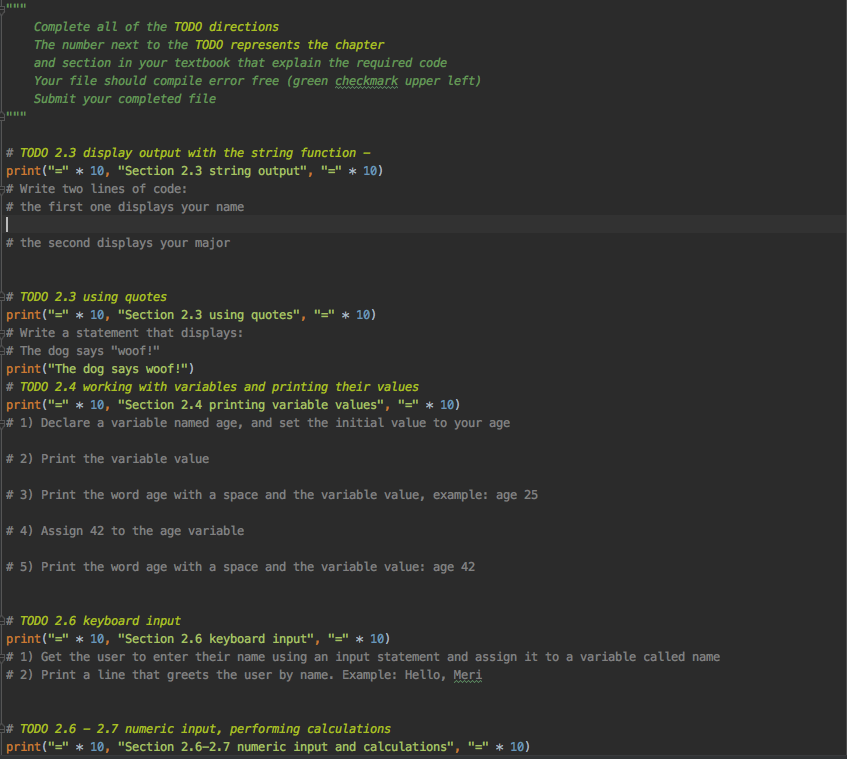
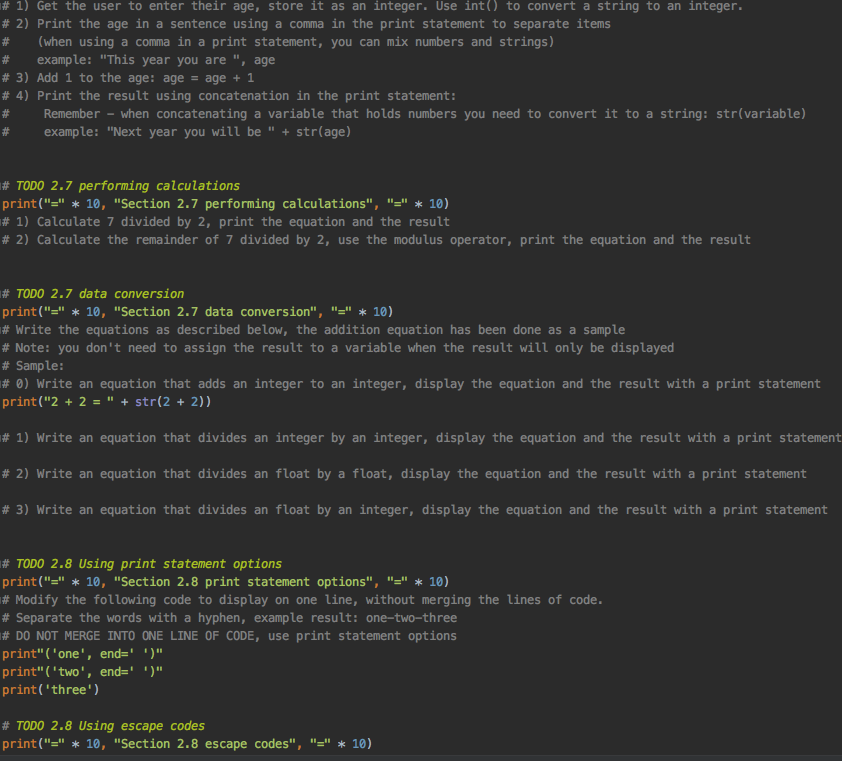
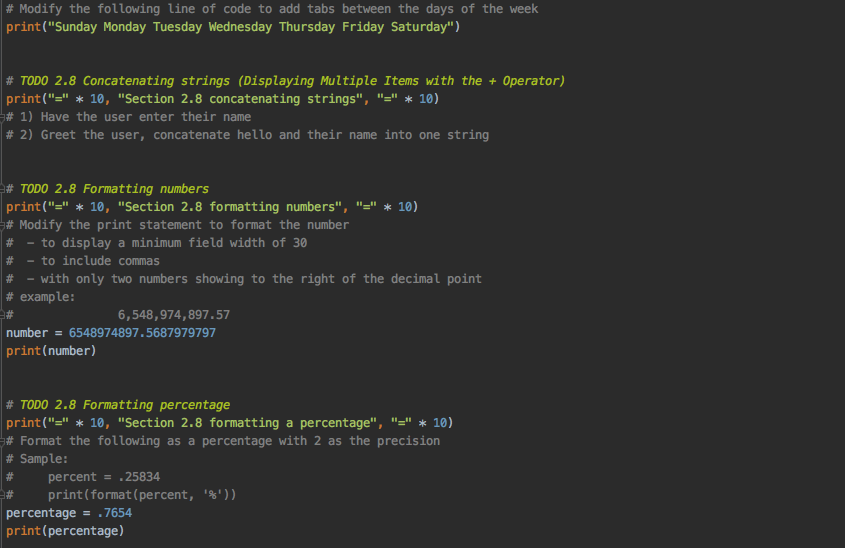
Complete all of the TODO directions The number next to the TODO represents the chapter and section in your textbook that explain the required code Your file should compile error free (green checkmark upper left) Submit your completed file # TODO 2.3 display output with the string function - print("=" * 10, "Section 2.3 string output", "-" * 10), # Write two lines of code: # the first one displays your name # the second displays your major # TODO 2.3 using quotes print("=" * 10, "Section 2.3 using quotes", "-" * 10), # Write a statement that displays: # The dog says "woof!" print("The dog says woof!") # TODO 2.4 working with variables and printing their values print("=" * 10, "Section 2.4 printing variable values", "-" * 10), # 1) Declare a variable named age, and set the initial value to your age # 2) Print the variable value # 3) Print the word age with a space and the variable value, example: age 25 # 4) Assign 42 to the age variable # 5) Print the word age with a space and the variable value: age 42 # TODO 2.6 keyboard input print("=" * 10, "Section 2.6 keyboard input", "-" * 10), # 1) Get the user to enter their name using an input statement and assign it to a variable called name # 2) Print a line that greets the user by name. Example: Hello, Meri # TODO 2.6 - 2.7 numeric input, performing calculations print("=" * 10, "Section 2.6-2.7 numeric input and calculations", "-" * 10), # 1) Get the user to enter their age, store it as an integer. Use int() to convert a string to an integer. # 2) Print the age in a sentence using a comma in the print statement to separate items # (when using a comma in a print statement, you can mix numbers and strings) # example: "This year you are ", age # 3) Add 1 to the age: age = age + 1 # 4) Print the result using concatenation in the print statement: # Remember - when concatenating a variable that holds numbers you need to convert it to a string: str(variable) # example: "Next year you will be " + str(age) # TODO 2.7 performing calculations print("=" * 10, "Section 2.7 performing calculations", "-" * 10) # 1) Calculate 7 divided by 2, print the equation and the result # 2) Calculate the remainder of 7 divided by 2, use the modulus operator, print the equation and the result # TODO 2.7 data conversion print("=" * 10, "Section 2.7 data conversion", "-" * 10) # Write the equations as described below, the addition equation has been done as a sample # Note: you don't need to assign the result to a variable when the result will only be displayed # Sample: # 0) Write an equation that adds an integer to an integer, display the equation and the result with a print statement print("2 + 2 = " + str(2 + 2)) # 1) Write an equation that divides an integer by an integer, display the equation and the result with a print statement # 2) Write an equation that divides an float by a float, display the equation and the result with a print statement # 3) Write an equation that divides an float by an integer, display the equation and the result with a print statement # TODO 2.8 Using print statement options print("=" * 10, "Section 2.8 print statement options", "=" * 10) # Modify the following code to display on one line, without merging the lines of code. # Separate the words with a hyphen, example result: one-two-three # DO NOT MERGE INTO ONE LINE OF CODE, use print statement options print" ('one', end=' ')" print"('two', end=' ')" print('three') # TODO 2.8 Using escape codes print("=" * 10, "Section 2.8 escape codes", "-" * 10), # Modify the following line of code to add tabs between the days of the week print("Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturday"), # TODO 2.8 Concatenating strings (Displaying Multiple Items with the + Operator), print("=" * 10, "Section 2.8 concatenating strings", "-" * 10), # 1) Have the user enter their name # 2) Greet the user, concatenate hello and their name into one string # TODO 2.8 Formatting numbers print("=" * 10, "Section 2.8 formatting numbers", "-" * 10), # Modify the print statement to format the number # - to display a minimum field width of 30 # - to include commas # - with only two numbers showing to the right of the decimal point # example: 6,548,974,897.57 number = 6548974897.5687979797 print(number) # TODO 2.8 Formatting percentage print("=" * 10, "Section 2.8 formatting a percentage", "=" * 10), # Format the following as a percentage with 2 as the precision # Sample: # percent = .25834 # print (format(percent, '8')) percentage = .7654 print(percentage)









