Question
Code below in SI units: clc; clear all; close all; % g=9.81; % acceleration under gravity in m/s^2 B=-0.0065; % temp lapse rate in ISA

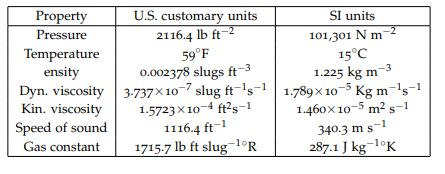
Code below in SI units:
clc; clear all; close all; % g=9.81; % acceleration under gravity in m/s^2 B=-0.0065; % temp lapse rate in ISA in K/m R=287.05; % gas constant for air % T_sl=288.15; % ISA MSL standard temperature in Kelvin p_sl=1.01325e+5; % standard pressure at sea level in Pa % rho_sl=p_sl/(R*T_sl) % use gas law to get density a_sl=sqrt(1.40*p_sl/rho_sl) % speed of sound at sea level % calculate ISA at a single altitude i.e. z is a number z=10000 % altitude in m % T_z=T_sl+B*z p_z=p_sl*((1+B*z/T_sl)^(-g/(R*B))) rho_z=p_z/(R*T_z) mu_z=1.458E-6*sqrt(T_z)/(1.0+0+110.40/T_z) % Sutherland's law for viscosity a=sqrt(1.40*p_z/rho_z) % speed of sound % calculate ISA over a range lf altitudes and plot i.e., z is a vector % Observe how the periods (.) are placed. Also note the plots how now both % the fontsize and the font types have been explicitly set. z=linspace(0,10000,1000); T_z=T_sl+B.*z; p_z=p_sl.*((1+B.*z./T_sl).^(-g/(R*B))); rho_z=p_z./(R.*T_z); mu_z=1.458e-6.*sqrt(T_z)./(1.0+0+110.40./T_z); % Sutherland's law for viscosity a_z=sqrt(1.40.*p_z./rho_z); % speed of sound % figure plot(T_z-273.15,z,'-r','LineWidth',2) xlabel('T_z in ^oC') ylabel('z in m') set(gca,'FontSize',18,'FontName','Times') % figure plot(p_z*1e-3,z,'-r','LineWidth',2) xlabel('p_z in kPa') ylabel('z in m') set(gca,'FontSize',18,'FontName','Times') % figure plot(rho_z,z,'-r','LineWidth',2) xlabel(' ho_z in kg m^{-3}') ylabel('z in m') set(gca,'FontSize',18,'FontName','Times') % figure plot(a_z,z,'-r','LineWidth',2) xlabel('a_z in m s^{-1}') ylabel('z in m') set(gca,'FontSize',18,'FontName','Times') % figure plot(T_z./T_sl,z,'-k',p_z./p_sl,z,'-r',rho_z./rho_sl,z,'-b',... a_z./a_sl,z,'-g','LineWidth',2) hl=legend('T_z/T_{sl}','p_z/p_{sl}',' ho_z/ ho_{sl}',... 'a_z/a_{sl}'); set(hl,'Location','SouthWest') ylabel('z in m') set(gca,'FontSize',18,'FontName','Times')
4. (10 pts) Use Matlab to calculate the properties of the ISA in USC units. Plot the temperature, pressure and density (in appropriate units) as a function of altitude up to 36,000 ft. Hint: Make sure your plots are properly labeled. 4. (10 pts) Use Matlab to calculate the properties of the ISA in USC units. Plot the temperature, pressure and density (in appropriate units) as a function of altitude up to 36,000 ft. Hint: Make sure your plots are properly labeledStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


