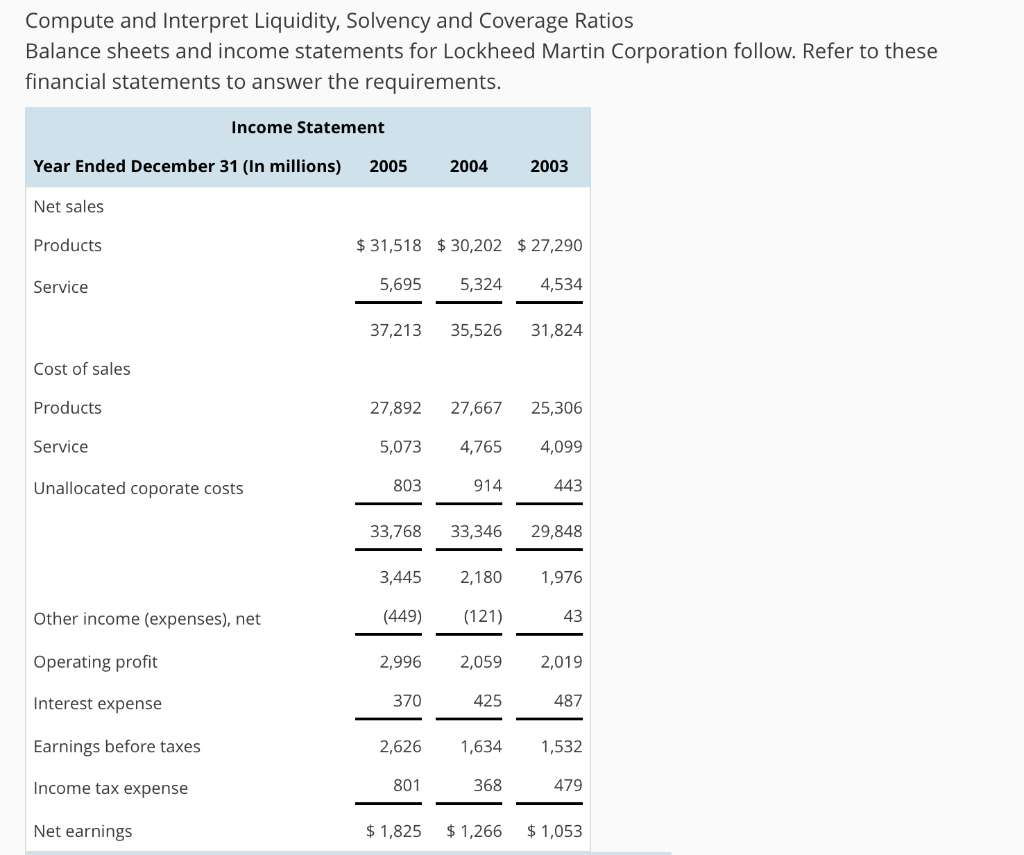
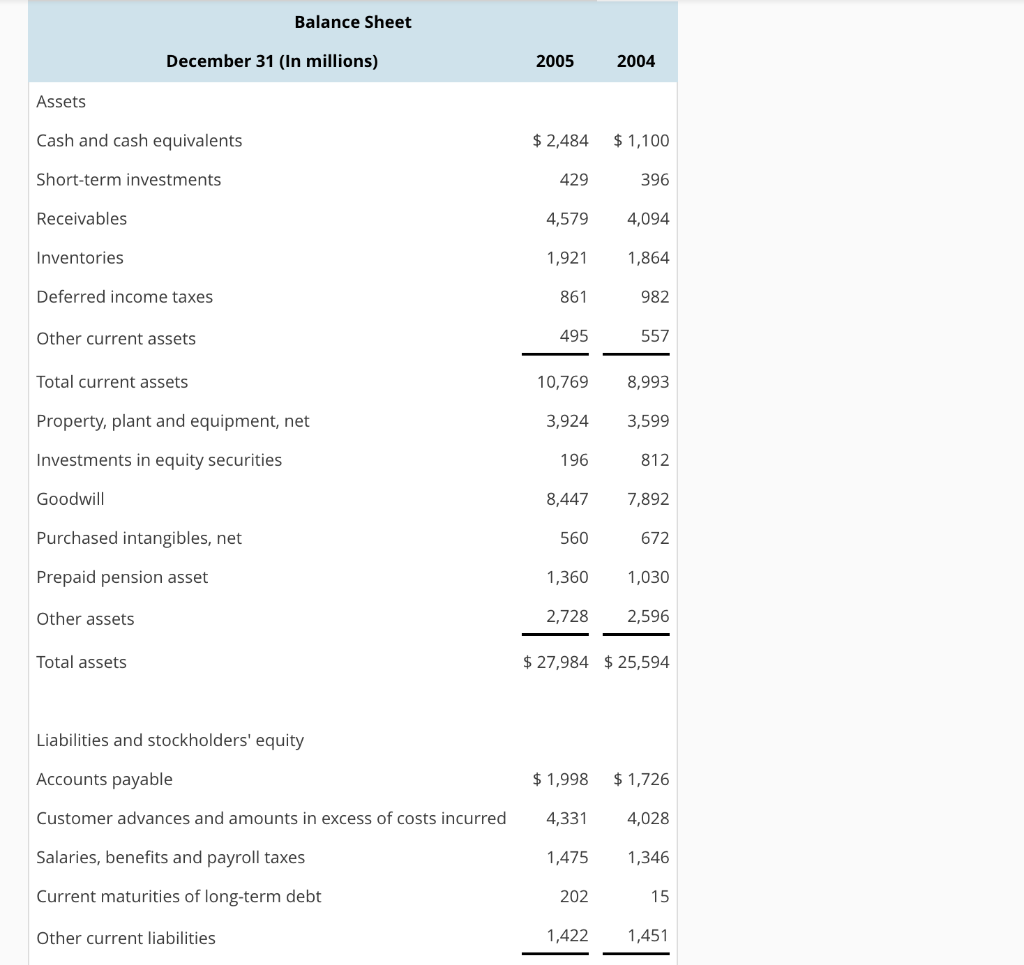
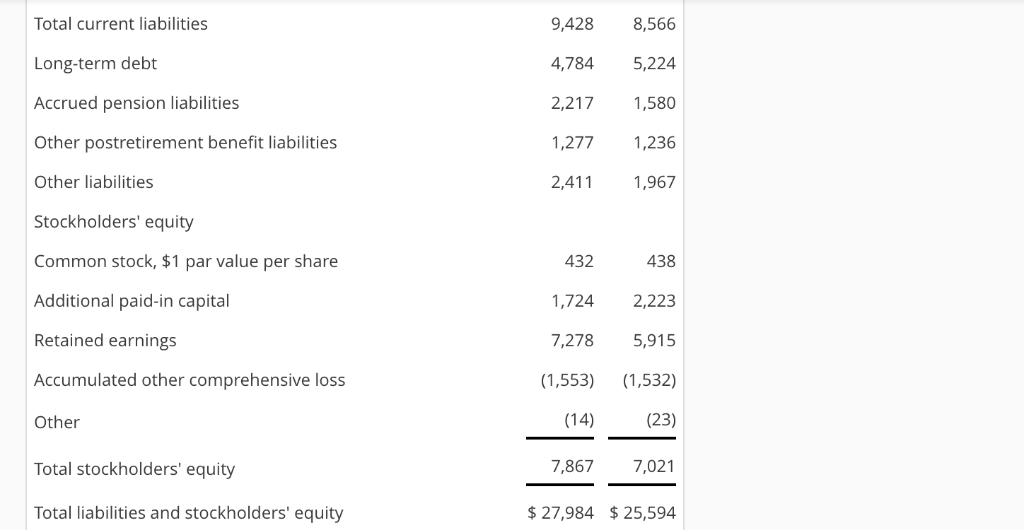
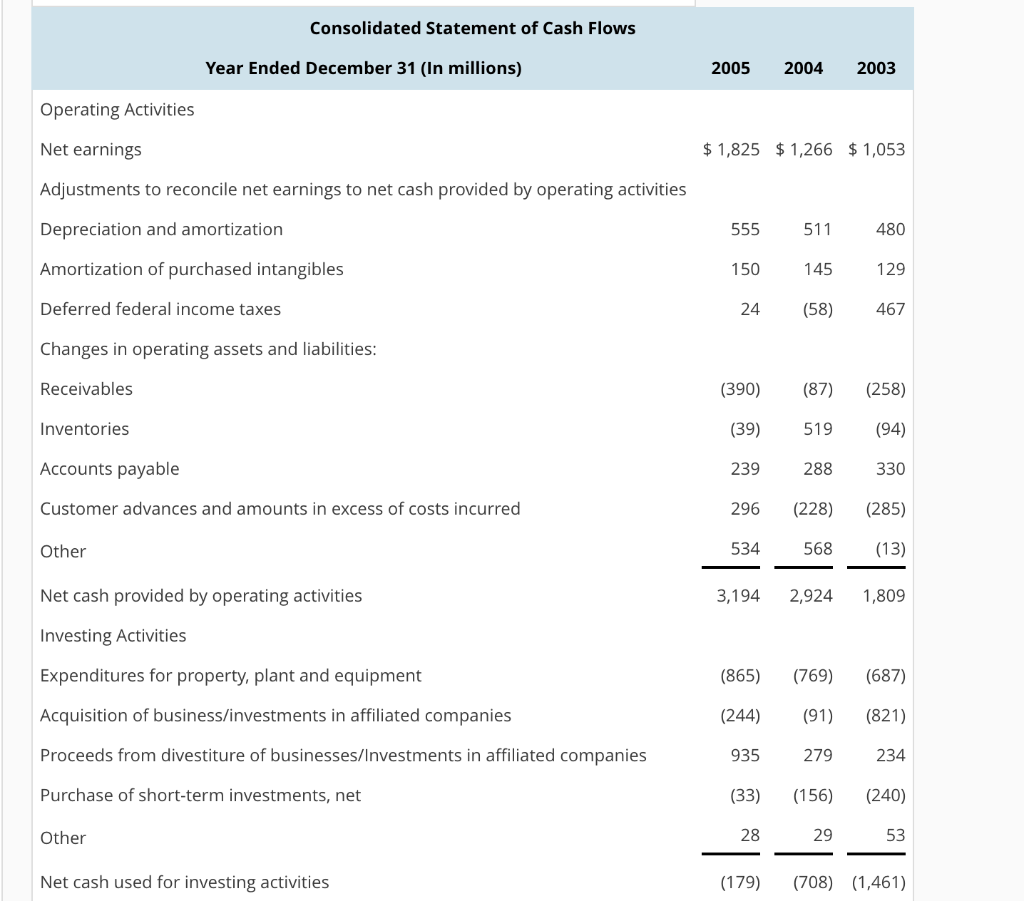
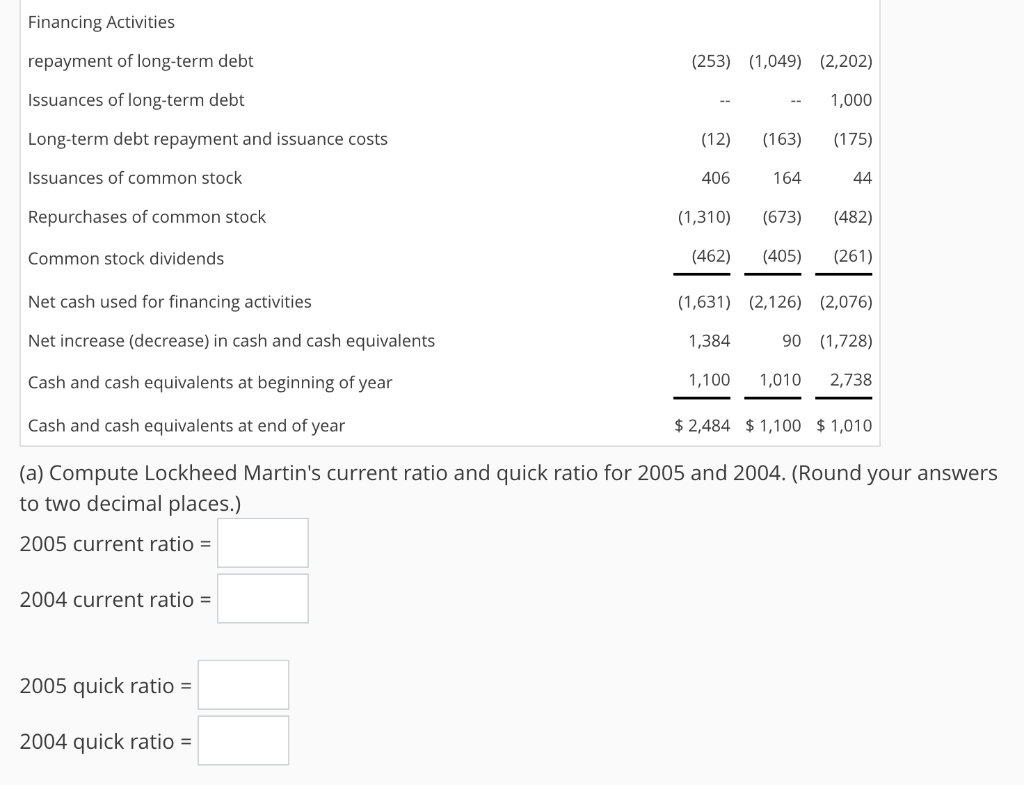


Compute and Interpret Liquidity, Solvency and Coverage Ratios Balance sheets and income statements for Lockheed Martin Corporation follow. Refer to these financial statements to answer the requirements. Income Statement Year Ended December 31 (In millions) Net sales Products Service 20052004 2003 $31,518 $30,202 $ 27,290 5,695 5,324 4,534 37,213 35,526 31,824 Cost of sales Products Service Unallocated coporate costs 27,892 27,667 25,306 5,073 4,7654,099 443 803 914 33,768 33,346 29,848 3,445 2,180 1,976 43 449) 121) Other income (expenses), net Operating profit Interest expense Earnings before taxes Income tax expense Net earnings 2,996 2,059 2,019 487 1,634 1,532 479 425 370 2,626 801 368 $1,825 1,266 $1,053 Balance Sheet December 31 (In millions) 2005 2004 Assets Cash and cash equivalents Short-term investments Receivables Inventories Deferred income taxes Other current assets Total current assets Property, plant and equipment, net Investments in equity securities Goodwill Purchased intangibles, net Prepaid pension asset Other assets Total assets $2,484 1,100 396 4,5794,094 1,864 982 557 10,769 8,993 3,924 3,599 812 8,4477,892 672 1,360 1,030 2,728 2,596 $27,984 $25,594 429 1,921 861 495 196 560 Liabilities and stockholders' equity Accounts payable Customer advances and amounts in excess of costs incurred Salaries, benefits and payroll taxes Current maturities of long-term debt Other current liabilities $1,998 1,726 4,028 1,475 1,346 4,331 202 1,422 1,451 Total current liabilities Long-term debt Accrued pension liabilities Other postretirement benefit liabilities Other liabilities Stockholders' equity Common stock, $1 par value per share Additional paid-in capital Retained earnings Accumulated other comprehensive loss Other 9,428 8,566 4,7845,224 2,217,580 1,277 1,236 2,411 1,967 438 1,7242,223 7,278 5,915 (1,553) 1,532) (23) 7,8677,021 $27,984 $ 25,594 432 (14) Total stockholders' equity Total liabilities and stockholders' equity Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows Year Ended December 31 (In millions) 2005 2004 2003 Operating Activities Net earnings Adjustments to reconcile net earnings to net cash provided by operating activities Depreciation and amortization Amortization of purchased intangibles Deferred federal income taxes Changes in operating assets and liabilities Receivables Inventories Accounts payable Customer advances and amounts in excess of costs incurred Other Net cash provided by operating activities Investing Activities Expenditures for property, plant and equipment Acquisition of business/investments in affiliated companies Proceeds from divestiture of businesses/Investments in affiliated companies Purchase of short-term investments, net Other Net cash used for investing activities $1,825 $1,266 $ 1,053 480 511 145 24(58) 467 150 129 (390 (87) (258) (39) 519 (94) 330 296 (228) (285) 534 568(13) 3,194 2,9241,809 239 288 (865) (769) (687) (244)(91) (821) 279 234 (33) (156) (240) 53 935 28 29 (179) (708) (1,461) Financing Activities repayment of long-term debt Issuances of long-term debt Long-term debt repayment and issuance costs Issuances of common stock Repurchases of common stock Common stock dividends Net cash used for financing activities Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year Cash and cash equivalents at end of year (a) Compute Lockheed Martin's current ratio and quick ratio for 2005 and 2004. (Round your answers (253) (1,049) (2,202) 1,000 (12) (163) 175) 406 164 (1,310 (673 (482) (462) (405) (261) (1,631) (2,126) (2,076) 90 (1,728) 1,100 1,010 2,738 $2,484 1,100 $1,010 1,384 to two decimal places.) 2005 current ratio 2004 current ratio- 2005 quick ratio - 2004 quick ratio - Which of the following best describes the company's current ratio and quick ratio for 2005 and 2004? Both the current and quick ratios have increased from 2004 to 2005. The company is fairly liquid OThe current ratio has increased while the quick ratio has decreased in the period from 2004 to 2005, which suggests the company has a shortage of liquid assets Both the current and quick ratios have decreased from 2004 to 2005. The company is fairly illiquid OThe current ratio has decreased while the quick ratio has increased in the period from 2004 to 2005, which suggests the company has a shortage of current assets. (b) Compute total liabilities-to-equity ratios and total debt-to-equity ratios for 2005 and 2004. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) 2005 total liabilities-to-stockholders' equity 2004 total liabilities-to-stockholders' equity 2005 total debt-to-equity 2004 total debt-to-equity Which of the following best describes the company's total liabilities-to-equity ratios and total debt-to- equity ratios for 2005 and 2004? OThe total liabilities-to-equity ratio has decreased while the total debt-to-equity ratio has increased in the period from 2004 to 2005, which suggests the company has decreased the use of short-term debt financing Both the total liabilities-to-equity and total debt-to-equity ratios have decreased from 2004 to 2005. The difference between these two measures reveals that any solvency concerns would be for the short run. OThe total liabilities-to-equity ratio has increased while the total debt-to-equity ratio has decreased in the period from 2004 to 2005, which suggests the company has increased the use of short-term debt financing. Both the total liabilities-to-equity and total debt-to-equity ratios have increased from 2004 to 2005. These increases suggest that the company is less solvent. c) Compute times interest earned ratio, cash from operations to total debt ratio, and free operating cash flow to total debt ratios. (Round your answers to two decimal places.) 2005 times interest earned- 2004 times interest earned 2005 cash from operations to total debt 2004 cash from operations to total debt- 2005 free operating cash flow to total debt 2004 free operating cash flow to total debt- Which of the following describes the company's times interest earned, cash from operations to total debt, and free operating cash flow to total debt ratios for 2005 and 2004? (Select all that apply) Lockheed Martin's free operating cash flow to total debt ratio increased slightly over the yes 5 due to increased cash flow from operations and decreased levels of debt. no Lockheed Martin's cash from operations to total debt ratio increased slightly over the year 2005 due to increased cash flow from operations and decreased levels of debt. Lockheed Martin's times interest earned increased significantly during 2005, due to both an increase in profitability and a decrease in interest expense. *Lockheed Martin's times interest earned decreased significantly during 2005, due to both a decrease in profitability and an increase in interest expense. (d) Summarize your findings in a conclusion about the company's credit risk. Do you have any concerns about the company's ability to meet its debt obligations? CLockheed Martin's times interest earned ratio is high, thus lessening any immediate solvency concerns. The company's ability to meet its debt requirements will depend on its continued profitability CLockheed Martin's total debt-to-equity is very low, thus increasing any immediate solvency concerns. The company's ability to meet its debt requirements will depend on increasing short-term debt. CLockheed Martin's quick ratio is very low, thus increasing immediate solvency concerns. The company's ability to meet its debt requirements will depend on liquidating inventories for emergency cash CLockheed Martin's total liabilities-to-equity is high, thus lessening any immediate solvency concerns. The company's ability to meet its debt requirements will depend on its use of equity financing














