Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
[ Chemical Engineering ] Please explain the process mechanisms: All auger tubes of the pyrolyzer were under negative pressure, which caused volatiles and gases (
Chemical Engineering
Please explain the process mechanisms:
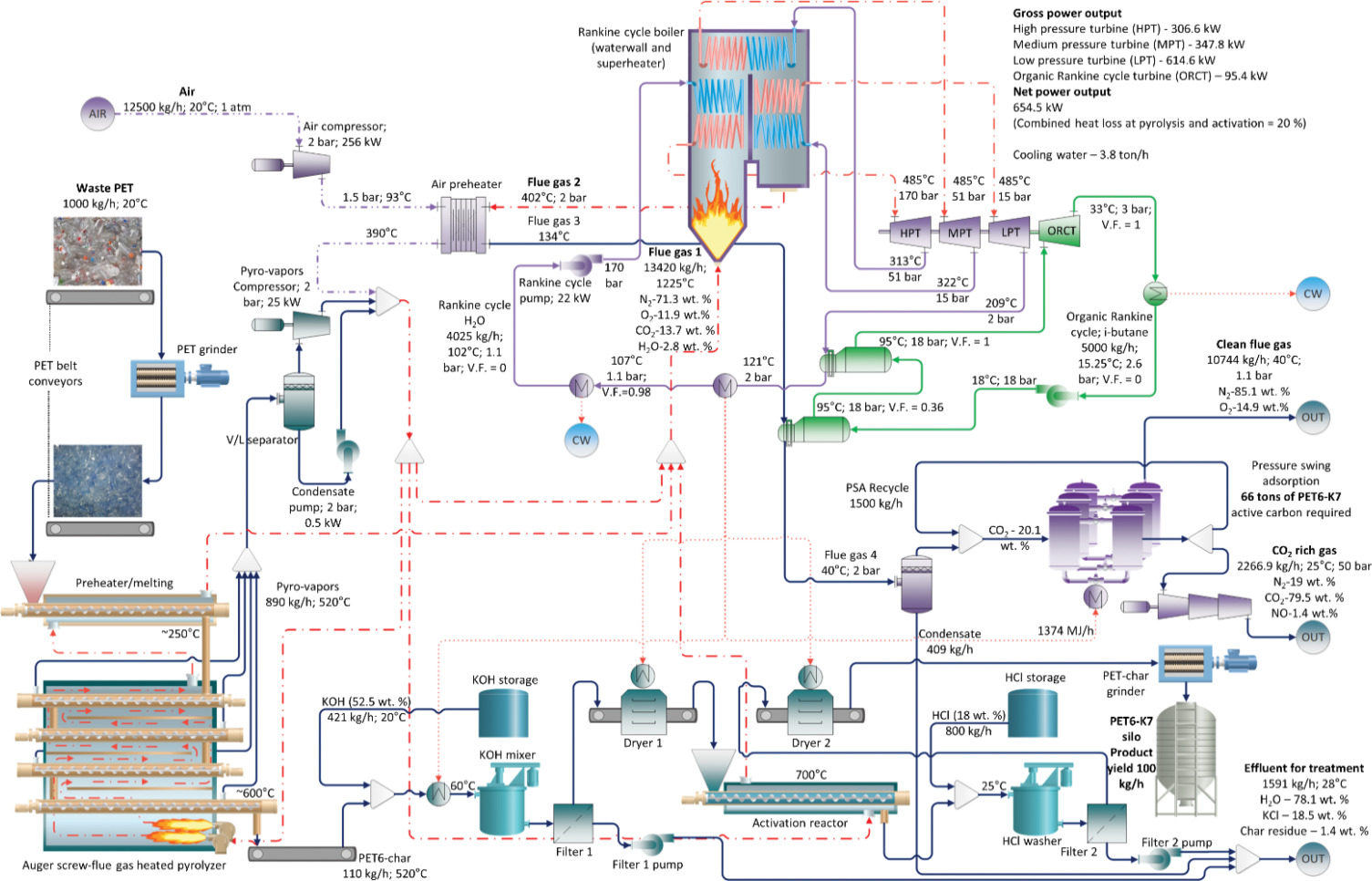
All auger tubes of the pyrolyzer were under negative pressure, which caused volatiles and gases kg h to be transported to a temporary storage drum a vaporliquid separator The assumed heat losses lowered the temperature of the pyrolysis products from deg C to deg C during transportation. Approximately t h of air was compressed and heated to deg C in an air preheater. A combustion mixture of hot air and pyrolysis products was then
utilized for three major sinks of hightemperature heat: the pyrolyzer, activation reactor, and Rankine cycle boiler. Eventually, all combustion products were utilized in the Rankine cycle as they vaporized and superheated the steam. Approximately t h of water was utilized in the Rankine cycle for electricity generation. After the last turbine expansion, the hot watersteam mixture at deg C and bar first transferred heat in the ORC boiler and then emitted heat to meet the unit operation requirements of preheating, drying, and desorption. The steam was completely reliquefied in a cooling water condenser, after which it was compressed to a maximum pressure of bar to restart the cycle. The flue gases exited the Rankine cycle boiler at deg C and were used to preheat the combustion air, which cooled the gases down to deg C This temperature was too high for CO capture using the pressure swing adsorption PSA system and would require a large amount of cooling water to reduce the temperature
below deg C owing to the sheer flow rate of the flue gas Therefore, an ORC was introduced to utilize this large amount of waste heat. The ORC working fluid t h of isobutane was compressed to bar and entered the first reboiler at deg C where it absorbed the flue gas heat and cooled the gas to deg C As it exited the reboiler, the isobutane had a vapor fraction of only ; therefore, the heat needed to achieve total vapor was provided by the Rankine cycle hot water in the second reboiler. The ORC turbine expanded the isobutane to bar and generated kW of work, after which it was condensed to liquid at deg C and was recompressed. In all the cases, the total gross power generated from the combined power cycles was approximately MW or MW net when all unit operations were considered. The cooled flue gas was first separated from the condensed water in a flash drum, after which the CO was separated using a series of PSA beds that utilized the three WPDPCs The amount of PSA adsorbent bed material calculated from the flue gas composition, flow rate, and experimental isotherms necessary for complete CO separation varied from to tons based on the activation route. The COrich gas was compressed to a pipeline pressure of bar and was removed from the process either as a secondary product or for storage.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


