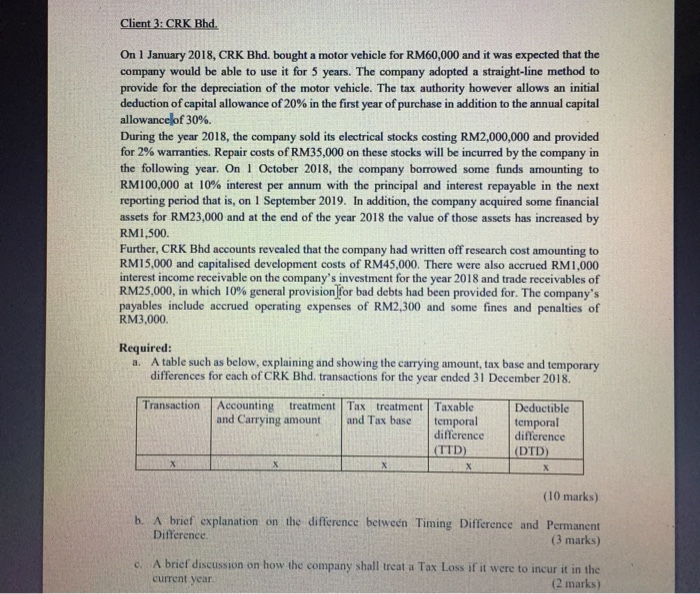
Client 3: CRK Bhd. year On 1 January 2018, CRK Bhd. bought a motor vehicle for RM60,000 and it was expected that the company would be able to use it for 5 years. The company adopted a straight-line method to provide for the depreciation of the motor vehicle. The tax authority however allows an initial deduction of capital allowance of 20% in the first year of purchase in addition to the annual capital allowance of 30%. During the 2018, the company sold its electrical stocks costing RM2,000,000 and provided for 2% warranties. Repair costs of RM35,000 on these stocks will be incurred by the company in the following year. On 1 October 2018, the company borrowed some funds amounting to RM100,000 at 10% interest per annum with the principal and interest repayable in the next reporting period that is, on 1 September 2019. In addition, the company acquired some financial assets for RM23,000 and at the end of the year 2018 the value of those assets has increased by RM1,500 Further, CRK Bhd accounts revealed that the company had written off research cost amounting to RM15,000 and capitalised development costs of RM45,000. There were also accrued RM1,000 interest income receivable on the company's investment for the year 2018 and trade receivables of RM25,000, in which 10% general provision for bad debts had been provided for. The company's payables include accrued operating expenses of RM2,300 and some fines and penalties of RM3,000 Required: A table such as below, explaining and showing the carrying amount, tax base and temporary differences for each of CRK Bhd. transactions for the year ended 31 December 2018. Transaction Accounting treatment Tax treatment Taxable Deductible and Carrying amount and Tax base temporal temporal difference difference (TTD) (DTD) X X X (10 marks) b. A brief explanation on the difference between Timing Difference and Permanent Difference (3 marks) c. A brief discussion on how the company shall treat a Tax Loss if it were to incur it in the current year (2 marks) Client 2: ZES Bhd. On 1 January 2018, ZES Bhd. purchased a machine costing RM400,000 with a useful life of 5 years. It is the company's policy to provide for the depreciation of the machine on a straight line basis. However, the tax depreciation or capital allowance for the machine is 40% in the first two years and 10% in subsequent years. I Required: a. A table showing the computation of Deferred Tax from years 1 to 5, assuming profit before tax for each year is RM1,000,000 and income tax is 20%. (5 marks) b. An explanation on how those deferred tax is accounted for over 5-year period and its implication to the amount of tax expense charged to the company's Statement of Profit and Loss and the amount of tax payable by the company. (5 marks) Client 3: CRK Bhd. year On 1 January 2018, CRK Bhd. bought a motor vehicle for RM60,000 and it was expected that the company would be able to use it for 5 years. The company adopted a straight-line method to provide for the depreciation of the motor vehicle. The tax authority however allows an initial deduction of capital allowance of 20% in the first year of purchase in addition to the annual capital allowance of 30%. During the 2018, the company sold its electrical stocks costing RM2,000,000 and provided for 2% warranties. Repair costs of RM35,000 on these stocks will be incurred by the company in the following year. On 1 October 2018, the company borrowed some funds amounting to RM100,000 at 10% interest per annum with the principal and interest repayable in the next reporting period that is, on 1 September 2019. In addition, the company acquired some financial assets for RM23,000 and at the end of the year 2018 the value of those assets has increased by RM1,500 Further, CRK Bhd accounts revealed that the company had written off research cost amounting to RM15,000 and capitalised development costs of RM45,000. There were also accrued RM1,000 interest income receivable on the company's investment for the year 2018 and trade receivables of RM25,000, in which 10% general provision for bad debts had been provided for. The company's payables include accrued operating expenses of RM2,300 and some fines and penalties of RM3,000 Required: A table such as below, explaining and showing the carrying amount, tax base and temporary differences for each of CRK Bhd. transactions for the year ended 31 December 2018. Transaction Accounting treatment Tax treatment Taxable Deductible and Carrying amount and Tax base temporal temporal difference difference (TTD) (DTD) X X X (10 marks) b. A brief explanation on the difference between Timing Difference and Permanent Difference (3 marks) c. A brief discussion on how the company shall treat a Tax Loss if it were to incur it in the current year (2 marks) Client 2: ZES Bhd. On 1 January 2018, ZES Bhd. purchased a machine costing RM400,000 with a useful life of 5 years. It is the company's policy to provide for the depreciation of the machine on a straight line basis. However, the tax depreciation or capital allowance for the machine is 40% in the first two years and 10% in subsequent years. I Required: a. A table showing the computation of Deferred Tax from years 1 to 5, assuming profit before tax for each year is RM1,000,000 and income tax is 20%. (5 marks) b. An explanation on how those deferred tax is accounted for over 5-year period and its implication to the amount of tax expense charged to the company's Statement of Profit and Loss and the amount of tax payable by the company