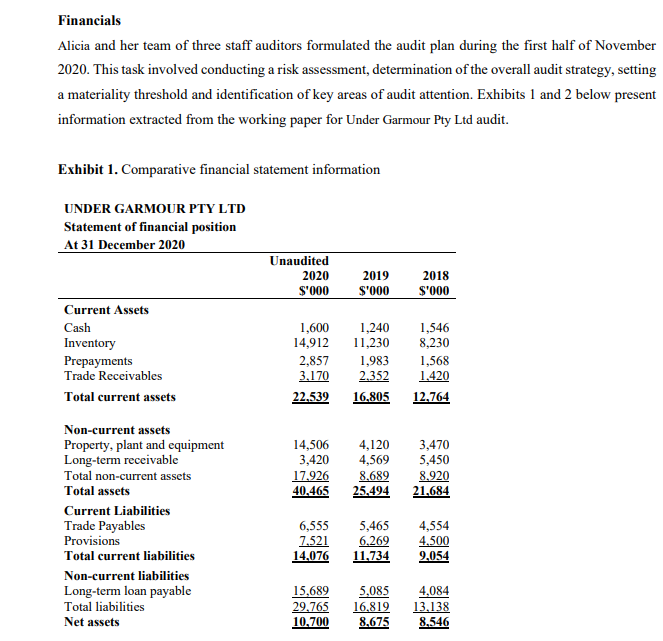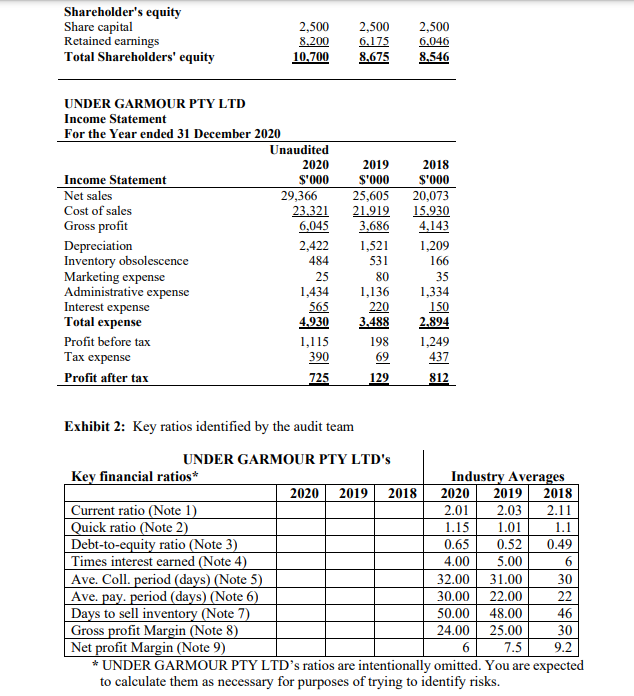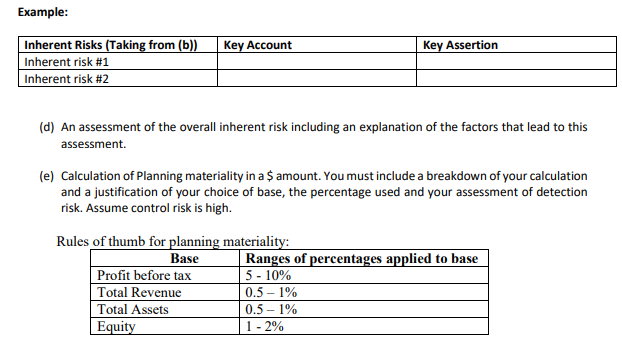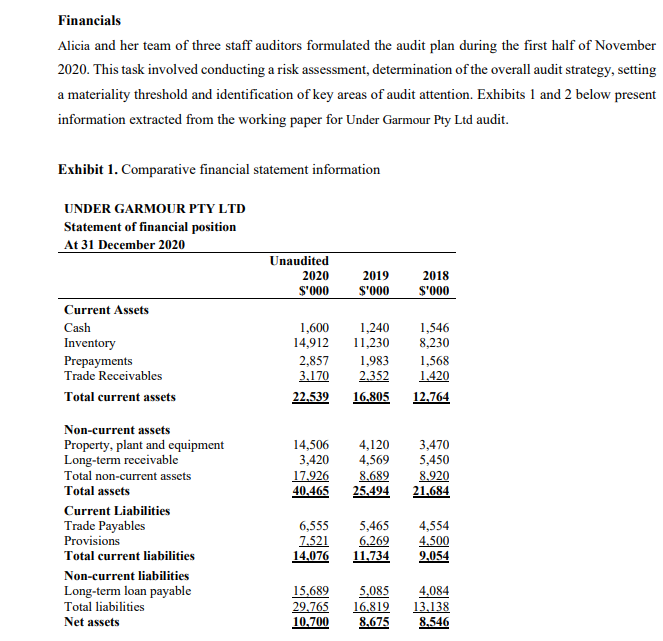
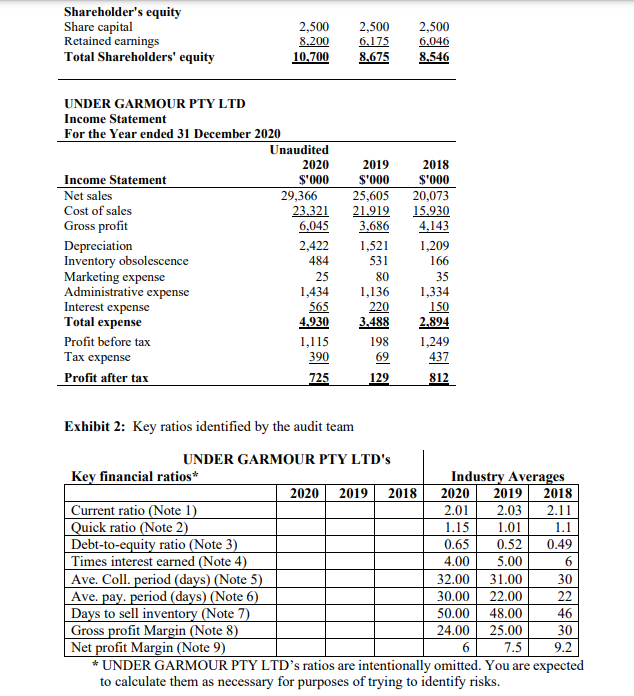

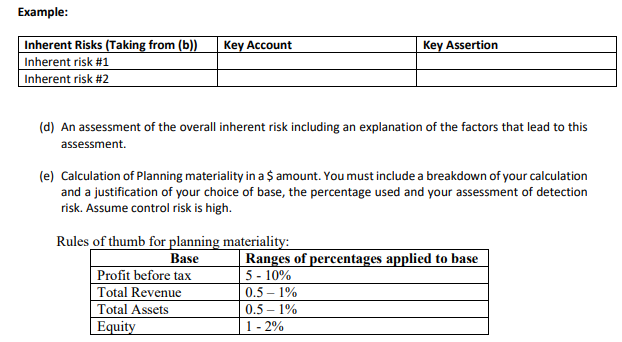
Case Study - Under Garmour Pty Ltd Introduction In October 2020, Stephanie Ng, an audit partner at Smit & Ng Accounting (S&N), a second-tier auditing firm based in Melbourne evaluated and recommended accepting a new audit client, Under Garmour Pty Ltd. Under Garmour Pty Ltd is a medium sized unlisted retail trading company operating in several parts of Victoria. Stephanie evaluated the client and assessed S&N's independence as well as competence to carry out the audit. S&N issued an engagement letter for the audit. Alicia Jones was assigned as an audit manager in charge of planning and supervising the conduct of the Under Garmour Pty Ltd audit. Under Garmour Pty Ltd's background Under Garmour Pty Ltd is a retailer of active wear garments. It operates with seven warehouses based in Victoria, New South Wales and Western Australia. The company was established as a small family business in 1980 in Melbourne and has gradually grown in size. Under Garmour Pty Ltd has a large outstanding long-term loan from Eastern Bank. The loan agreement requires Under Garmour Pty Ltd to submit its audited financial statements to East Bank by January 31 of every year until the loan is fully paid. Under Garmour Pty Ltd has a board of directors comprising of five members. Two of the members of the board of directors are newly appointed members as previous two members resigned during the 2020 financial year. The Directors and CEO receive a fixed full-time salary plus bonuses based on the company's net asset position and profit after tax amounts. The company does not have an audit committee. Under Garmour Pty Ltd's internal audit manager reports to the board of directors. All major transaction cycles, e.g., sales, purchases, payroll, etc. are supported by off-the-shelf software packages that have been sufficiently tested in the market. Under Garmour Pty Ltd employees receive necessary training on the computer systems before being assigned to their duties.Under Garmour Pty Ltd markets its products by emphasizing that it is a socia]ly responsible organisation and highlighting its moral commitment to sell only products that have minimal impact on the environment and the suppliers do not exploit their employees for a prot. This policy was introduced largely because, Jake Miller, a major shareholder with a controlling vote had advocated for it. Mr. Miller also has a major input on all policy decisions of Under Garmour Pty Ltd. Under Garmuur Pty Ltd's major product lines include tee-shirts, sweatshirts and pants. In addition, the company also sells other accessories such as towels and headbanm. Most of the suppliers are based overseas. The suppliers based overseas are paid in US Dollars whilst the local suppliers are paid in Australian Dollars. Under Garmuur Pty Ltd sells its products through retail stores and online via its website. In recent years, Under Garmour Pty Ltd experienced a trend of decreasing sales through the retail stores but the online sales have been on the rise. Under Garmeur Pty Ltd pays higher prices for some of its products for which alternative products with better value-for-money could be found in the market. Under GHII'IJD'LIJ' Pty Ltd pursues this strategy in order to maintain its commitment with its suppliers who also depend on Under Garmour Pty Ltd. With this spirit, the company aJso pays its suppliers in advance of placing purchase orders. This business practice has resulted in a large amount of advance payments to increasing number of suppliers worldwide. Financials Alicia and her team of three staff auditors formulated the audit plan during the first half of November 2020. This task involved conducting a risk assessment, determination of the overall audit strategy, setting a materiality threshold and identification of key areas of audit attention. Exhibits 1 and 2 below present information extracted from the working paper for Under Garmour Pty Ltd audit. Exhibit 1. Comparative financial statement information UNDER GARMOUR PTY LTD Statement of financial position At 31 December 2020 Unaudited 2020 2019 2018 $'000 S'000 Current Assets Cash 1,600 1,240 1,546 Inventory 14,912 11,230 8,230 Prepayments 2,857 1,983 1,568 Trade Receivables 3.170 2.352 1.420 Total current assets 22.539 16.805 12.764 Non-current assets Property, plant and equipment 14,506 4,120 3,470 Long-term receivable 3,420 4,569 5,450 Total non-current assets 17.926 8.689 8.920 Total assets 40.465 25.494 21.684 Current Liabilities Trade Payables 6,555 5,465 4,554 Provisions 7.521 6,269 4.500 Total current liabilities 14,076 11.734 9.054 Non-current liabilities Long-term loan payable 15,689 5,085 4,084 Total liabilities 29.765 16.819 13.138 Net assets 10.700 8.675 8.546Shareholder's equity Share capital 2,500 2,500 2,500 Retained earnings 8.200 6.175 6.046 Total Shareholders' equity 10.700 8.675 8.546 UNDER GARMOUR PTY LTD Income Statement For the Year ended 31 December 2020 Unaudited 2020 2019 2018 Income Statement $'000 S'000 S'000 Net sales 29,366 25,605 20,073 Cost of sales 23.321 21.919 15.930 Gross profit 6.045 3,686 4,143 Depreciation 2,422 1,521 1,209 Inventory obsolescence 484 531 166 Marketing expense 25 80 35 Administrative expense 1,434 1,136 1,334 Interest expense 565 220 150 Total expense 4.930 3.488 2.894 Profit before tax 1,115 198 1.249 Tax expense 390 69 437 Profit after tax 725 129 812 Exhibit 2: Key ratios identified by the audit team UNDER GARMOUR PTY LTD's Key financial ratios* Industry Averages 2020 2019 2018 2020 2019 2018 Current ratio (Note 1) 2.01 2.03 2.11 Quick ratio (Note 2) 1.15 1.01 1.1 Debt-to-equity ratio (Note 3) D.65 0.52 D.49 Times interest earned (Note 4) 4.00 5.00 Ave. Coll. period (days) (Note 5) 32.00 31.00 30 Ave. pay. period (days) (Note 6) 30.00 22.00 22 Days to sell inventory (Note 7) 50.00 48.00 46 Gross profit Margin (Note 8) 24.00 25.00 30 Net profit Margin (Note 9) 6 7.5 9.2 * UNDER GARMOUR PTY LTD's ratios are intentionally omitted. You are expected to calculate them as necessary for purposes of trying to identify risks.Notes: 1. Current ratio = (Total current assets/Total current liabilities) 2. Quick ratio = (Cash + trade receivable)/(total current liabilities) 3. Debt to equity ratio = (Total liabilities)/total shareholders' equity 4. Times interest earned = (profit before interest and tax)/ interest expense 5. Ave. Collection period (days) = [(Trade receivables balance)/Net Sales]*365 6. Ave. payment period (days) = [(Trade payables balance)/(Cost of Goods sold)]*365 7. Days to sell inventory = [(Inventory balance)/(Cost of Goods sold)]*365 8. Gross profit Margin = (Gross profit)/Net Sales 9. Net profit Margin = (profit after tax )/Net sales This task requires you to complete many of the audit procedures undertaken by the audit team in the planning stage of the audit. Required: Assume that you are in the position of Alicia Jones. Based on the 31 December 2020 unaudited financial reports for Under Garmour Pty Ltd, prepare a planning memorandum for the audit partner, Stephanie Ng, which includes the following: (a) Results of analytical procedures. (Please include your workings in an appendix). You should prepare a horizontal analysis and calculate key ratios. Identify and explain which changes in the horizontal analysis and which ratio results would trigger further investigation in the audit. Note: You are not required to conduct a ratio interpretation. You are to focus on the explanation of the ratios which would trigger further investigation. (b) Your identification and explanation of four (4) inherent risks that you identify from the case study and the results of the analytical procedures performed. (c) Identification of a key account and a key related assertion at risk of material misstatement based on the inherent risks you identify in part (b). (Identify a key account and a key assertion for each of the four inherent risks identified in part (b))Example: Inherent Risks (Taking from (b)) Key Account Key Assertion Inherent risk #1 Inherent risk #2 (d) An assessment of the overall inherent risk including an explanation of the factors that lead to this assessment. (e) Calculation of Planning materiality in a $ amount. You must include a breakdown of your calculation and a justification of your choice of base, the percentage used and your assessment of detection risk. Assume control risk is high. Rules of thumb for planning materiality: Base Ranges of percentages applied to base Profit before tax 5 - 10% Total Revenue 0.5- 1% Total Assets 0.5 - 1% Equity 1 - 2%