Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Conduct a static analysis, so the M matrix is 0 and the equation is to be solved is KU =R The material has a
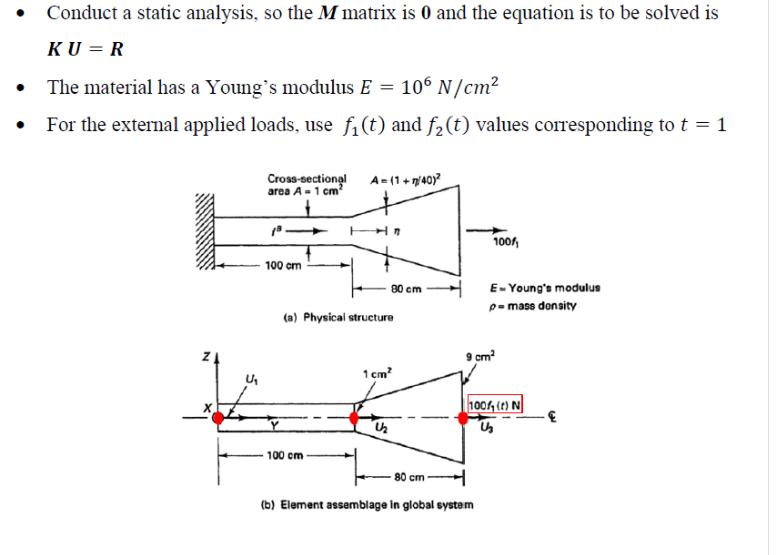
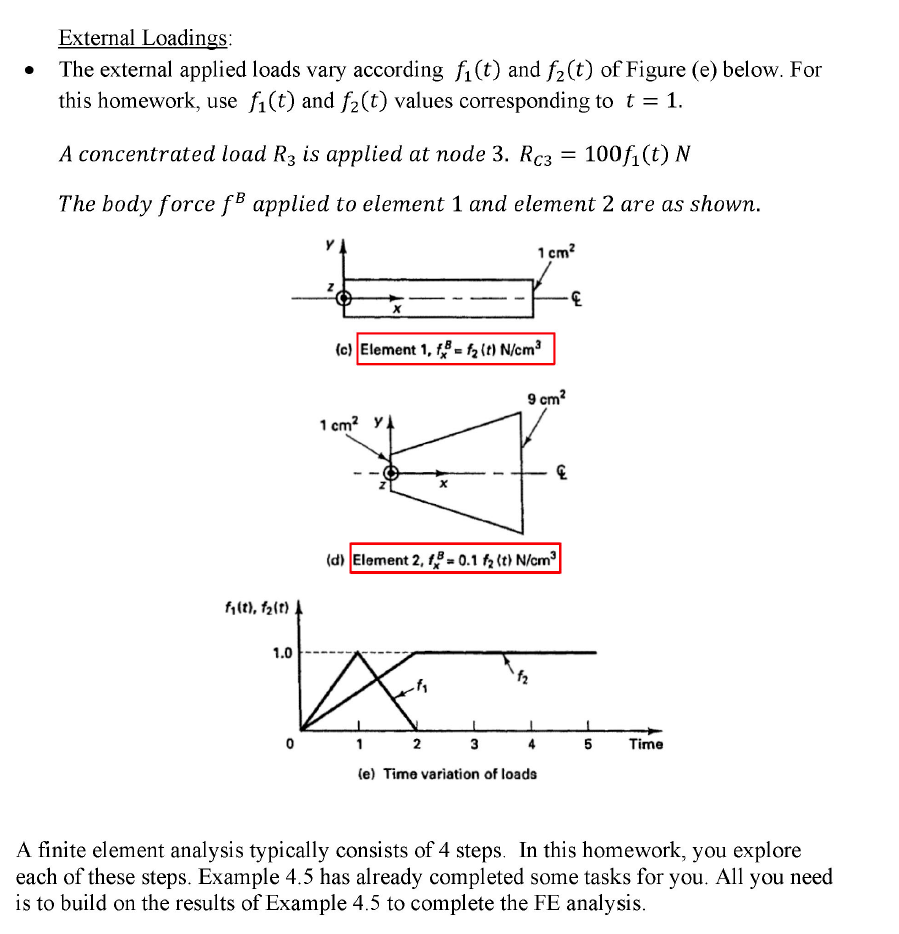


Conduct a static analysis, so the M matrix is 0 and the equation is to be solved is KU =R The material has a Young's modulus E = 106 N/cm For the external applied loads, use f (t) and f (t) values corresponding to t = 1 U Cross-sectional area A-1 cm 100 cm A= (1+n/40) 100 cm (a) Physical structure 80 cm 1cm 1/2 100/ E-Young's modulus p=mass density 9 cm 80 cm (b) Element assemblage in global system 100%, (t) N U External Loadings: The external applied loads vary according f(t) and f (t) of Figure (e) below. For this homework, use f(t) and f(t) values corresponding to t = 1. A concentrated load R3 is applied at node 3. Rc3 The body force fB applied to element 1 and element 2 are as shown. 1 cm f(t), f(t) 1.0 0 (c) Element 1, f=f (t) N/cm 1 cm YA 3 9 cm (d) Element 2, f3= 0.1 f (t) N/cm 1 2 (e) Time variation of loads = 100f(t) N & 5 Time A finite element analysis typically consists of 4 steps. In this homework, you explore each of these steps. Example 4.5 has already completed some tasks for you. All you need is to build on the results of Example 4.5 to complete the FE analysis. Step 1: Make the FE Model Where to place the nodes (how to spatially discretize the geometry): Example 4.5 discretizes the geometry into a mesh consisting of 3 nodes along the axis of the bar. The node at the left end (fixed end) is Node-1, the node where the taper part starts is Node-2, and the node at the right end is Node-3. The displacements of the nodes are U U and U3 respectively. How many elements and what type of element to use: Example 4.5 uses 1 linear element to model the constant cross-section part of the bar. It uses a linear interpolation function for u in the element --- a two-node bar element. 2 Example 4.5 models the tapered part of the bar with 1 element. It uses a linear interpolation function in the element (i.e., a two-node bar element). The FE mesh consists of a total of 3 nodes and 2 elements. Material properties: Young's modulus E = 106 N/cm Boundary condition: Node-1 is constrained not to move (i.e., U = 0 ) External loadings: See above description for the concentrated force and body forces. The type of analysis: Choose to do a static analysis. i.e., there is no M matrix. The equation to be solved is KU = R Step 2: Determine the element matrices, and assemble the global matrix equation (a) Determine the H(m), B(m) matrices of each of the 2 elements, (m = 1, m = 2). (b) Determine the element stiffness matrices K(m) for each element. (c) Assemble the global stiffness matrix K from the element stiffness matrices K(m) (d) Determine the element load vector R(m) for each element. (e) Assemble the global load vector R from the element load vectors R(m) Step 3: Solve for the nodal displacements Impose the boundary condition that U = 0 With BC imposed, solve the resulting global equation KU = R. Step 4: Post processing of results With the nodal displacements known, we can do post processing to generate results. (a) Determine R (the force at node 1). (b) Plot the stress o(x) versus distance x along the length of the bar. (c) Plot the displacement u(x) versus distance x along the length of the bar. (d) Print the magnitude of the nodal displacements (i.e., U, U, U3). (e) Print the magnitude of element-center stresses (stress at the center of each element.)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


