Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
ch 4 p3 The balance sheet of a company shows a firm's assets and liabilities (and stockholders' balance sheet illustrates a firm's overall financial position.
ch 4 p3 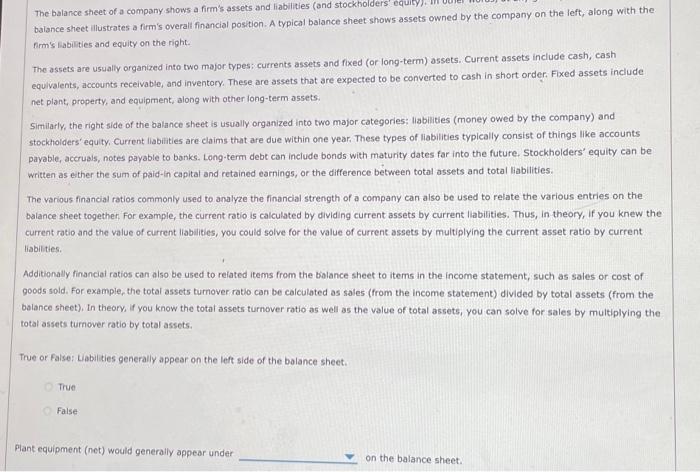
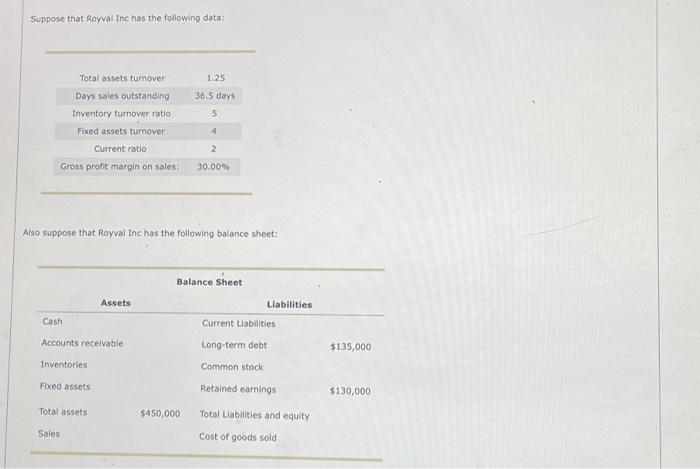
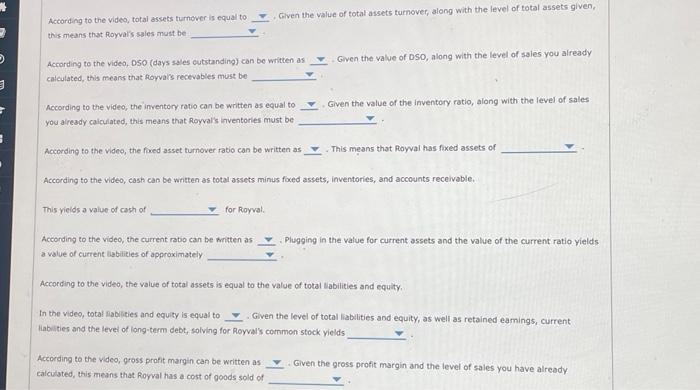
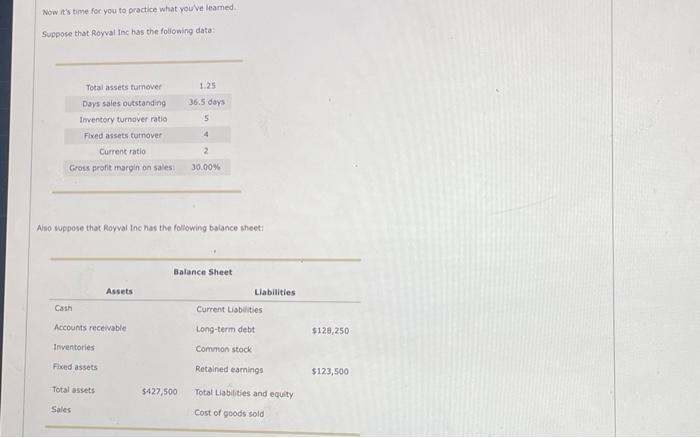
The balance sheet of a company shows a firm's assets and liabilities (and stockholders' balance sheet illustrates a firm's overall financial position. A typical balance sheet shows assets owned by the company on the left, along with the. firm's rabilities and equity on the right. The assets are usually organized into two major types; currents assets and fixed (or long-term) assets. Current assets include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, and inventory. These are assets that are expected to be converted to cash in short order. Fixed assets include net plant, property, and equipment, along with other long-term assets. Similarly, the right side of the balance sheet is usually organized into two major categories: liabilities (money owed by the company) and stockholders' equity, Current liabiities are claims that are due within one year. These types of liabilities typically consist of things like accounts payable, accruals, notes payable to banks. Long-term debt can include bonds with maturity dates far into the future. Stockholders' equity can be written as ether the sum of paid-in capital and retained earnings, or the difference between total assets and total liabilities. The various financial ratios commonly used to analyze the financial strength of a company can also be used to relate the various entries on the balance sheet together. For example, the current ratio is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities. Thus, in theory, if you knew the current ratio and the value of current liabilities, you could solve for the value of current assets by multiplying the current asset ratio by current liabilities. Additionally financial ratios can also be used to related items from the balance sheet to items in the income statement; such as sales or cost of goods sold. For example, the total assets tumover ratio can be calculated as sales (from the income statement) divided by total assets (from the balance sheet), In theory, if you know the total assets turnover ratio as well as the value of total assets, you can solve for sales by multiplying the total assets turnover ratio by total assets. True or False: Liabilities generally appear on the left side of the balance sheet. True False Plant equipment (net) would generally appear under on the balance sheet. Suppose that Royval Inc has the following data: Also suppose that Royval Inc has the following balance sheet: Actording to the video, total assets fumover is equal to Civen the value of total assets turnover, along with the level of total assets given, this means that Royvar's sales must be Acrording to the video, DSO (days sales cutstanding) can be written as Given the value of DSO, along with the level of sales you already calculated, this means that forvals recevables must be According to the video, the inventory rotio can be written as equal to - Given the value of the inventory ratio, along with the level of sales you already calculated, this means that Royval's inventories must be Accerding to the video, the fored asset turnover rabio can be written as . This means that Royval has fixed assets of According to the video, cash can be written as total assets minus foced assets, inventories, and accounts receivable. This vieids a value of cash of for Royral. According to the video, the current ratio can be written as - Plugging in the value for current assets and the value of the current ratio yields. a value of current labilities of approximately According to the video, the value of total assets. is equal to the value of total Labilities and equity. In the video, total rabilities and equity is equal to - Given the level of total liabilities and equity, as well as retained eamings, current liabilities and the levei of long-term debt, solving for Royval's cornmon stock vields According to the video, gross profit margin can be written as calculated, this means that forval has a cost of goods sold of Given the gross profit margin and the level of sales you have alreody. Now its time for you to practice what you ve leamed. Suppose that Rorval Inc has the following data: Also wppose that Rowal the has the following balance sheet: Use the formulas you learned about in the prevlous stage of the problem to answer the following questions. Given the value of total assets turnover, along with the level of total assets given, this means that Royval's sales must be Given the value of DSO, along with the level of sales you already calculated, this means that Royval's recelvables must be Given the value of the inventory ratio, along with the level of sales you already calculated, this means that Royval's inventories must be - Given the value of the foxed assets tumover ratio, as well as the level of sales, this means that Royval's foxed assets must be equal to Solving for cash yields a value of cash of for Royval. Given the current ratio of 2 and values of cash, accounts receivable, and inventories, the level of current liabilities must be Given the level of retained eamings, current liabilties, and long-term debt, along with the relationship between total assets and total liabilities and equity, this means that Rayval's common stock must be Given the gross profit margin and the level of sales you have already calculated, this means that Royral has a cost of goods sold of 




Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


