Question
Complete this assignment and submit it as a file attachment to the Assignment 12 Submission link. You are to build an abstract data type (ADT)
Complete this assignment and submit it as a file attachment to the Assignment 12 Submission link.
You are to build an abstract data type (ADT) for the set of letters using a bit string. The bit string representation for the set of letters can use a 32-bit word with the least-significant bit associated with the letter 'A', etc.
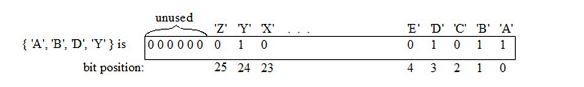
The set of letters ADT should have the following operations (subprograms):
| Subprogram Name | Parameters | Description |
| bitString |
| Returns a bit string corresponding to the set of letters in the .ASCIIZ string. Non-letter characters are ignored, and both upper and lower-case letters should be represented as the upper-case letter. |
| union |
| The resulting set should contain the elements that are in one or both of the input sets. |
| intersection |
| The resulting set should contain the elements that are in both of the input sets. |
| difference |
| The resulting set should contain the elements that are in the first set, but not also in the second set. |
| contains |
| Returns 1 (true) if the .ASCII character is in the bitString set; otherwise return 0 (false). |
| |
| Prints the bitString to the console using the print_string system call. The set should be printed in the conventional format, i.e., "{ E, G, T, Y }" |
Additionally, you should have a main program that
1) allows a user to interactively enter two strings (use the PCSpim I/O),
2) constructs two bitString sets from these strings,
3) prints the set of letters contained in each string,
4) determines and prints the union, intersection, and difference of two bitString sets,
5) checks to see if the first bitString set contains the letters: 'A', 'Q', 'Y', and 'Z'. The results of each of these checks should be printed to the console.
Turn in the following:
1) The MIPS assembly language program. Use the MIPS register conventions correctly and include comments describing which registers are being used for parameters and local variables.
starter code:
# Partial code to implement a bit-string of letters
.data
set1: .word 0
set2: .word 0
unionSet: .word 0
str1: .asciiz "Cape3?!AE"
str2: .asciiz "A d y B**#&."
.text
.globl main
main:
la $a0, str1
jal bitString
sw $v0, set1
la $a0, str2
jal bitString
sw $v0, set2
# pass sets in $a0 and $a1; returns union in $v0
lw $a0, set1
lw $a1, set2
jal union
sw $v0, unionSet
li $v0, 10
syscall
union: # pass in bitString sets in $a0 and $a1; returns union bitString in $v0
or $v0, $a0, $a1
jr $ra
bitString:
# bitString Algorithm:
# resultSet = {}
# index = 0
# while True:
# nextChar = str[index]
# if nextChar == 0 then // the NULL character
# break
# end if
# if nextChar >= ascii of 'a' and nextChar
# convert it upper-case letter by subtracting 32
# end if
# if nextChar >= ascii of 'A' and nextChar
# resultSet = resultSet U {nextChar}
# end if (no else because we are ignoring non-letters)
# index = index + 1
# end while
# return resultSet
# Register Usage - NOTE: doesn't call anything so by using only $a and $t registers, doesn't need to save on stack
# $a0 parameter contains address of .asciiz string, but will be walked down the string
# $v0 used for the resultSet
# $t0 used to hold nextChar ASCII value
# $t3 used to hold the mask for the str[index] character
li $v0, 0 # resultSet = {}
while: lb $t0, 0($a0)
beq $t0, 0, end_while # NULL character (0) detected at end of .asciiz
if_1: blt $t0, 97, end_if_1 # ASCII for 'a' is 97
bgt $t0, 122, end_if_1 # ASCII for 'z' is 122
addi $t0, $t0, -32 # convert to upper-case letter
end_if_1:
if_2: blt $t0, 65, end_if_2 # ASCII for 'A' is 65
bgt $t0, 90, end_if_2 # ASCII for 'Z' is 90
addi $t8, $t0, -65 # determine bit position of letter in bit-string
li $t3, 1 # Build mask: start with 1 at right-most position
sllv $t3, $t3, $t8 # Build mask: move 1 to correct position to finish building mask
or $v0, $v0, $t3 # update resultSet in $v0 = $v0 bit-wise-OR with mask
end_if_2:
addi $a0, $a0, 1 # walk-pointer to str[index] to next character
j while
end_while:
jr $ra
unused 'Z' "Y" X { 'A', 'B', D', 'Y') is 0000000 1 0 bit position: 25 24 23 E' D' C 'B' 'A' 0 1 0 1 1 4 3 2 1 0 unused 'Z' "Y" X { 'A', 'B', D', 'Y') is 0000000 1 0 bit position: 25 24 23 E' D' C 'B' 'A' 0 1 0 1 1 4 3 2 1 0
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


