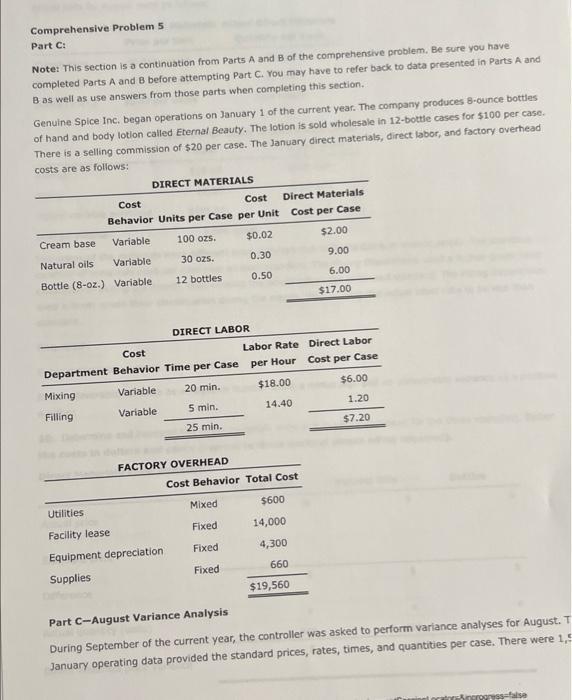
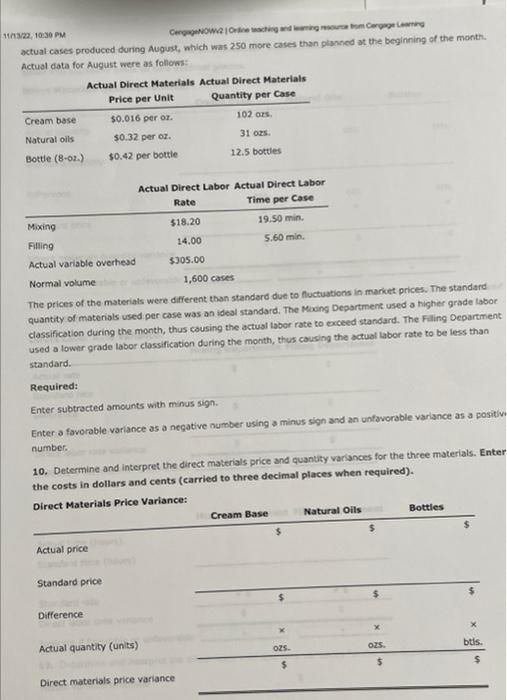
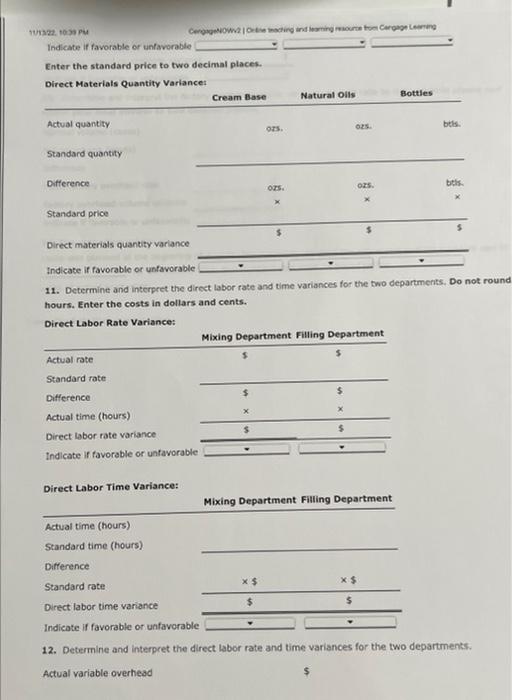
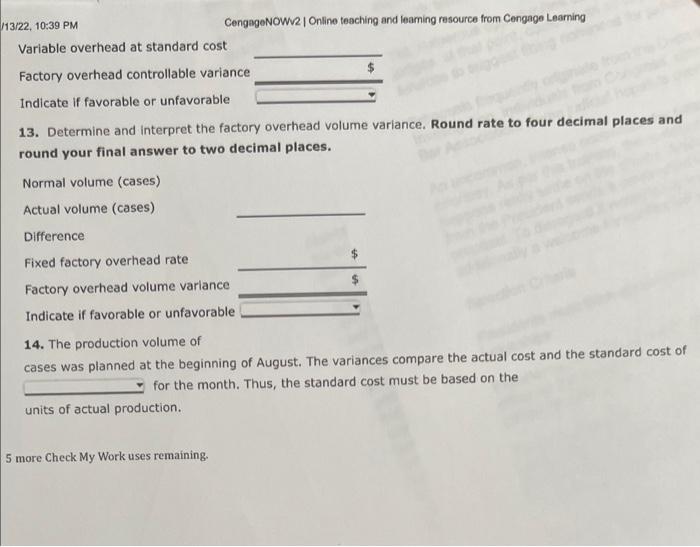
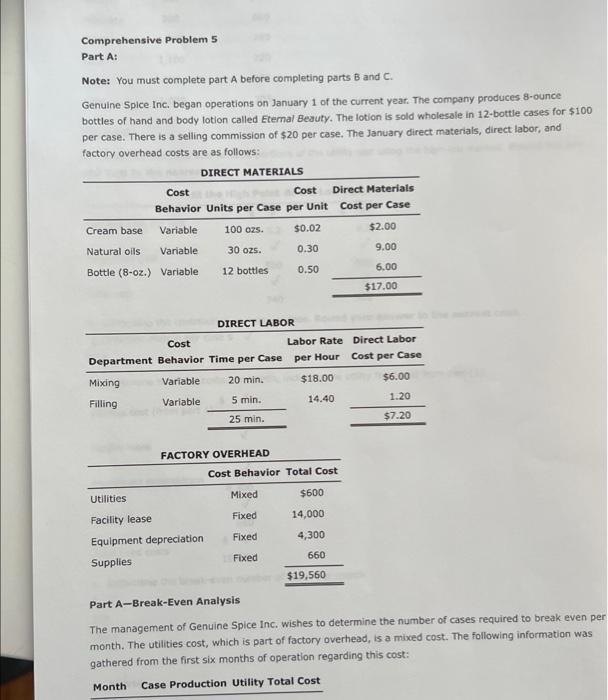
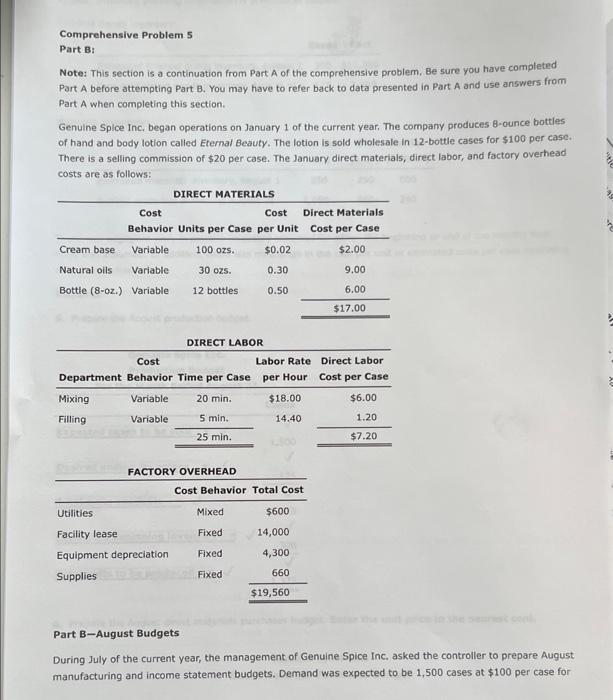
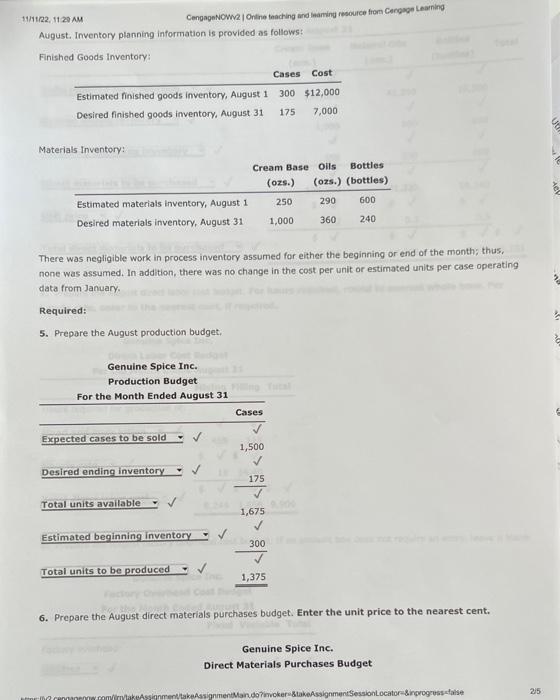
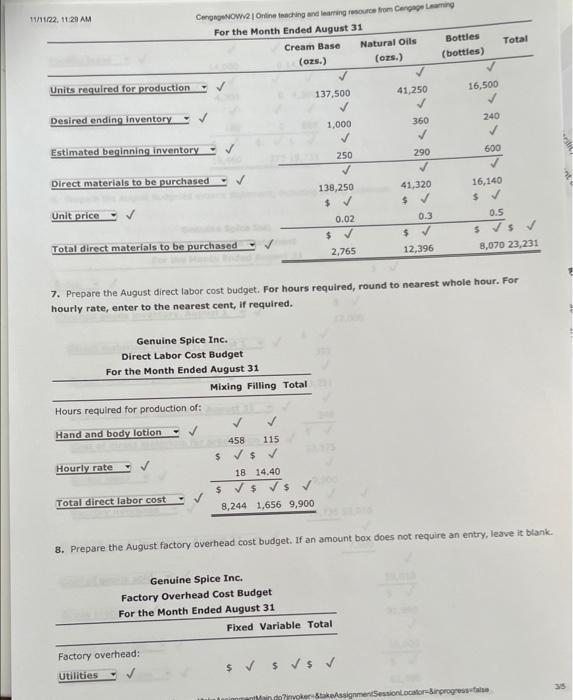
Comprehensive Problem 5 Part C: Notet This section is a continuation from Parts A and B of the comprehensive problem, Be sure you have completed Parts A and B before attempting Part C. You may have to refer back to data presented in Parts A and B as well as use answers from those parts when completing this section. Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces 8-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Eternal Beauty. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12b0t-be cases for $100 per casc. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The January direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead rnets are as follows: Part C-August Variance Analysis During September of the current year, the controller was asked to perform variance analyses for August. January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1 . 1.32, 1030 PM actuat cases produced during Augus, which was 250 more cases than planned at the beginning of the month. Actual cata for August were as follows: The prices of the materials were different than standard due to nuctuacons in mariket prices. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an idesl standard. The Maing Department used a higher grade labor classification during the month, thus cousing the actusl tabor rate to exceed standard. The Filing Departiment used a lower grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual laber rate to be less than standard. Required: Enter subtracted amounts with minus sigh. Enter a favorable varlance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positivi number. 10. Determine and interpret the direct materials price and quantity variances for the three materials. Enter the costs in dollars and cents (carried to three decimal places when required). 4tha22. +0 7) PM Indicate if favorable or unfavorable Enter the standard price to two decimal places. 11. Determine and interpret the direct labor rate and time variances for the two departmerits, Do not roune hours. Enter the costs in dollars and cents. Direct Labor Rate Variance: 12. Determine and interpret the direct Labor rate and time variances for the two departments. Actual variable overhead 5 3/22,10:39PM CengagoNOWV 1 Online teaching and leaming resource from Congnge Leaming Variable overhead at standard cost Factory overhead controllable variance Indicate if favorable or unfavorable 13. Determine and interpret the factory overhead volume variance. Round rate to four decimal places and round your final answer to two decimal places. 14. The production volume of cases was planned at the beginning of August. The variances compare the actual cost and the standard cost of for the month. Thus, the standard cost must be based on the units of actual production. more Check My Work uses remaining. Comprehensive Problem 5 Part A: Note: You must complete part A before completing parts B and C. Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces 8-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Etemal Beauty. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12 -bottle cases for $100 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The January direct materials, direct laber, and factory overhead costs are as follows: Part A-Break-Even Analysis The management of Genuine Spice Inc, wishes to determine the number of cases required to break even per month. The utilities cost, which is part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. The following information was gathered from the first six months of operation regarding this cost: IOritine teactiog and lesting rescurce tron Cengsge Lesting Required: 1. Determine the fixed and variable portions of the utility cost using the high-low method. Round the per unit cost to the nearest cent. 2. Determine the contribution margin per case, Round your answer to the nearest cent. Contribution margin per case $ 55.6 3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part (1). 4. Determine the break-even number of cases per month. 5 350 cases Chock My Work 1. Divide the difference between the highest and lowest total costs by the difference between the highest and lowest production units, Multiply the variable unit cost by the number of units for a month. Subtract this variable cost from the month's total cost. 2. Sales minus variable costs equals contribution margin. 3. Add all the fixed costs. 4. Divide fixed costs by unit contribution margin. 0 more Check My Work uses remaining Comprehensive Problem. 5 Part B: Note: This section is a continuation from Part A of the comprehensive problem. Be sure you have completed Part A before attempting Part B. You may have to refer back to data presented in Part A and use answers from Part A when completing this section. Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces 8-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Etemal Beauty. The lotion Is sold wholesale in 12-bottle cases for $100 per casc. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The lanuary direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead costs are as follows: Part B-August Budgets During July of the current year, the management of Genuine Spice Inc, asked the controller to prepare August manufacturing and income statement budgets. Demand was expected to be 1,500 cases at $100 per case for 11/1122, 1129AM August, Inventory planning information is provided as follows: Finished Goods Inventory: Materials Inventory: There was negligible work in process inventory assumed for either the beginning or end of the month; thus. none was assumed. In addition, there was no change in the cost per unit or estimated units per case operating data from January. Required: 5. Prepare the August production budget, 6. Prepare the August direct materials purchases budget. Enter the unit price to the nearest cent. 7. Prepare the August direct labor cost budget, For hours required, round to nearest whole hour. For hourly rate, enter to the nearest cent, if required. 8. Prepare the August factory overhead cost budget. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 1171122.11:20AM 9. Prepare the August budgeted income statement, including selling expenses. Check My Work 5. Expected sales plus desired ending inventory minus estimated beginning inventory equals production. 6. Production quantity plus desired ending inventory minus estimated beginning inventory equals quantity to be purchased. Multiply quantity by the unit price. 7. Multiply direct labor hours required by the direct labor rate per hour B. Show all of the variable costs and all of the fixed costs. 9. Start with budgeted sales. Add the cost of direct materials used in production, the direct labor, and the factory overhead to the beginning finished goods inventory. Subtract the ending finished goods inventory. Subtract cost of goods sold from sales. Subtract selling expenses. Comprehensive Problem 5 Part C: Notet This section is a continuation from Parts A and B of the comprehensive problem, Be sure you have completed Parts A and B before attempting Part C. You may have to refer back to data presented in Parts A and B as well as use answers from those parts when completing this section. Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces 8-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Eternal Beauty. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12b0t-be cases for $100 per casc. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The January direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead rnets are as follows: Part C-August Variance Analysis During September of the current year, the controller was asked to perform variance analyses for August. January operating data provided the standard prices, rates, times, and quantities per case. There were 1 . 1.32, 1030 PM actuat cases produced during Augus, which was 250 more cases than planned at the beginning of the month. Actual cata for August were as follows: The prices of the materials were different than standard due to nuctuacons in mariket prices. The standard quantity of materials used per case was an idesl standard. The Maing Department used a higher grade labor classification during the month, thus cousing the actusl tabor rate to exceed standard. The Filing Departiment used a lower grade labor classification during the month, thus causing the actual laber rate to be less than standard. Required: Enter subtracted amounts with minus sigh. Enter a favorable varlance as a negative number using a minus sign and an unfavorable variance as a positivi number. 10. Determine and interpret the direct materials price and quantity variances for the three materials. Enter the costs in dollars and cents (carried to three decimal places when required). 4tha22. +0 7) PM Indicate if favorable or unfavorable Enter the standard price to two decimal places. 11. Determine and interpret the direct labor rate and time variances for the two departmerits, Do not roune hours. Enter the costs in dollars and cents. Direct Labor Rate Variance: 12. Determine and interpret the direct Labor rate and time variances for the two departments. Actual variable overhead 5 3/22,10:39PM CengagoNOWV 1 Online teaching and leaming resource from Congnge Leaming Variable overhead at standard cost Factory overhead controllable variance Indicate if favorable or unfavorable 13. Determine and interpret the factory overhead volume variance. Round rate to four decimal places and round your final answer to two decimal places. 14. The production volume of cases was planned at the beginning of August. The variances compare the actual cost and the standard cost of for the month. Thus, the standard cost must be based on the units of actual production. more Check My Work uses remaining. Comprehensive Problem 5 Part A: Note: You must complete part A before completing parts B and C. Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces 8-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Etemal Beauty. The lotion is sold wholesale in 12 -bottle cases for $100 per case. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The January direct materials, direct laber, and factory overhead costs are as follows: Part A-Break-Even Analysis The management of Genuine Spice Inc, wishes to determine the number of cases required to break even per month. The utilities cost, which is part of factory overhead, is a mixed cost. The following information was gathered from the first six months of operation regarding this cost: IOritine teactiog and lesting rescurce tron Cengsge Lesting Required: 1. Determine the fixed and variable portions of the utility cost using the high-low method. Round the per unit cost to the nearest cent. 2. Determine the contribution margin per case, Round your answer to the nearest cent. Contribution margin per case $ 55.6 3. Determine the fixed costs per month, including the utility fixed cost from part (1). 4. Determine the break-even number of cases per month. 5 350 cases Chock My Work 1. Divide the difference between the highest and lowest total costs by the difference between the highest and lowest production units, Multiply the variable unit cost by the number of units for a month. Subtract this variable cost from the month's total cost. 2. Sales minus variable costs equals contribution margin. 3. Add all the fixed costs. 4. Divide fixed costs by unit contribution margin. 0 more Check My Work uses remaining Comprehensive Problem. 5 Part B: Note: This section is a continuation from Part A of the comprehensive problem. Be sure you have completed Part A before attempting Part B. You may have to refer back to data presented in Part A and use answers from Part A when completing this section. Genuine Spice Inc. began operations on January 1 of the current year. The company produces 8-ounce bottles of hand and body lotion called Etemal Beauty. The lotion Is sold wholesale in 12-bottle cases for $100 per casc. There is a selling commission of $20 per case. The lanuary direct materials, direct labor, and factory overhead costs are as follows: Part B-August Budgets During July of the current year, the management of Genuine Spice Inc, asked the controller to prepare August manufacturing and income statement budgets. Demand was expected to be 1,500 cases at $100 per case for 11/1122, 1129AM August, Inventory planning information is provided as follows: Finished Goods Inventory: Materials Inventory: There was negligible work in process inventory assumed for either the beginning or end of the month; thus. none was assumed. In addition, there was no change in the cost per unit or estimated units per case operating data from January. Required: 5. Prepare the August production budget, 6. Prepare the August direct materials purchases budget. Enter the unit price to the nearest cent. 7. Prepare the August direct labor cost budget, For hours required, round to nearest whole hour. For hourly rate, enter to the nearest cent, if required. 8. Prepare the August factory overhead cost budget. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank. 1171122.11:20AM 9. Prepare the August budgeted income statement, including selling expenses. Check My Work 5. Expected sales plus desired ending inventory minus estimated beginning inventory equals production. 6. Production quantity plus desired ending inventory minus estimated beginning inventory equals quantity to be purchased. Multiply quantity by the unit price. 7. Multiply direct labor hours required by the direct labor rate per hour B. Show all of the variable costs and all of the fixed costs. 9. Start with budgeted sales. Add the cost of direct materials used in production, the direct labor, and the factory overhead to the beginning finished goods inventory. Subtract the ending finished goods inventory. Subtract cost of goods sold from sales. Subtract selling expenses