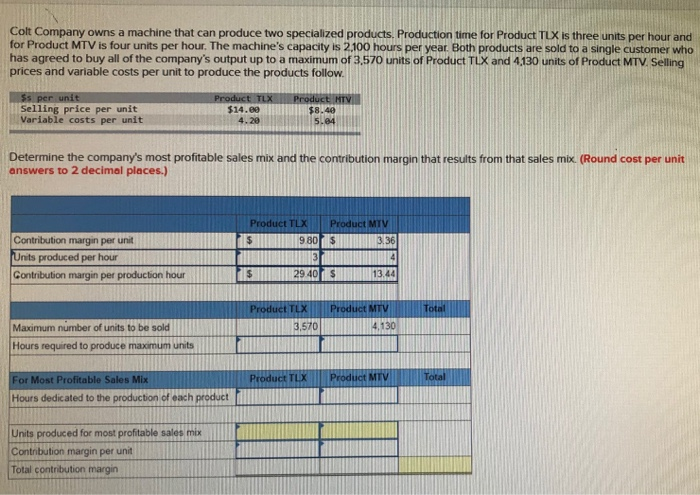
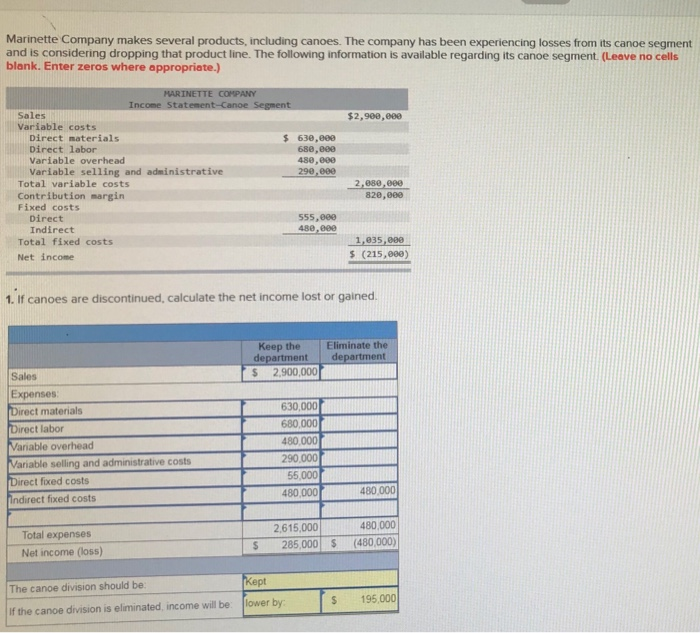
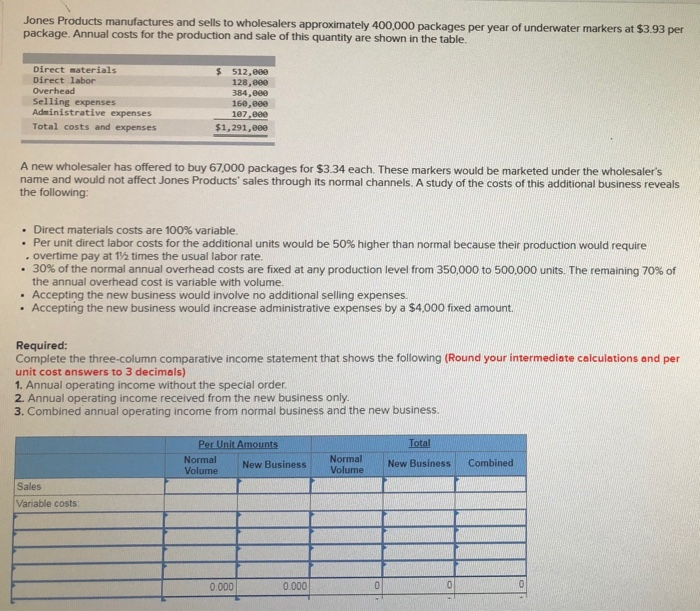
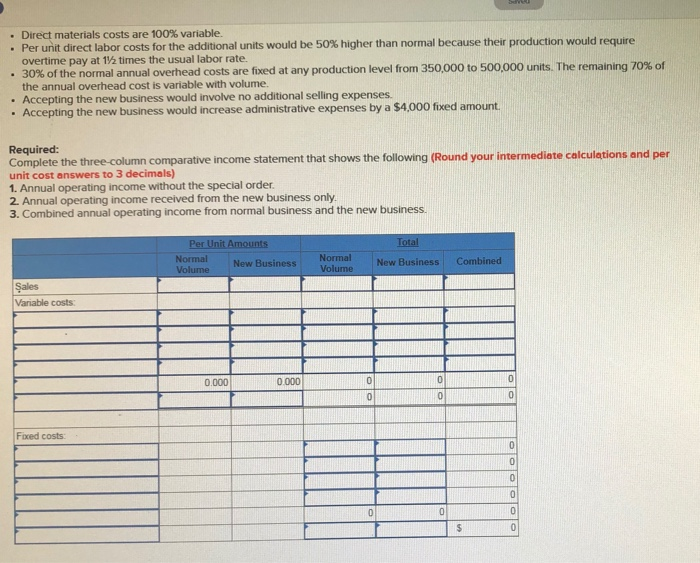
Colt Company owns a machine that can produce two specialized products. Production time for Product TLX is three units per hour and for Product MTV is four units per hour. The machine's capacity is 2.100 hours per year. Both products are sold to a single customer who has agreed to buy all of the company's output up to a maximum of 3,570 units of Product TLX and 4130 units of Product MTV. Selling prices and variable costs per unit to produce the products follow. $5 per unit Selling price per unit Variable costs per unit $14.69 4.20 Determine the company's most profitable sales mix and the contribution margin that results from that sales mix (Round cost per unit answers to 2 decimal places.) Product TLX Product MTV Contribution margin per unit Units produced per hour Contribution margin per production hour $ 29 40 s 13.44 Product TLX Product MTV 3.570 Maximum number of units to be sold Hours required to produce maximum units Product TLX | Product MTV For Most Profitable Sales Mix Hours dedicated to the production of each product Units produced for most profitable sales mix Contribution margin per unit Total contribution margin Marinette Company makes several products, including canoes. The company has been experiencing losses from its canoe segment and is considering dropping that product line. The following information is available regarding its canoe segment. (Leave no cells blank. Enter zeros where appropriate.) $2,900,000 MARINETTE COMPANY Income Statement-Canoe Segment Sales Variable costs Direct materials $ 630,000 Direct labor 680,eee Variable overhead 480,000 Variable selling and administrative 290.000 Total variable costs Contribution margin Fixed costs Direct 555,000 Indirect 480,000 Total fixed costs Net income 2,880,000 820,000 1,835,000 $ (215,000) 1. If canoes are discontinued, calculate the net income lost or gained. Keep the Eliminate the department department $ 2,900,0001 Sales Expenses 630,000 480.000 Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Variable selling and administrative costs Direct fixed costs indirect fixed costs 290.000 55.000 480,000 480.000 Total expenses Net income (loss) 2.615,000 285 000 480,000 480,000) $ $ The canoe division should be: if the canoe division is eliminated income will be Kept lower by: $ 195,000 Jones Products manufactures and sells to wholesalers approximately 400,000 packages per year of underwater markers at $3.93 per package. Annual costs for the production and sale of this quantity are shown in the table. Direct materials Direct labor Overhead Selling expenses Administrative expenses Total costs and expenses $ 512.000 128,00 3.84,00 160.869 107.000 $1,291,600 A new wholesaler has offered to buy 67,000 packages for $3.34 each. These markers would be marketed under the wholesaler's name and would not affect Jones Products' sales through its normal channels. A study of the costs of this additional business reveals the following: Direct materials costs are 100% variable. Per unit direct labor costs for the additional units would be 50% higher than normal because their production would require . Overtime pay at 172 times the usual labor rate. 30% of the normal annual overhead costs are fixed at any production level from 350,000 to 500.000 units. The remaining 70% of the annual overhead cost is variable with volume. Accepting the new business would involve no additional selling expenses. Accepting the new business would increase administrative expenses by a $4.000 fixed amount Required: Complete the three-column comparative income statement that shows the following (Round your intermediate calculations and per unit cost answers to 3 decimals) 1. Annual operating income without the special order. 2. Annual operating income received from the new business only. 3. Combined annual operating income from normal business and the new business Per Unit Amounts Normal New Business Volume Normal Total New Business Volume Combined Sales Variable costs: ........ 0.000 0.000 00 Direct materials costs are 100% variable. Per unit direct labor costs for the additional units would be 50% higher than normal because their production would require overtime pay at 15 times the usual labor rate. . 30% of the normal annual overhead costs are fixed at any production level from 350,000 to 500,000 units. The remaining 70% of the annual overhead cost is variable with volume. Accepting the new business would involve no additional selling expenses. Accepting the new business would increase administrative expenses by a $4,000 fixed amount. Required: Complete the three column comparative income statement that shows the following (Round your intermediate calculations and per unit cost answers to 3 decimals) 1. Annual operating income without the special order. 2. Annual operating income received from the new business only 3. Combined annual operating income from normal business and the new business Per Unit Amounts New Business Volume Normal Volume Total New Business Combined Sales Variable costs 0.0000 .000 Fixed cost ODOT Cobe Company has already manufactured 22,000 units of Product A at a cost of $30 per unit. The 22,000 units can be sold at this stage for $480,000. Alternatively, the units can be further processed at a $260,000 total additional cost and be converted into 6,000 units of Product B and 12,000 units of Product C. Per unit selling price for Product B is $100 and for Product C is $60. 1. Prepare an analysis that shows whether the 22,000 units of Product A should be processed further or not. Sell as is Process Further $ 480,000 Sales Relevant costs: Costs to process further Manufacturing costs incurred to date Total relevant costs Income (loss) ntal income Incremental net income (or loss) if processed further The company should process further