Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
1. Compute and plot the velocity distribution in the duct. Discuss your results. 2. Discuss the use of a U-tube manometer for measuring the

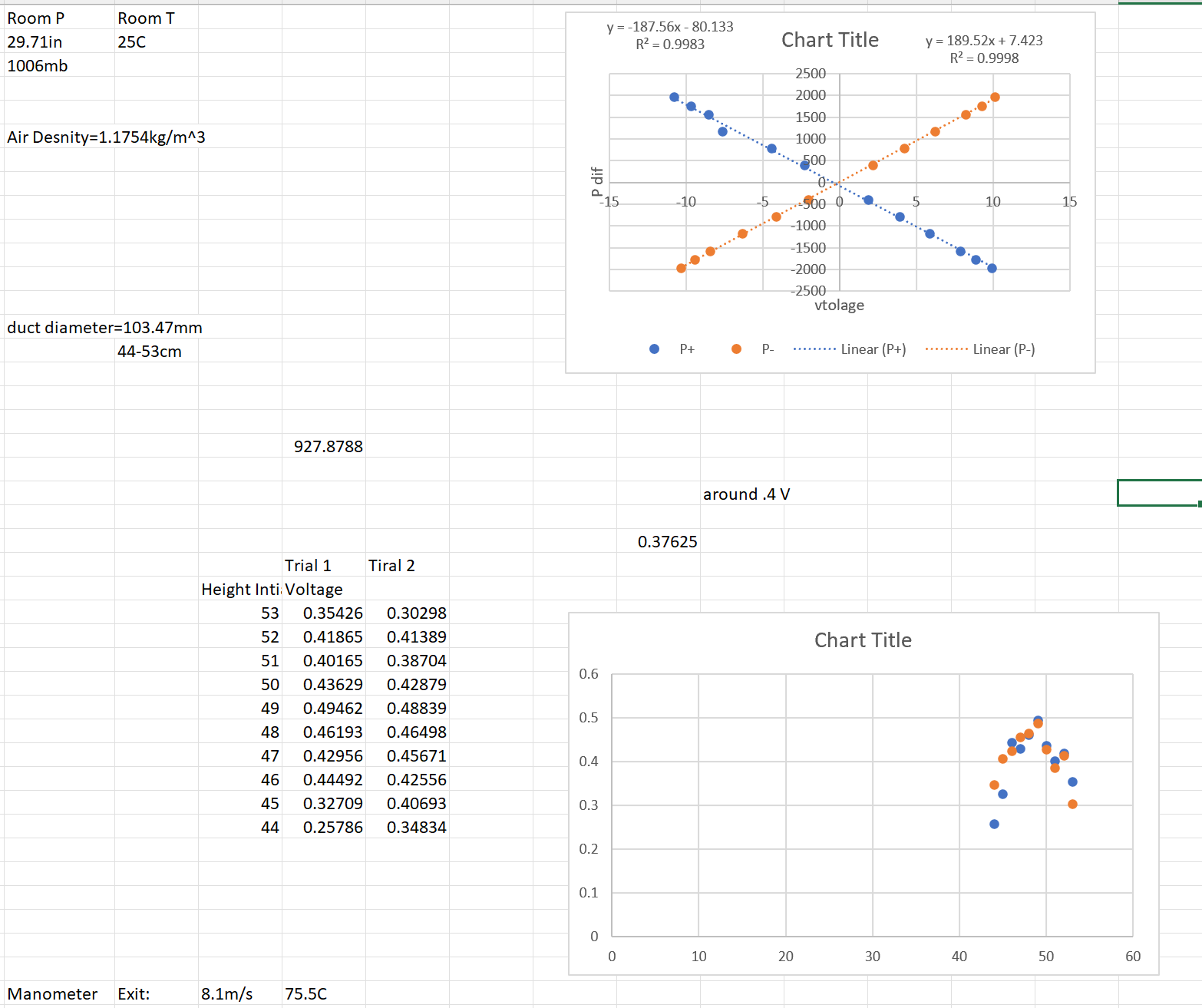
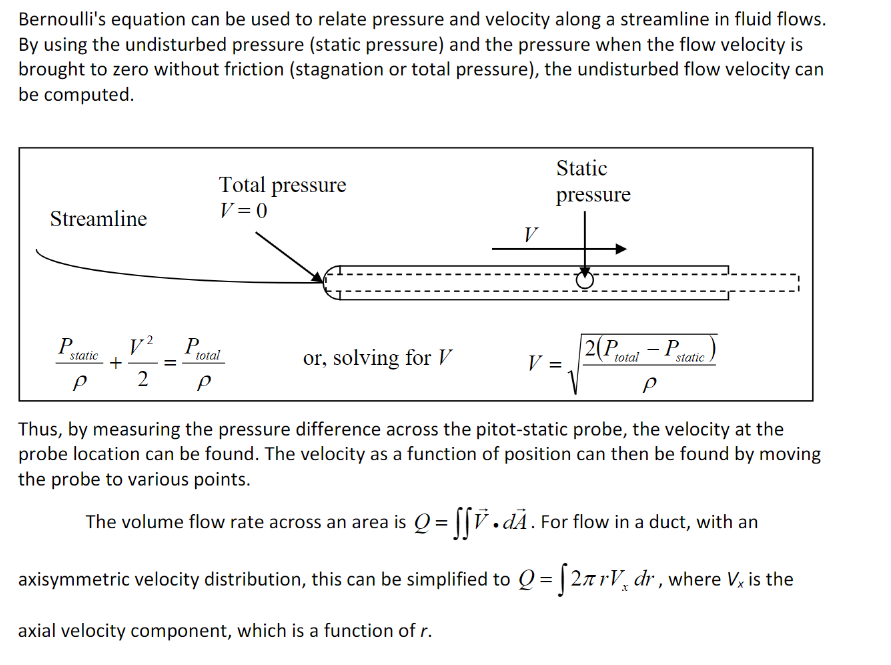


1. Compute and plot the velocity distribution in the duct. Discuss your results. 2. Discuss the use of a U-tube manometer for measuring the velocity instead of the pressure transducer. 3. Assuming axisymmetric flow in the duct, compute the VOLUME flow rate from the average of the radial profiles (include upper and lower radial profiles). Compare this with an estimate from the anemometer, assuming uniform flow in the duct. Room P 29.71in 1006mb Room T 25C Air Desnity=1.1754kg/m^3 duct diameter-103.47mm 44-53cm Manometer Exit: 927.8788 Trial 1 Height Inti Voltage 53 Tiral 2 0.35426 0.30298 52 0.41865 0.41389 51 0.40165 0.38704 50 0.43629 0.42879 49 0.49462 0.48839 48 0.46193 0.46498 47 0.42956 0.45671 46 0.44492 0.42556 45 0.32709 0.40693 44 0.25786 0.34834 8.1m/s 75.5C P dif 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 y = -187.56x - 80.133 R = 0.9983 0 -10 P+ 0.37625 P- 10 Chart Title 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 500 0 -1000 -1500 -2000 -2500 around .4 V vtolage ......... Linear (P+) 20 Chart Title 30 y = 189.52x + 7.423 R = 0.9998 40 10 Linear (P-) 50 15 60 Bernoulli's equation can be used to relate pressure and velocity along a streamline in fluid flows. By using the undisturbed pressure (static pressure) and the pressure when the flow velocity is brought to zero without friction (stagnation or total pressure), the undisturbed flow velocity can be computed. Streamline P static P + V2 2 = P Total pressure V=0 total P or, solving for V V Static pressure V = 2(P total - P P static Thus, by measuring the pressure difference across the pitot-static probe, the velocity at the probe location can be found. The velocity as a function of position can then be found by moving the probe to various points. The volume flow rate across an area is Q=.. For flow in a duct, with an axisymmetric velocity distribution, this can be simplified to Q=[27V dr, where Vx is the axial velocity component, which is a function of r. 1. Measure the barometric pressure and room temperature and compute the air density. 2. Measure the duct inside diameter using the sample duct piece. Carefully align the test section and inlet flow straightener section. (misalignment will distort the velocity profile) 3. Align the Pitot-static probe along the duct axis. Note the location of the axis on the probe traverse. 4. Connect your pressure transducer to the Pitot-static probe to measure the pressure difference and to the proper power supplies. 5. Set the tunnel centerline velocity to 12m/s using Bernoulli's equation and your pressure transducer calibration. Do NOT use the display on the blower control to judge the air speed. You will only set the air velocity once. 6. Measure the velocity distribution along the duct diameter, repeating the traverse at least twice. Take enough data points to accurately determine the velocity profile. 7. Use the hand-held anemometer at the fan exit to estimate the average velocity in the duct. Keep the anemometer at least 3" above the exit.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


