Question
Compile C to RISC-V assembly code. Instructions that you might use include: add rd, rs1, rs2 # rd = rs1 + rs2 addi rd, rs1,
- Compile C to RISC-V assembly code.
Instructions that you might use include:
add rd, rs1, rs2 # rd = rs1 + rs2
addi rd, rs1, #immediate # rd = rs1 + #immediate
sub rd, rs1, rs2 # rd = rs1 rs2
slli rd, rs1, #immediate # shift left logic rs1 by #immediate number
# of bits and store results in rd
lw rd, #offset(rs1) # load a word from memory at address rs1+#offset to rd
sw rs2, #offset(rs1) # store a word from rs2 to memory at address rs1 + #offset
beq rs1, rs2, #label # if rs1 == rs2, branch to the instruction labeled as #label
bne rs1, rs2, #label # if rs1 != rs2, branch to the instruction labeled as #label
bge rs1, rs2, #label # if rs1 >= rs2, branch to the instruction labeled as #label.
- Using ONLY the add, sub and slli instruction to convert the following C statement to the corresponding RISC-V assembly. Assume that the variables f, g, and j are integers assigned to registers t0, t1, and t2 respectively. You can use other temporary registers such as t3, t4, t5, t6, etc.
f = g * 3 j * 16;
- Convert the following C statement to its corresponding RISC-V assembly code using arithmetic/logic and load/store instructions. Assume that the base address of array A is in register s0 and each element is a 4-byte word. i is in register t0 and f is in register t1. You can use temp registers t2, t3, t4
A[i] += A[i-1] + f;
- The following C code check whether two arrays (int A[N] and int B[N]) are the same or not. Convert the C code to its corresponding RISC-V assembly code using arithmetic/logic, load and branch instructions. Assume that the base address of array A and B is in register s0 and s1 respectively. i is in register t0 and Ns value is already in register t1. You can use temp registers t2, t3, etc. Register x0 always contains 0. The break statement terminates the loop.
i = 0;
while (A[i] == B[i]) {
i++;
if (i == N) break;
}
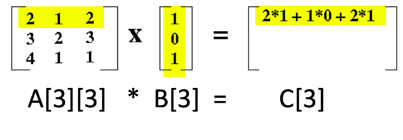
2*1 + 1*0+ 2*1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 1 1 X = 0 1 A[3][3] * B[3] C[3] 2*1 + 1*0+ 2*1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 1 1 X = 0 1 A[3][3] * B[3] C[3]Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


