
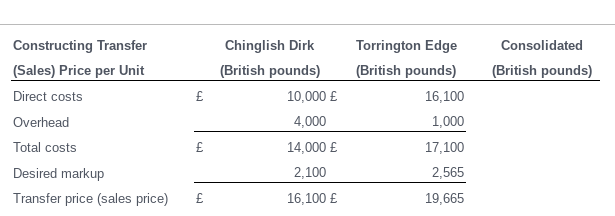
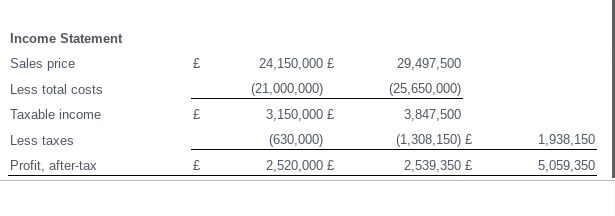
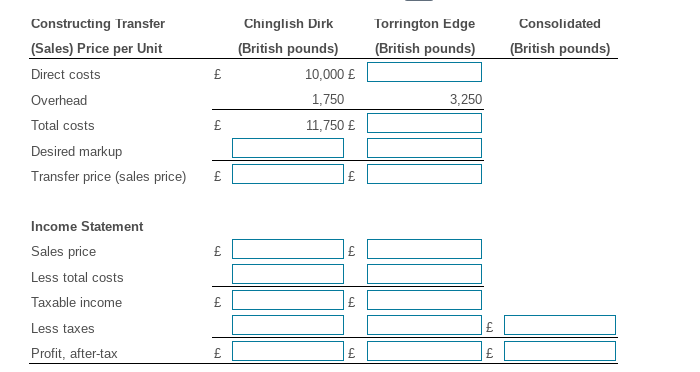
Chinglish Dirk (C). Chinglish Dirk Company (Hong Kong) exports razor blades to its wholly owned parent company, Torrington Edge (Great Britain). Hong Kong tax rates are 20% and British tax rates are 34%. The markup was 15% and the sales volume was 1,500 units. Chinglish calculates its profit per container as follows (all values in British pounds): Corporate management of Torrington Edge wishes to reposition profit in Hong Kong. It is, however, facing two constraints. First, the final sales price in Great Britain must be 20,000 or less to remain competitive. Secondly, the British tax authorities - in working with Torrington Edge's cost accounting staff-has established a maximum transfer price allowed (from Hong Kong) of 17,800. Not to leave any potential tax repositioning opportunities unexplored, Torrington Edge wants to combine the components described above with a redistribution of overhead costs. If overhead costs could be reallocated between the two units, but still total 5,000 per unit, and maintain a minimum of 1,750 per unit in Hong Kong, prove that the optimal combination of markups is a 35.0% markup at Chinglish and an 4.64% markup in Torrington Edge. What is the impact of this repositioning on consolidated after-tax profits and total tax payments? \begin{tabular}{lcccc} ConstructingTransfer(Sales)PriceperUnit & & ChinglishDirk(Britishpounds) & TorringtonEdge(Britishpounds) & Consolidated(Britishpounds) \\ \hline Direct costs & & 10,000 & 16,100 \\ Overhead & & 4,000 & 1,000 \\ Total costs & & 14,000 & 17,100 \\ Desired markup & & 2,100 & 2,565 \\ Transfer price (sales price) & & 16,100 & 19,665 \end{tabular} Income Statement \begin{tabular}{lccrr} Sales price & & 24,150,000 & 29,497,500 \\ Less total costs & & (21,000,000) & (25,650,000) \\ Taxable income & & 3,150,000 & 3,847,500 & \\ \cline { 2 - 5 } Less taxes & & (630,000) & (1,308,150) & 1,938,150 \\ \cline { 2 - 5 } Profit, after-tax & & 2,520,000 & 2,539,350 & 5,059,350 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \begin{tabular}{llcr|} ConstructingTranster(Sales)PriceperUnit & ChinglishDirk(Britishpounds) & TorringtonEdge(Britishpounds) & Consolidated(Britishpounds) \\ \hline Direct costs & & 10,000 \\ Overhead & & 1,750 \\ Total costs & & 11,750 \\ Desired markup & & \\ Transfer price (sales price) & & \end{tabular} Income Statement \begin{tabular}{lll|} Sales price & & \\ Less total costs & & \\ Taxable income & \\ Less taxes & \\ Profit, after-tax & \end{tabular}










