Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
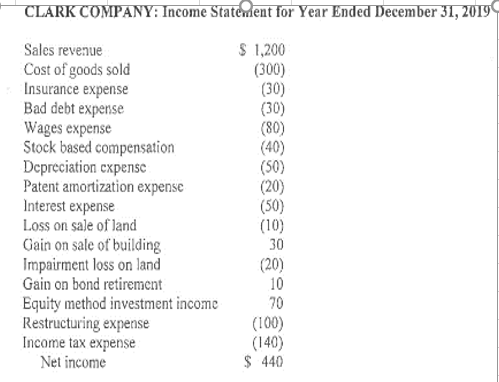
CASH FLOW STATEMENT BY BOTH DIRECT AND INDIRECT METHOD CLARK COMPANY: Income Statement for Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales revenue Cost of goods sold

CASH FLOW STATEMENT BY BOTH DIRECT AND INDIRECT METHOD
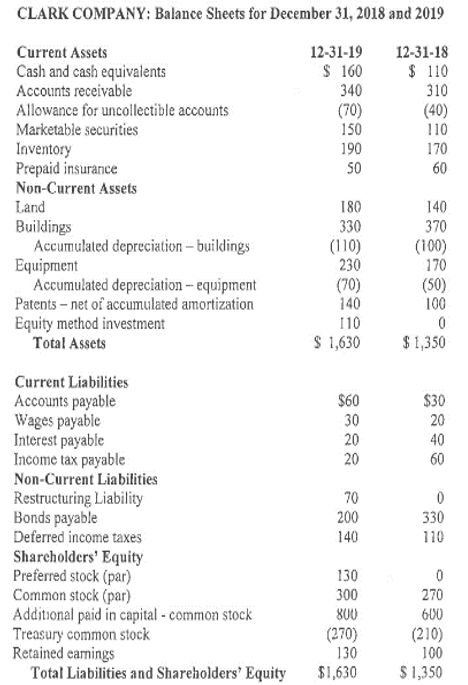
CLARK COMPANY: Income Statement for Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Insurance expense Bad debt expense Wages expense Stock based compensation Depreciation cxpense Patent amortization expense Interest expense Loss on sale of land Gain on sale of building Impairment loss on land Gain on bond retirement Equity method investment income Restructuring expense Income tax expense Net income $ 1,200 (300) (30) (30) (80) (40) (50) (20) (50) (10) 30 (20) 10 70 (100) (140) $ 440 CLARK COMPANY: Balance Sheets for December 31, 2018 and 2019 12-31-19 $ 160 340 (70) 150 190 50 12-31-18 $ 110 310 (40) 110 170 60 Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable Allowance for uncollectible accounts Marketable securities Inventory Prepaid insurance Non-Current Assets Land Buildings Accumulated depreciation - buildings Equipment Accumulated depreciation - equipment Patents - net of accumulated amortization Equity method investment Total Assets 180 330 (110) 230 (70) 140 110 $ 1,630 140 370 (100) 170 (50) 100 0 $1,350 $60 30 20 20 $30 20 40 60 Current Liabilities Accounts payable Wages payabic Interest payable Income tax payable Non-Current Liabilities Restructuring Liability Bonds payable Deferred income taxes Shareholders' Equity Preferred stock (par) Common stock (par) Additional paid in capital - common stock Treasury common stock Retained earnings Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity 70 200 140 0 330 110 130 300 800 (270) 130 $1,630 0 270 600 (210) 100 $1,350 . . ADDITIONAL DATA FOR 2019 Purchased marketable securities. Regarding marketable securities at the beginning of the year, none were sold and their market value did not change during the year. Sold for cash some land that had cost $50. Also purchased other land that was judged to be impaired at year end. Sold for cash a building that had cost $70 and had a book value of $50. Also purchased a building. Purchased equipment for cash. Did not sell any equipment . Did not sell any patents. Obtained a patent in exchange for preferred stock valued at par. Made an equity method investment at the very beginning of the year. Received dividends on the equity method investment of $40 during the year. Created long-term restructuring plan. Reduced restructuring liability by paying severance packages. Bonds payable of $130 were retired by paying cash. No bonds were issued. Deferred income taxes pertain to operations. In addition to issuing preferred stock at par for a patent, sold preferred stock for cash at par. Issued common stock for cash. Declared and paid cash dividends. Purchased treasury common stock. This was the only transaction concerning treasury shares. o . . . CLARK COMPANY: Income Statement for Year Ended December 31, 2019 Sales revenue Cost of goods sold Insurance expense Bad debt expense Wages expense Stock based compensation Depreciation cxpense Patent amortization expense Interest expense Loss on sale of land Gain on sale of building Impairment loss on land Gain on bond retirement Equity method investment income Restructuring expense Income tax expense Net income $ 1,200 (300) (30) (30) (80) (40) (50) (20) (50) (10) 30 (20) 10 70 (100) (140) $ 440 CLARK COMPANY: Balance Sheets for December 31, 2018 and 2019 12-31-19 $ 160 340 (70) 150 190 50 12-31-18 $ 110 310 (40) 110 170 60 Current Assets Cash and cash equivalents Accounts receivable Allowance for uncollectible accounts Marketable securities Inventory Prepaid insurance Non-Current Assets Land Buildings Accumulated depreciation - buildings Equipment Accumulated depreciation - equipment Patents - net of accumulated amortization Equity method investment Total Assets 180 330 (110) 230 (70) 140 110 $ 1,630 140 370 (100) 170 (50) 100 0 $1,350 $60 30 20 20 $30 20 40 60 Current Liabilities Accounts payable Wages payabic Interest payable Income tax payable Non-Current Liabilities Restructuring Liability Bonds payable Deferred income taxes Shareholders' Equity Preferred stock (par) Common stock (par) Additional paid in capital - common stock Treasury common stock Retained earnings Total Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity 70 200 140 0 330 110 130 300 800 (270) 130 $1,630 0 270 600 (210) 100 $1,350 . . ADDITIONAL DATA FOR 2019 Purchased marketable securities. Regarding marketable securities at the beginning of the year, none were sold and their market value did not change during the year. Sold for cash some land that had cost $50. Also purchased other land that was judged to be impaired at year end. Sold for cash a building that had cost $70 and had a book value of $50. Also purchased a building. Purchased equipment for cash. Did not sell any equipment . Did not sell any patents. Obtained a patent in exchange for preferred stock valued at par. Made an equity method investment at the very beginning of the year. Received dividends on the equity method investment of $40 during the year. Created long-term restructuring plan. Reduced restructuring liability by paying severance packages. Bonds payable of $130 were retired by paying cash. No bonds were issued. Deferred income taxes pertain to operations. In addition to issuing preferred stock at par for a patent, sold preferred stock for cash at par. Issued common stock for cash. Declared and paid cash dividends. Purchased treasury common stock. This was the only transaction concerning treasury shares. oStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


