Question: CD3 is a signaling protein that is typically found only in the plasma membrane of immune system T lymphocytes. CD3 is composed of several different
CD3 is a signaling protein that is typically found only in the plasma membrane of immune system T lymphocytes. CD3 is composed of several different polypeptides, including a gamma chain, CD3? . Scientists analyzed the promoter of the CD3? chain gene for regulatory sequences that might have positive or negative effects on expression of the gene. The scientists cloned fragments of the CD3? gene that included the first transcribed nucleotides plus up to 789 nucleotides of upstream regulatory sequences into plasmids in which the gene for the firefly enzyme luciferase immediately follows the fragments. The plasmids were then introduced into a line of T lymphocytes (Figure 1), and the cells were allowed to grow for a short while. Because the regulatory sequences of the CD3? gene immediately precede the luciferase gene in the plasmids, the activity, either positive or negative, of the regulatory sequences affected the amount of luciferase gene expression by the T lymphocytes. Luciferase catalyzes a reaction that results in the release of light and is responsible for the bioluminescence (light flashes) of fireflies. By quantifying the bioluminescence, or luciferase activity, in the cells, the scientists were able to determine the effects of each CD3? gene fragment cloned into the plasmids (Figure 2) on expression of the gene.

Figure 1. Summary of experimental procedure. A series of plasmids containing fragments of the CD3? upstream regulatory sequences cloned immediately before the luciferase gene were constructed. Each type of plasmid was introduced into T lymphocytes. The amount of luciferase produced by the lymphocytes was dependent on the regulatory sequences present in each plasmid.
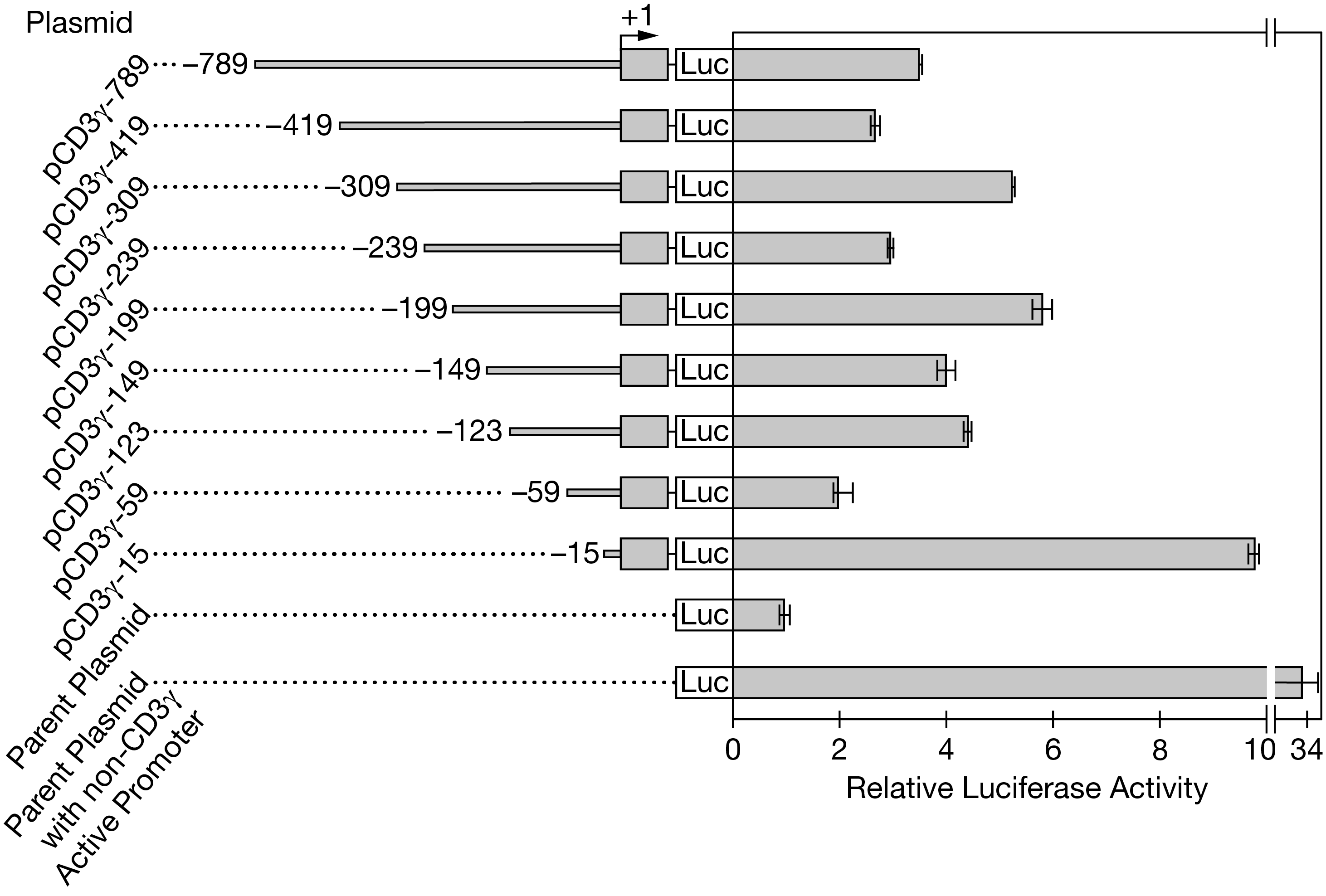
Figure 2. Analysis of the luciferase activity of T lymphocytes containing plasmids with different amounts of the CD3? regulatory sequence. Names of the plasmids are shown on the left. Included regulatory sequences and the resulting luciferase activity are shown on the right. Error bars represent ?2SEx?. The transcription start site is indicated by +1.
(a) Identify both the cellular component and the location of the component that is responsible for producing the luciferase protein from mRNAs transcribed in the plasmid-containing T lymphocytes. Explain what dictates to the lymphocytes the correct order in which amino acids should be linked to form the luciferase protein.
(b) Identify the independent variable in the experiment described. Identify the plasmid that was used as a negative control for luciferase activity. Justify including the plasmid with the non-CD3? active promoter in the experiments.
(c) Identify the plasmid that must contain the CD3? core promoter sequence but the fewest or no negative regulatory sequences. Based on the data in Figure 2, describe the most likely cause of the variation in luciferase activity among the cells that contain plasmids pCD3?-419, pCD3?-309, pCD3?-239, and pCD3?-199. Calculate the approximate percent increase in luciferase activity between cells containing plasmid pCD3?-59and cells containing plasmid pCD3?-149. Round to the nearest whole number.
(d) Predict the most likely observed level of luciferase activity if plasmid pCD?3-789 is introduced into nonlymphoid cells such as a line of kidney tissue cells. Provide reasoning to justify your prediction.
Poly (A) Signal Upstream Regulatory Sequences +1 + Transcribed Region CD3y Gene Luciferase Gene Plasmid Location in Which CD3y Sequences Are Inserted Introduce Plasmids into T Lymphocytes Plasmid Luciferase Production T Lymphocytes with Plasmids Plasmid pCD3y-789. pCD3y-419. pCD3y-309, pCD3y-239 pCD3y-199 pCD3y-149 pCD3y-123. pCD3y-59 pCD3y-15 Parent Plasmid -789 Parent Plasmid. with non-CD3y Active Promoter -419 -309 -239 -199 -149 -123 -59- + -15- Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc Luc 0 + 2 + 4 + 6 Relative Luciferase + 8 Activity HI 10 34
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (153 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Cellular Component and Location Ribosome This is the cellular machinery responsible for synthesizing proteins from mRNA Ribosomes are found in the c... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


