Question: CMPT 295: Assignment 1 Note: Make sure to show your work for all questions! See the instructions on the course web-page for submitting your work.
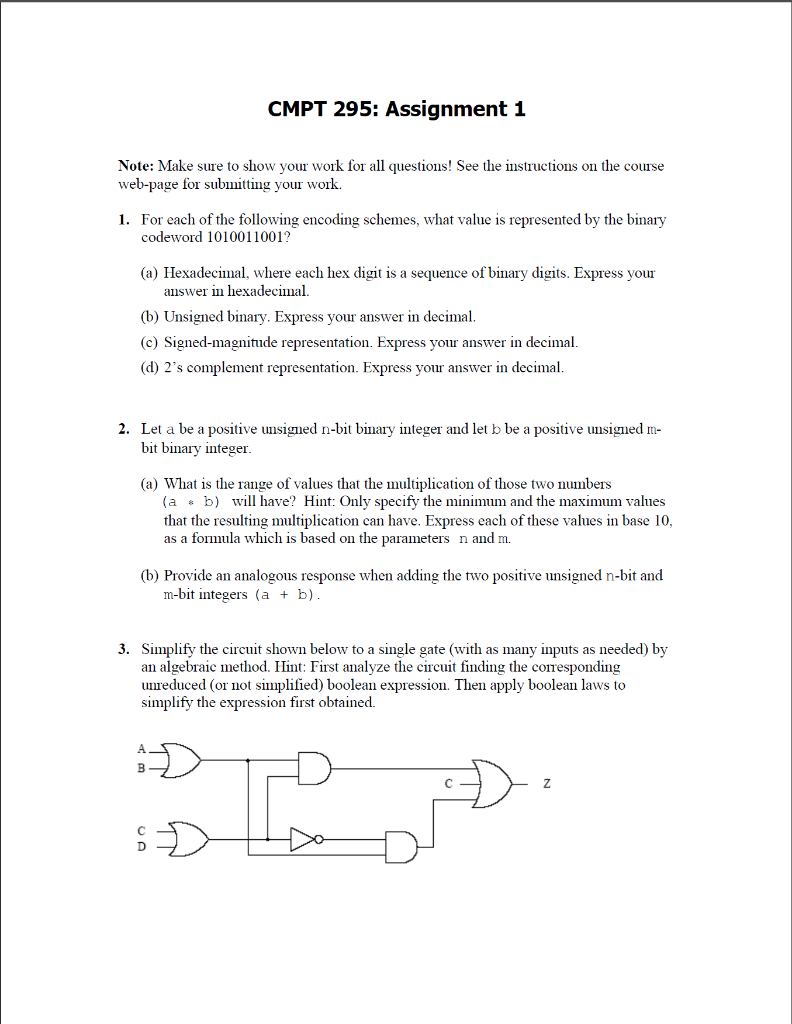
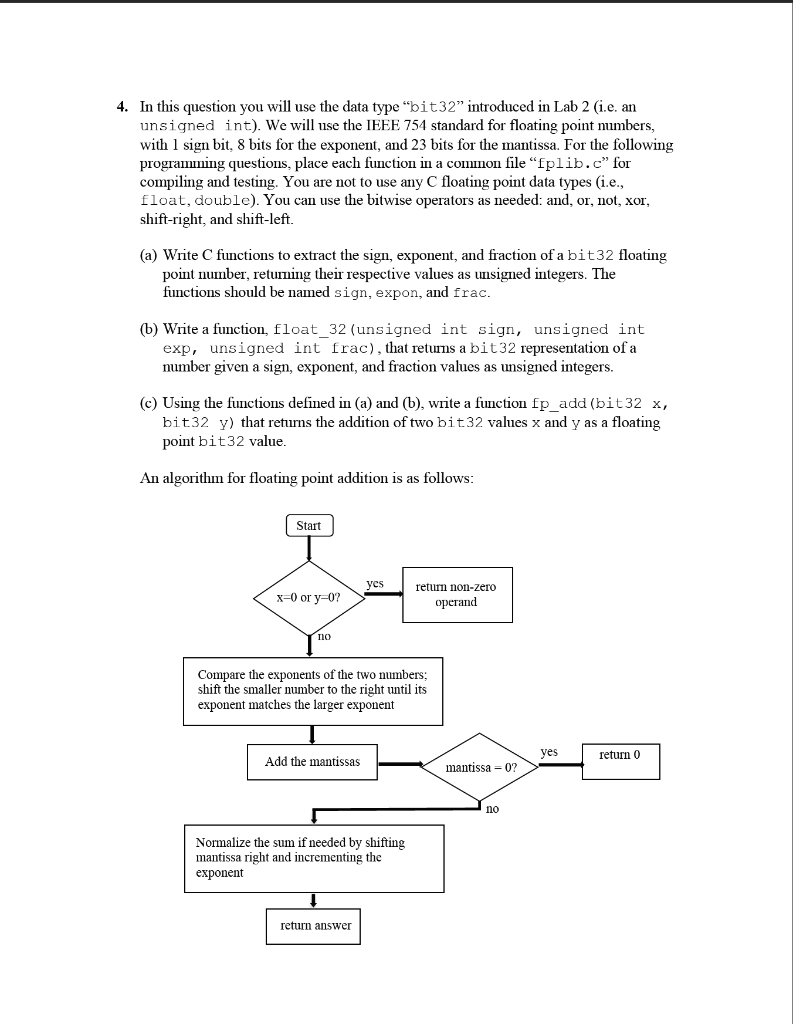

CMPT 295: Assignment 1 Note: Make sure to show your work for all questions! See the instructions on the course web-page for submitting your work. 1. For each of the following encoding schemes, what value is represented by the binary codeword 1010011001? (a) Hexadecimal, where each hex digit is a sequence of binary digits. Express your answer in hexadecimal. (b) Unsigned binary. Express your answer in decimal. (c) Signed-magnitude representation. Express your answer in decimal. (d) 2's complement representation. Express your answer in decimal. 2. Let a be a positive unsigned n-bit binary integer and let b be a positive unsigned m- bit binary integer (a) What is the range of values that the multiplication of those two numbers (a + b) will have? Hint: Only specify the minimum and the maximum values that the resulting multiplication can have. Express each of these values in base 10, as a formula which is based on the parameters n and m. (b) Provide an analogous response when adding the two positive unsigned n-bit and m-bit integers (a + b). 3. Simplify the circuit shown below to a single gate (with as many inputs as needed) by an algebraic method. Hint: First analyze the circuit finding the corresponding unreduced (or not simplified) boolean expression. Then apply boolean laws to simplify the expression first obtained. D D 4. In this question you will use the data type "bit32" introduced in Lab 2 (i.e. an unsigned int). We will use the IEEE 754 standard for floating point numbers, with 1 sign bit, 8 bits for the exponent, and 23 bits for the mantissa. For the following programning questions, place each function in a comminon file "fplib.c" for compiling and testing. You are not to use any C floating point data types (i.e., float, double). You can use the bitwise operators as needed: and, or, not, xor, shift-right, and shift-left. (a) Write C functions to extract the sign, exponent, and fraction of a bit32 floating point number, returning their respective values as unsigned integers. The functions should be named sign, expon, and frac. (b) Write a function, float_32 (unsigned int sign, unsigned int exp, unsigned int frac), that returns a bit32 representation of a number given a sign, exponent, and fraction values as unsigned integers. (c) Using the functions defined in (a) and (b), write a function fp_add (bit32 x, bit32 y) that returns the addition of two bit32 values x and y as a floating point bit32 value. An algorithm for floating point addition is as follows: Start yes x=0 or y=0? return non-zero operand Compare the exponents of the two numbers: shift the smaller number to the right until its exponent matches the larger exponent yes return 0 Add the mantissas Yes mantissa mantissa 07 0? Normalize the sum if needed by shifting mantissa right and incrementing the exponent return answer Notes: You should handle the case where the answer is zero. You may assume that both operands x and y are nonnegative (i.e., 0 or positive). You do not have to handle overflow or underflow Remember that the exponent is stored in bias-127 format. Test your fp_add function thoroughly! Use the printhex function from Lab 2 when testing to output the values returned from your function
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


