Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Compound Interest: [ begin{array}{l} F V=P V(1+i)^{n} P V=F V(1+i)^{-n} i=frac{j}{m} n=m cdot t C D text { or } C

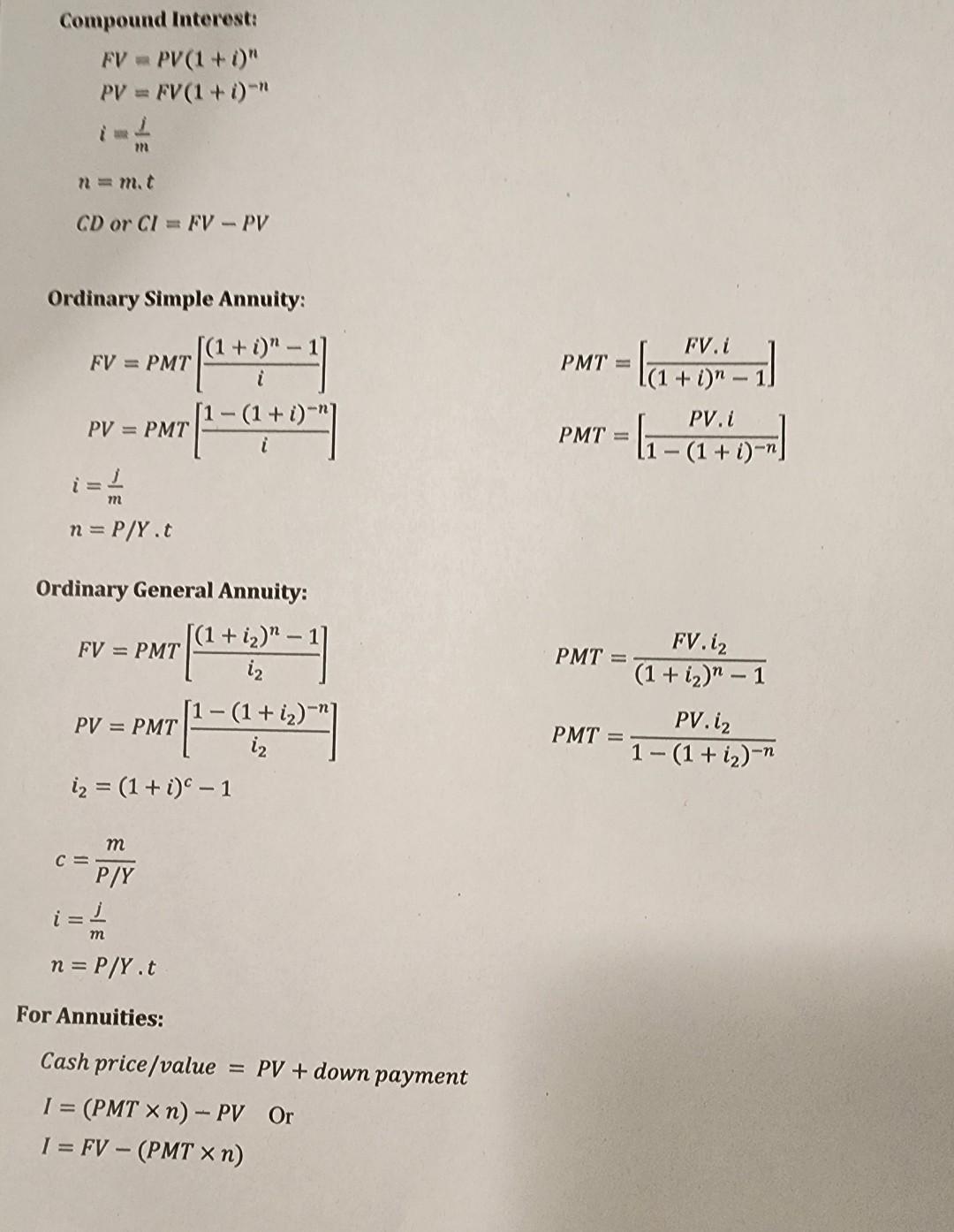
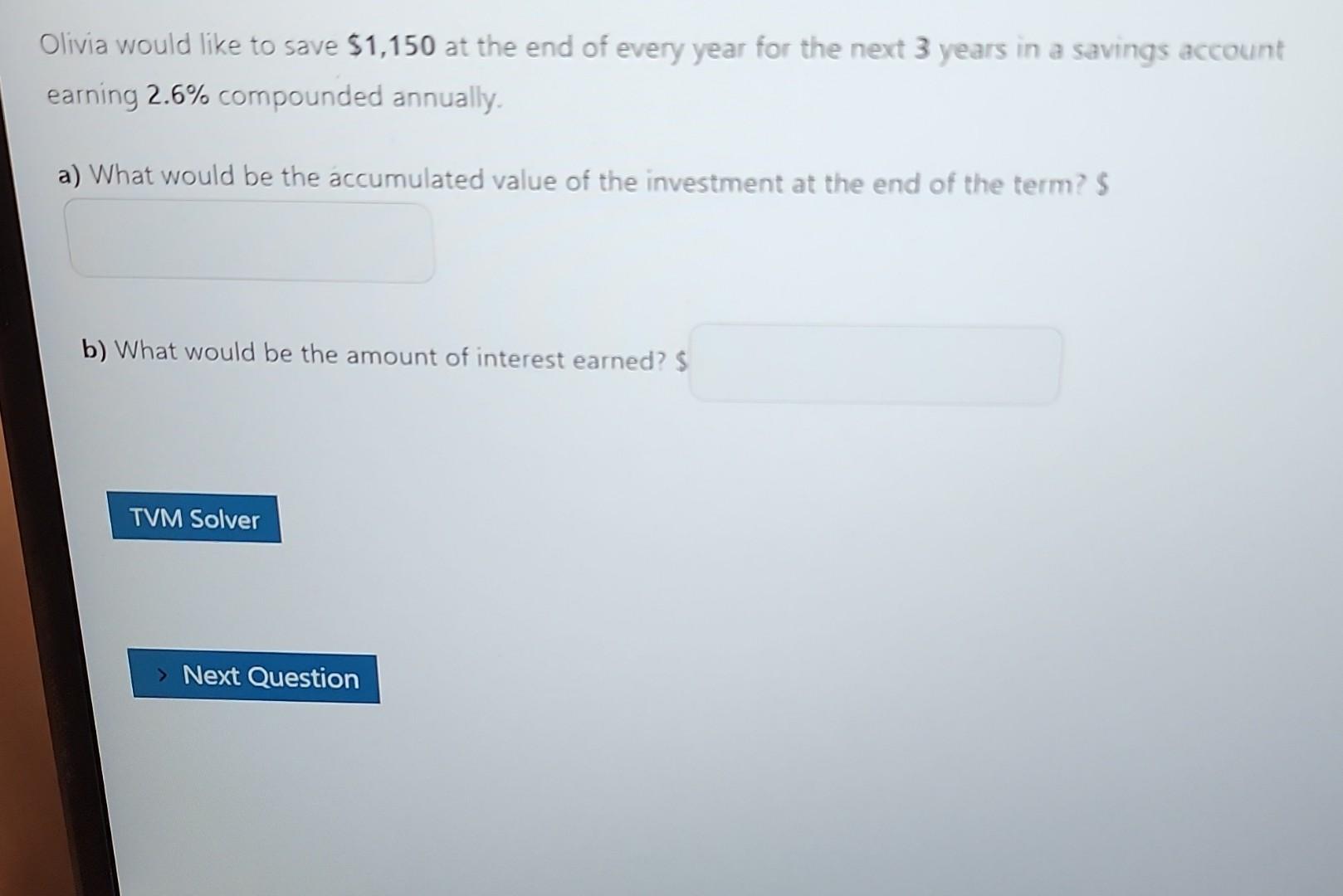
Compound Interest: \\[ \\begin{array}{l} F V=P V(1+i)^{n} \\\\ P V=F V(1+i)^{-n} \\\\ i=\\frac{j}{m} \\\\ n=m \\cdot t \\\\ C D \\text { or } C I=F V-P V \\end{array} \\] Ordinary Simple Annuity: \\[ \\begin{array}{l} F V=P M T\\left[\\frac{(1+i)^{n}-1}{i}\ ight] \\\\ P V=P M T\\left[\\frac{1-(1+i)^{-n}}{i}\ ight] \\\\ i=\\frac{j}{m} \\\\ n=P / Y . t \\end{array} \\] \\[ \\begin{array}{l} P M T=\\left[\\frac{F V \\cdot i}{(1+i)^{n}-1}\ ight] \\\\ P M T=\\left[\\frac{P V \\cdot i}{1-(1+i)^{-n}}\ ight] \\end{array} \\] Ordinary General Annuity: \\[ \\begin{array}{l} F V=P M T\\left[\\frac{\\left(1+i_{2}\ ight)^{n}-1}{i_{2}}\ ight] \\\\ P V=P M T\\left[\\frac{1-\\left(1+i_{2}\ ight)^{-n}}{i_{2}}\ ight] \\\\ i_{2}=(1+i)^{c}-1 \\\\ c=\\frac{m}{P / Y} \\\\ i=\\frac{j}{m} \\\\ n=P / Y . t \\end{array} \\] \\[ \\begin{aligned} P M T & =\\frac{F V \\cdot i_{2}}{\\left(1+i_{2}\ ight)^{n}-1} \\\\ P M T & =\\frac{P V \\cdot i_{2}}{1-\\left(1+i_{2}\ ight)^{-n}} \\end{aligned} \\] For Annuities: Cash price \\( / \\) value \\( =P V+ \\) down payment \\[ \\begin{array}{l} I=(P M T \\times n)-P V \\quad \\text { Or } \\\\ I=F V-(P M T \\times n) \\end{array} \\] Olivia would like to save \\( \\$ 1,150 \\) at the end of every year for the next 3 years in a savings account earning \2.6 compounded annually. a) What would be the accumulated value of the investment at the end of the term? \\( S \\) b) What would be the amount of interest earned? \\( \\$ \\) - \\( F V g= \\) the future value (or accumulated value) of an ordinary general annuity - \\( P M T= \\) the size of the periodic payment - J=nominal interest rate - \\( n= \\) the number of periodic payments \\( n=p / y^{*} t \\) - \\( c= \\) the number of interest conversion periods per payment interval \\( =\\frac{m}{p / y} \\) - \\( \\quad i= \\) the interest rate per interest conversion period \\( =\\frac{j}{m} \\) - \\( p= \\) the equivalent rate of interest per payment period \\[ \\begin{array}{l} F V_{n}=P M T\\left[\\frac{(1+i)^{n}-1}{i}\ ight] \\\\ P V_{n}=P M T\\left[\\frac{1-(1+i)^{-n}}{i}\ ight] \\\\ P M T=\\left[\\frac{F V_{n} i}{(1+i)^{n}-1}\ ight] \\\\ P M T=\\left[\\frac{P V_{n} i}{1-(1+i)^{-n}}\ ight] \\\\ c=\\frac{\\text { THE NUMBER OF INTEREST CONVERSION PERIODS PER YEAR }}{\\text { THE NUMBER OF PAYMENTS PER YEAR }}=\\frac{m}{p / y} \\\\ p=(1+i)^{c}-1 \\\\ F V_{g}=P M T\\left[\\frac{(1+p)^{n}-1}{p}\ ight] \\\\ P V_{g}=P M T\\left[\\frac{1-(1+p)^{-n}}{p}\ ight] \\\\ P M T=\\frac{F V_{g} p}{(1+p)^{n}-1} \\\\ P M T=\\frac{P V_{g} p}{1-(1+p)^{-n}} \\\\ \\end{array} \\] Compound interest \\[ \\begin{array}{l} F V=P V(1+i)^{n} \\\\ P V=\\frac{F V}{(1+i)^{n}} \\text { or. } P V=F V(1+i)^{-n} \\end{array} \\]
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


