Question
Connect the waveform generator output of the oscilloscope to Channel 1 of the oscilloscope. After turning the oscilloscope on, turn off the display for Channel
Connect the waveform generator output of the oscilloscope to Channel 1 of the oscilloscope. After turning the oscilloscope on, turn off the display for Channel 2. Make sure that Channel 1 is set to DC coupling. 2. Record the number of horizontal and vertical intervals represented in the plot area. The number of intervals is constant, but the scaling of these intervals can be set by the user. 3. In the waveform generator settings, set the output to be a sine wave of 200 Hz and an amplitude of 200 mV. Change the horizontal scale of the oscilloscope so that you can see 2-5 complete cycles of the sine wave on the screen. For each of the vertical scale intervals listed in the table below, use the Measure function of the oscilloscope and record the Peak-to-Peak voltage of Channel 1. At each vertical scale interval, observe the Peak-to- Peak measurement for a few seconds and record the observable resolution of the measurement.
In the waveform generator settings, set the output to be a sine wave of 1 MHz and an amplitude of 1 V. Adjust the vertical scale of the oscilloscope to maximize the height of the sine wave while capturing both the top and bottom peaks on the screen. For each of the horizontal scale intervals listed in the table below, use the Measure function of the oscilloscope and record Frequency of Channel 1. At each horizontal scale interval, observe the Frequency measurement for a few seconds and record the observable resolution of the measurement.

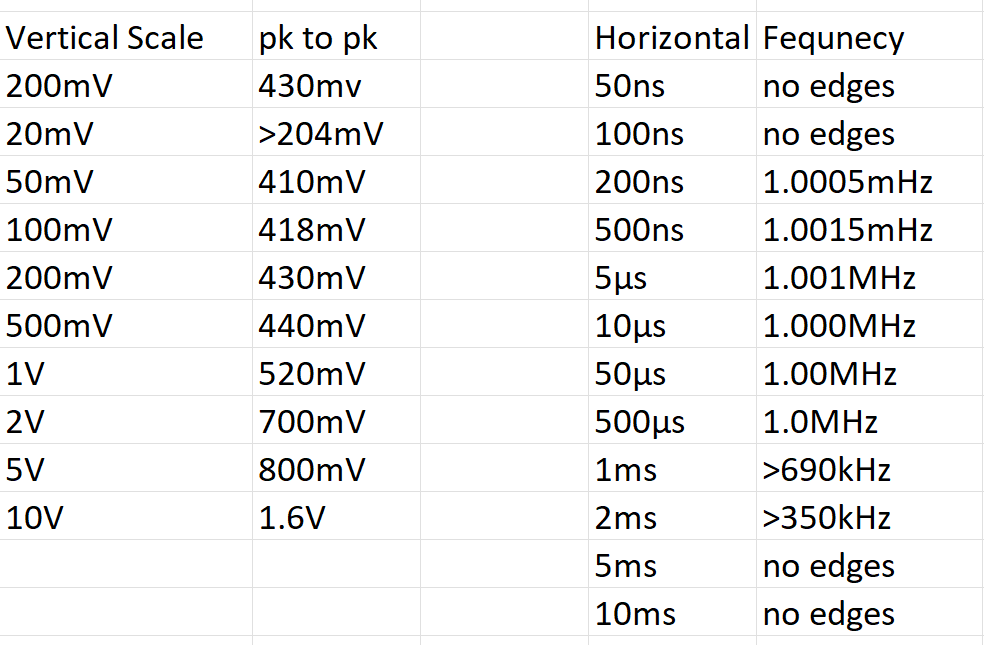
1. For each of the scale interval values given in step 3, calculate the voltage resolution based on the bit resolution and the range of voltage that can be represented at that vertical scale interval. As the scale interval becomes larger, how does the voltage resolution explain the peak-to-peak voltage values you recorded? 2. What is the minimum amount of time needed to record at least one complete cycle of the sine wave from step 4? Why does the oscilloscope require MORE than this time to calculate the wave frequency? 3. Consider the maximum memory depth from your pre-lab questions. If the 1M sample memory is completely filled when the oscilloscope is set to 50 s per scale interval, what is the corresponding sampling rate? How does this, along with Nyquist theory, explain the scale interval at which the oscilloscope no longer accurately measures the 1MHz frequency of the input signal?
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


