Question: Cisco Networking Configuration Just configuration Use Packet Tracer to complete this lab. 203.0.114.0/24 PPPoE with CHAP client auth only Gig0/0 Se[/0/0 (2301 Seo/0/1 Sloud PT-Empty
Cisco Networking Configuration Just configuration
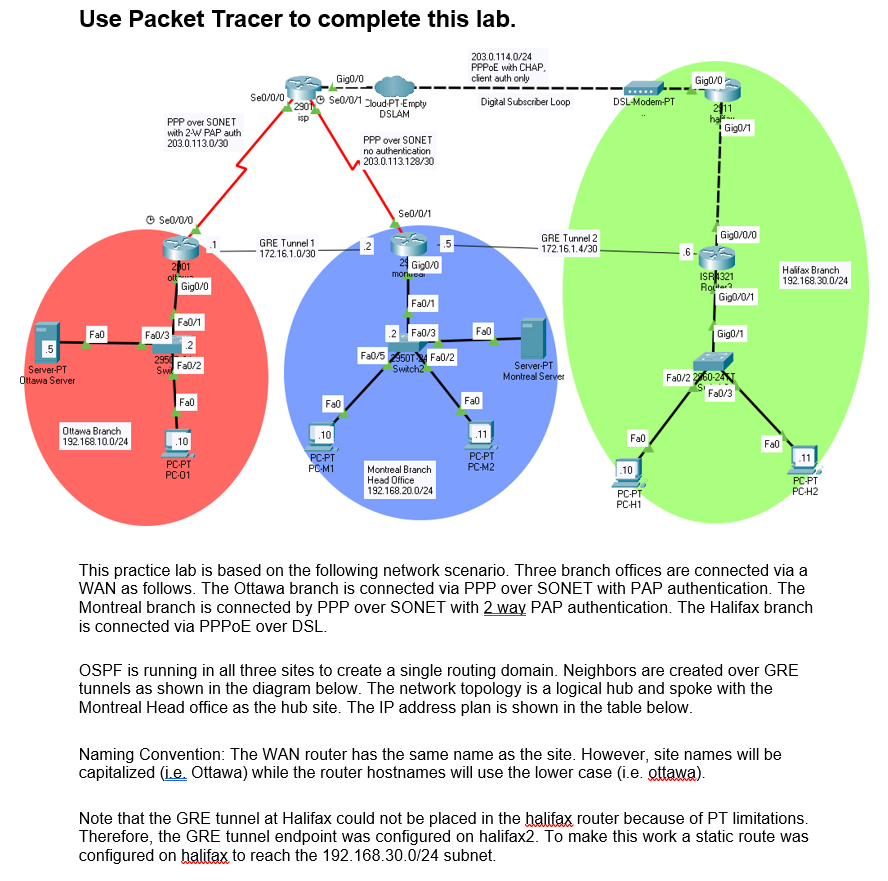




Use Packet Tracer to complete this lab. 203.0.114.0/24 PPPoE with CHAP client auth only Gig0/0 Se[/0/0 (2301 Seo/0/1 Sloud PT-Empty Digkal Subscriber Loop DSL-Modem-PT Gigo/ 2011 ha Gig0/1 isp DSLAM. PPP over SONET with 2 W PAP auth 203.0.113.0/30 PPP over SONET no authentication 203.0.113.128/30 Se0/0/0 Se[/0/1 GRE Tunnel 2 172.16.1.4/30 Gigo/0/0 GRE Tunnel 1 172.161.0/30 .6 201 Gig0/0 2 Gig0/0 monluca ott Halifax Branch 192.168.30.0/24 ISA321 Rol2 Gig0/0/1 Fa0/1 Fab Fa0/3 FO Gig0/1 5 Server-PT Ottawa Server Fa0/1 2 295 Fa0/2 2 F30/3 Fa0/52501 F20/2 Switch2 Server PT Montreal Server Fa0/2260-29 "Fa0/3 Fal Fall Fall Ottawa Branch 192.168.10.0/24 .10 .11 .10 Fal Fall PC-PT PC-M1 PC-PT PC-01 PC-PT PC-M2 .11 .10 Montreal Branch Head Office 192.168.20.0/24 PCPT PC-H2 PC-PT PC-H1 This practice lab is based on the following network scenario. Three branch offices are connected via a WAN as follows. The Ottawa branch is connected via PPP over SONET with PAP authentication. The Montreal branch is connected by PPP over SONET with 2 way PAP authentication. The Halifax branch is connected via PPPoE over DSL. OSPF is running in all three sites to create a single routing domain. Neighbors are created over GRE tunnels as shown in the diagram below. The network topology is a logical hub and spoke with the Montreal Head office as the hub site. The IP address plan is shown in the table below. Naming Convention: The WAN router has the same name as the site. However, site names will be capitalized (ie. Ottawa) while the router hostnames will use the lower case (i.e. ottawa). Note that the GRE tunnel at Halifax could not be placed in the halifax router because of PT limitations. Therefore, the GRE tunnel endpoint was configured on halifax2. To make this work a static route was configured on halifax to reach the 192.168.30.0/24 subnet. Part 1: Network Configuration Step 1: Housekeeping Config For All Network Devices a. disable ip domain lookup b. logging synchronous on console C. disable exec timeout Step 2: Interface Configuration a. The Packet Tracer file includes the network devices and the basic configuration for the branch sites. The ISP router and DSLAM are fully configured. b. Your role in this lab is the configuration of the branch site routers for provide WAN connectivity and OSPF routing. Step 3: Ottawa router WAN Configuration a. Configure the WAN interface with PPP encapsulation. b. Configure 2-way PAP authentication as follows. 1) Use the hostname as username. 2) ottawa password = stardust; This means the Ottawa router sends username ottawa and password stardust to the isp router. The isp router validates this from its local auth database. 3) isa password = bonds. Step 4: Montreal router WAN Configuration a. Configure the WAN interface with PPP encapsulation. 1) Authentication is not used on this interface. Step 5: Halifax router WAN Configuration a. The WAN is already configured. You need to configure the site router for PPPoE. b. Configure PPPoE on the halifax router as follows: 1) The IP address will be provided by the ISP. Use the following command for IP address: ip address negotiated This is a fixed address 203.0.114.10 which is provided by the ise. The address is fixed to permit site to site VPN using GRE tunnels. 2) The ip to adjust-mss is not supported so do not use it. 3) Configure the interface expect CHAP authentication request. Use the following information: hostname: lansing password: brook. 4) Map the virtual Dialer interface to GO/O. Step 6: OSPF Configuration (all sites) a. Configure a GRE tunnel from ottawa router to montreal couer Configure another GRE tunnel from the halifax router to the montreal router. b. Configure OSPF at each site. Configure the OSPF as a hub and spoke with montreal as the hub site. 2) Notice the addresses in the IP header. e. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches the ottawa WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) Which protocol header was removed? 2) Which protocol headers were added? Why? 3) Which IP address are in the IP headers now? f. Advance the simulator until the packet reaches the ISP router. Inspect the outbound packet. 1) Was there any change in the header stack? 9. Advance the simulation again. It will reach the router. 1) What was the destination router. 2) If the packet is destined for the Halifax why does it take a detour via Montreal? h. Advance the simulation again. The packet should reach the ISP router again. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) What changes were made in the packet header stack? 2) Why were these changes made. 3) There are now two levels of tunneling (ie, a tunnel inside a tunnel). What are they? 4) What is the purpose of the PPPoE header? 5) What is the purpose of the PPP header. 6) Which fields surround the PPP header. i Advance the simulation again. The packet should reach the haliax WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. Tunnel end point. The router was configured as the PPPoE tunnel end point. 1) In PPPoE, which protocol is the passenger (inside header) and which is the carrier protocol (outside header) j Advance the simulation once again. The packet should reach the halifax2 router. The G0/0/0 interface is the GRE tunnel endpoint. 1) Notice that the GRE header have been removed. 2) The packet is left with the original headers but a new local Ethernet header. k. Advance the simulation until it reaches the destination. Inspect the inbound PDU. 1) Notice the original IP addresses. Step 2: ACL Established Keyword a. The established key means that a TCP session must be established before the packet can be permitted. The is used to block devices trying to use port 80 to break through the firewall. b. A session is established only when the TCP session setup completes using SYN-SY/ACK-SYN. After session setup the ACK flag stays set. If the ACK flag is not set, the packet is rejected. Let's use the simulator to see this. C. Here are the TCP flags. The important flags for our discussion are FIN, SYN, and ACK. @ 1 2 3 @ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ 1 Source Port Destination Port -+-+-+ -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- 1 Sequence Number +-+ -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- 1 Acknowledgment Number +-+-+-+ Data | JULAI PRISIF | Offset Reserved IRICISI SYI! Window G|KHTINN -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ 1 Checksum Urgent Pointer +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- 1 Options Padding -+-+-+-+-+-+ data d. Enable the simulator. Filter on the HTTP and TCP packets. e. From PC-01 send an HTTP request to the Montreal server. f. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches the Ottawa WAN router. g. Inspect the TCP flags of the outgoing PDU. 1) Which TCP flags are set? h. Advance the simulator until the TCP reply reach the Ottawa router. 1) Which TCP flags are set? i. Advance the simulator until the PC sends the 3rd TCP packet in the 3W handshake. j. Advance the simulator until the PC sends the HTTP Request packet. k. Advance the simulator until the HTTP Reply reaches the Ottawa WAN router. Inspect the inbound PDU. 1) What flags are set? 2) Which flag indicates that this an established session? 3) Will this flag be set if a hacker tries to send an unsolicited HTTP reply? Step 3: Source Port vs Destination Port a. When ACLs filter a request packet the well-known source port is specified. When and ACL filters a reply packet the well-known destination port is specified. b. Let's test this using the simulator. C. Reset the simulator and filter on HTTP. d. From PC-H2 send an HTTP request to the Montreal Server. e. Advance the simulator until the HTTP Request packet reaches the Ottawa WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) Which Port is set to the well-known port number of HTTP? 2) How is the other port set? f. Advance the simulator until the HTTP reply reaches the Ottawa WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) Which Port is set to the well-known port number of HTTP? 2) How is the other port set? Step 4: ICMP Keywords a. There are two important key words for the ICMP protocol: echo and echo-reply. If we only want to block incoming ismp requests use the echo keyword. If we only want to block ismp replies, use the echo-reply key word. If we want to block both, do not use any keyword. b. Reset the simulator and filter on ICMP only. C. From PC-H1 ping the Ottawa server. Use the simulator to follow the packet. 1) Was the ping successful? d. Reset the simulator and repeat. From PC-H1 ping PC-01 instead. 1) What happens to the packet at the Ottawa router? 2) A response packet is returned. Inspect the response packet. What is the ICMP type and code? 3) What does the ICMP type and code field mean? Step 5: QOS a. Reset the simulation. Set the HTTP filter only. b. Initiate an HTTP request to the Ottawa Server. C. Advance the simulation 1click and inspect the packet at the PC. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the packet? d. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches the Halifax WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the packet? e. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches its destination at the Ottawa server. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the inbound PDU? 2) Did it change at any time along its path? f. Advance the simulation another click until the HTTP reply reaches the Ottawa WAN switch. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the inbound PDU? 2) Has it change changed from the original HTTP request message? Why? Use Packet Tracer to complete this lab. 203.0.114.0/24 PPPoE with CHAP client auth only Gig0/0 Se[/0/0 (2301 Seo/0/1 Sloud PT-Empty Digkal Subscriber Loop DSL-Modem-PT Gigo/ 2011 ha Gig0/1 isp DSLAM. PPP over SONET with 2 W PAP auth 203.0.113.0/30 PPP over SONET no authentication 203.0.113.128/30 Se0/0/0 Se[/0/1 GRE Tunnel 2 172.16.1.4/30 Gigo/0/0 GRE Tunnel 1 172.161.0/30 .6 201 Gig0/0 2 Gig0/0 monluca ott Halifax Branch 192.168.30.0/24 ISA321 Rol2 Gig0/0/1 Fa0/1 Fab Fa0/3 FO Gig0/1 5 Server-PT Ottawa Server Fa0/1 2 295 Fa0/2 2 F30/3 Fa0/52501 F20/2 Switch2 Server PT Montreal Server Fa0/2260-29 "Fa0/3 Fal Fall Fall Ottawa Branch 192.168.10.0/24 .10 .11 .10 Fal Fall PC-PT PC-M1 PC-PT PC-01 PC-PT PC-M2 .11 .10 Montreal Branch Head Office 192.168.20.0/24 PCPT PC-H2 PC-PT PC-H1 This practice lab is based on the following network scenario. Three branch offices are connected via a WAN as follows. The Ottawa branch is connected via PPP over SONET with PAP authentication. The Montreal branch is connected by PPP over SONET with 2 way PAP authentication. The Halifax branch is connected via PPPoE over DSL. OSPF is running in all three sites to create a single routing domain. Neighbors are created over GRE tunnels as shown in the diagram below. The network topology is a logical hub and spoke with the Montreal Head office as the hub site. The IP address plan is shown in the table below. Naming Convention: The WAN router has the same name as the site. However, site names will be capitalized (ie. Ottawa) while the router hostnames will use the lower case (i.e. ottawa). Note that the GRE tunnel at Halifax could not be placed in the halifax router because of PT limitations. Therefore, the GRE tunnel endpoint was configured on halifax2. To make this work a static route was configured on halifax to reach the 192.168.30.0/24 subnet. Part 1: Network Configuration Step 1: Housekeeping Config For All Network Devices a. disable ip domain lookup b. logging synchronous on console C. disable exec timeout Step 2: Interface Configuration a. The Packet Tracer file includes the network devices and the basic configuration for the branch sites. The ISP router and DSLAM are fully configured. b. Your role in this lab is the configuration of the branch site routers for provide WAN connectivity and OSPF routing. Step 3: Ottawa router WAN Configuration a. Configure the WAN interface with PPP encapsulation. b. Configure 2-way PAP authentication as follows. 1) Use the hostname as username. 2) ottawa password = stardust; This means the Ottawa router sends username ottawa and password stardust to the isp router. The isp router validates this from its local auth database. 3) isa password = bonds. Step 4: Montreal router WAN Configuration a. Configure the WAN interface with PPP encapsulation. 1) Authentication is not used on this interface. Step 5: Halifax router WAN Configuration a. The WAN is already configured. You need to configure the site router for PPPoE. b. Configure PPPoE on the halifax router as follows: 1) The IP address will be provided by the ISP. Use the following command for IP address: ip address negotiated This is a fixed address 203.0.114.10 which is provided by the ise. The address is fixed to permit site to site VPN using GRE tunnels. 2) The ip to adjust-mss is not supported so do not use it. 3) Configure the interface expect CHAP authentication request. Use the following information: hostname: lansing password: brook. 4) Map the virtual Dialer interface to GO/O. Step 6: OSPF Configuration (all sites) a. Configure a GRE tunnel from ottawa router to montreal couer Configure another GRE tunnel from the halifax router to the montreal router. b. Configure OSPF at each site. Configure the OSPF as a hub and spoke with montreal as the hub site. 2) Notice the addresses in the IP header. e. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches the ottawa WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) Which protocol header was removed? 2) Which protocol headers were added? Why? 3) Which IP address are in the IP headers now? f. Advance the simulator until the packet reaches the ISP router. Inspect the outbound packet. 1) Was there any change in the header stack? 9. Advance the simulation again. It will reach the router. 1) What was the destination router. 2) If the packet is destined for the Halifax why does it take a detour via Montreal? h. Advance the simulation again. The packet should reach the ISP router again. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) What changes were made in the packet header stack? 2) Why were these changes made. 3) There are now two levels of tunneling (ie, a tunnel inside a tunnel). What are they? 4) What is the purpose of the PPPoE header? 5) What is the purpose of the PPP header. 6) Which fields surround the PPP header. i Advance the simulation again. The packet should reach the haliax WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. Tunnel end point. The router was configured as the PPPoE tunnel end point. 1) In PPPoE, which protocol is the passenger (inside header) and which is the carrier protocol (outside header) j Advance the simulation once again. The packet should reach the halifax2 router. The G0/0/0 interface is the GRE tunnel endpoint. 1) Notice that the GRE header have been removed. 2) The packet is left with the original headers but a new local Ethernet header. k. Advance the simulation until it reaches the destination. Inspect the inbound PDU. 1) Notice the original IP addresses. Step 2: ACL Established Keyword a. The established key means that a TCP session must be established before the packet can be permitted. The is used to block devices trying to use port 80 to break through the firewall. b. A session is established only when the TCP session setup completes using SYN-SY/ACK-SYN. After session setup the ACK flag stays set. If the ACK flag is not set, the packet is rejected. Let's use the simulator to see this. C. Here are the TCP flags. The important flags for our discussion are FIN, SYN, and ACK. @ 1 2 3 @ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ 1 Source Port Destination Port -+-+-+ -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- 1 Sequence Number +-+ -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- 1 Acknowledgment Number +-+-+-+ Data | JULAI PRISIF | Offset Reserved IRICISI SYI! Window G|KHTINN -+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+-+ 1 Checksum Urgent Pointer +-+-+-+-+-+-+-+- 1 Options Padding -+-+-+-+-+-+ data d. Enable the simulator. Filter on the HTTP and TCP packets. e. From PC-01 send an HTTP request to the Montreal server. f. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches the Ottawa WAN router. g. Inspect the TCP flags of the outgoing PDU. 1) Which TCP flags are set? h. Advance the simulator until the TCP reply reach the Ottawa router. 1) Which TCP flags are set? i. Advance the simulator until the PC sends the 3rd TCP packet in the 3W handshake. j. Advance the simulator until the PC sends the HTTP Request packet. k. Advance the simulator until the HTTP Reply reaches the Ottawa WAN router. Inspect the inbound PDU. 1) What flags are set? 2) Which flag indicates that this an established session? 3) Will this flag be set if a hacker tries to send an unsolicited HTTP reply? Step 3: Source Port vs Destination Port a. When ACLs filter a request packet the well-known source port is specified. When and ACL filters a reply packet the well-known destination port is specified. b. Let's test this using the simulator. C. Reset the simulator and filter on HTTP. d. From PC-H2 send an HTTP request to the Montreal Server. e. Advance the simulator until the HTTP Request packet reaches the Ottawa WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) Which Port is set to the well-known port number of HTTP? 2) How is the other port set? f. Advance the simulator until the HTTP reply reaches the Ottawa WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) Which Port is set to the well-known port number of HTTP? 2) How is the other port set? Step 4: ICMP Keywords a. There are two important key words for the ICMP protocol: echo and echo-reply. If we only want to block incoming ismp requests use the echo keyword. If we only want to block ismp replies, use the echo-reply key word. If we want to block both, do not use any keyword. b. Reset the simulator and filter on ICMP only. C. From PC-H1 ping the Ottawa server. Use the simulator to follow the packet. 1) Was the ping successful? d. Reset the simulator and repeat. From PC-H1 ping PC-01 instead. 1) What happens to the packet at the Ottawa router? 2) A response packet is returned. Inspect the response packet. What is the ICMP type and code? 3) What does the ICMP type and code field mean? Step 5: QOS a. Reset the simulation. Set the HTTP filter only. b. Initiate an HTTP request to the Ottawa Server. C. Advance the simulation 1click and inspect the packet at the PC. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the packet? d. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches the Halifax WAN router. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the packet? e. Advance the simulation until the packet reaches its destination at the Ottawa server. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the inbound PDU? 2) Did it change at any time along its path? f. Advance the simulation another click until the HTTP reply reaches the Ottawa WAN switch. Inspect the outbound PDU. 1) What is the DSCP marking of the inbound PDU? 2) Has it change changed from the original HTTP request message? Why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


