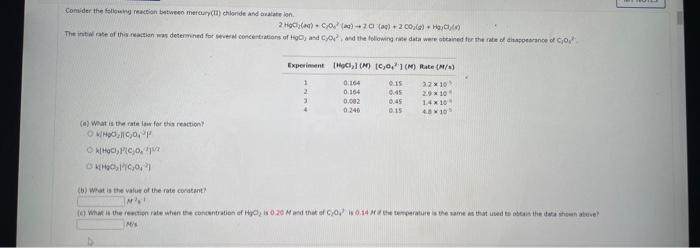
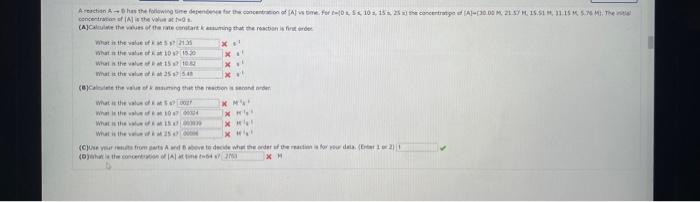
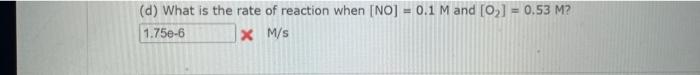
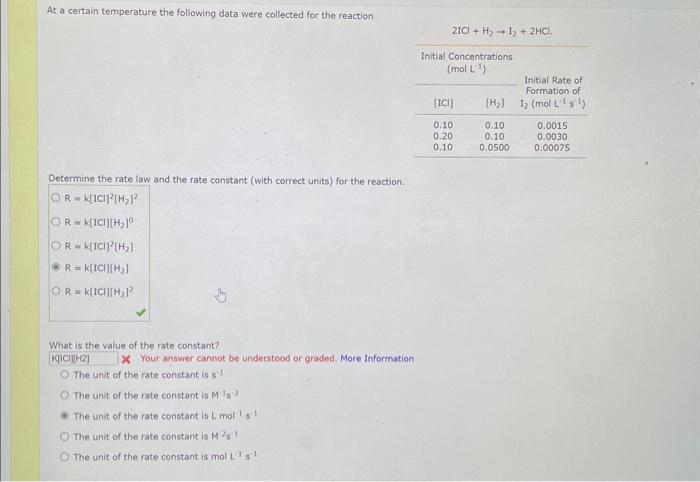
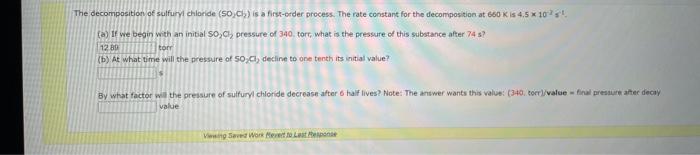
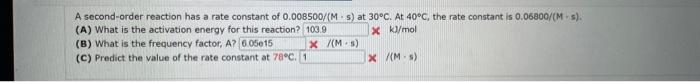
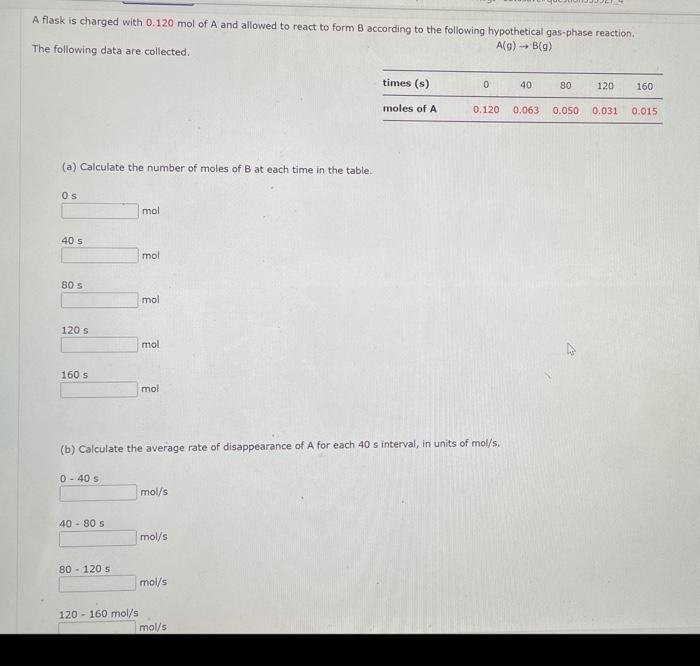
Comider the folisuing reakeion botweeo mereanc(ri) chibride and analate ion. 2HgCliad+C08(aq)+2Cl(aq)+2c02()+H2jCh(9) (e) What is ther rate itut for this reationl WulHoO HHHO2ThCsO4 ? (b). What is the value of the rate conatent? N2II Mis concertration of A is the velin at fied A. (O) 14 (d) What is the rate of reaction when [NO]=0.1M and [O2]=0.53M ? M/s At a certain temperature the following data were collected for the reaction 2ICl+H2I2+2HCl Determine the rate law and the rate constant (with correct units) for the reaction. R=k[ICl]2[H2]2R=k[ICl][H2]OR=k[ICl]2[H2]R=k[ICl][H2]R=k[ICl][H2]2. What is the value of the rate constant? X Your answer cannot be understood or graded. More Information The unit of the rate constant is s1 The unit of the rate constant is M1s? ? The unit of the rate constant is Lmol1s1 The unit of the rate constant is MNVsI. The unit of the rate constant is mol L151 Cona ier the following reaction becween merespriIf chlorige ard twa ince ian: La) What is the rate law fer this reaction? bliggejici P42r2 HNigClJlC D22j2a Cbs what is the value of the ratelonitant? arisi Mis The decomposition of sulfuryl chloride (50,Cl2) is a firs-order process. The rate constant for the decomposition at 660K is 4,5102s1. (a) If ye begin with an inital SO2Cl2 pressure of 340 , torr, what is the pressure of this substance after 74 s? torr (b) At what time will the pressure of SO2Cl2 decline to one tenth its intial value? Bv what factor will the pressure of sulfuryl chloride decrease after 6 half lives? Note: The answer wants this value: (3+0, corri)value = final presaure anter decay value A second-order reaction has a rate constant of 0.008500/(M5) at 30C. At 40C, the rate constant is 0.06800/(M - s). (A) What is the activation energy for this reaction? de kJ/mol (B) What is the frequency factor, A? X /(Ms) (c) Predict the value of the rate constant at 78C. x/(Ms) A flask is charged with 0.120mol of A and allowed to react to form B according to the following hypothetical gas-phase reaction. The following data are collected. A(g)B(g) (a) Calculate the number of moles of B at each time in the table. 0. mol 40s mol 805 mol 120s mol 160.5 mol (b) Calculate the average rate of disappearance of A for each 40s interval, in units of mol/s