
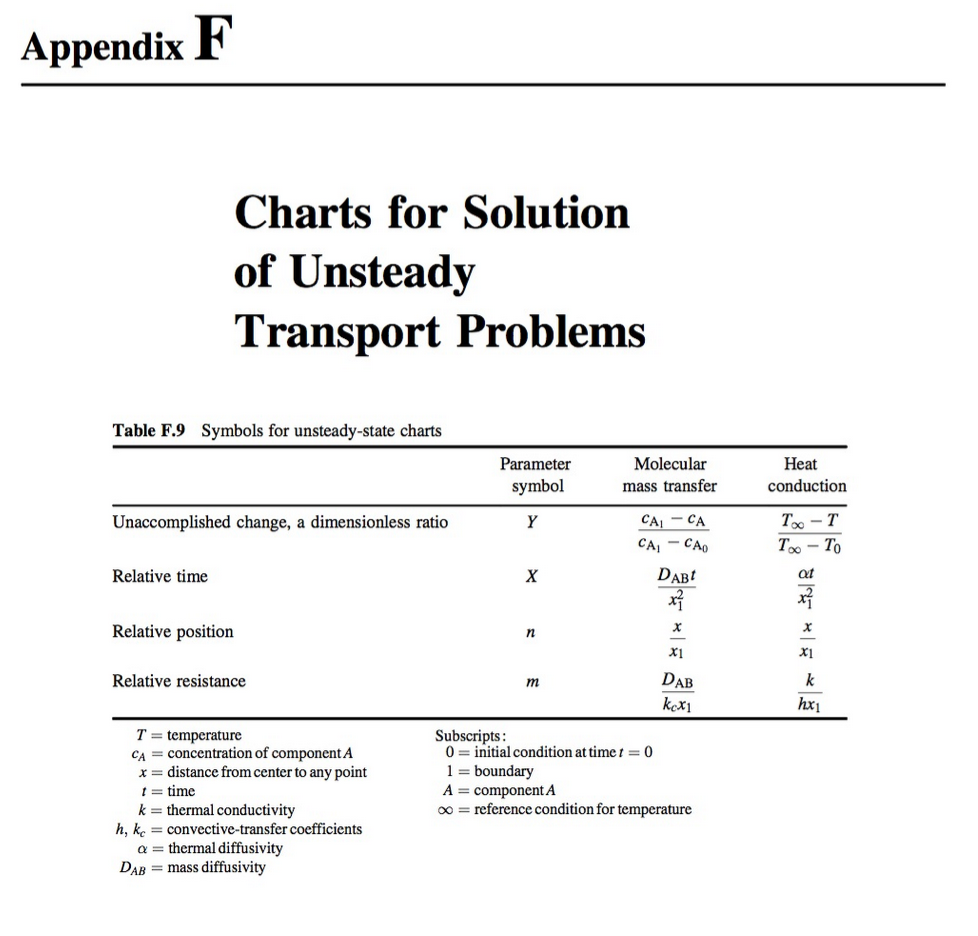
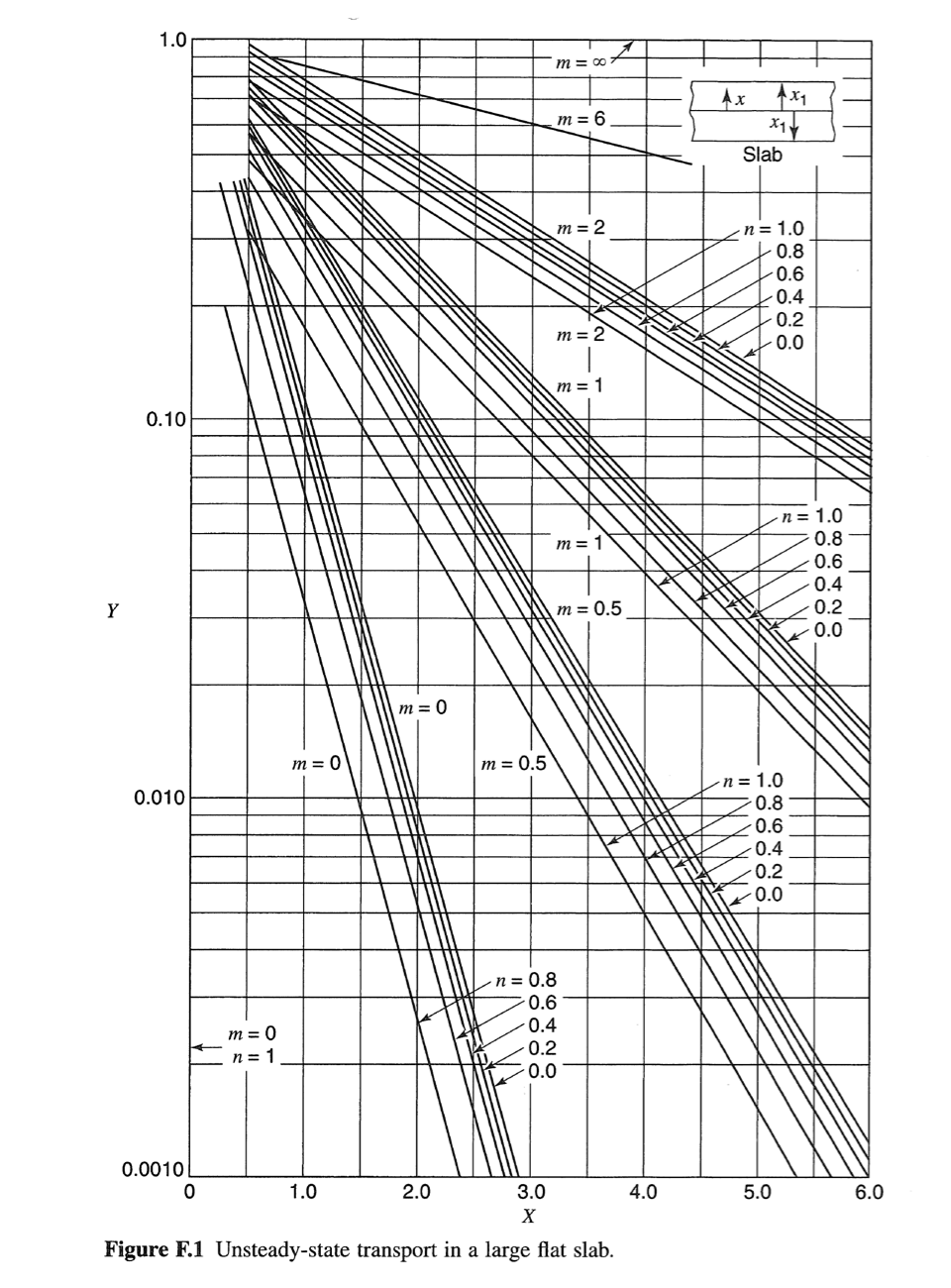
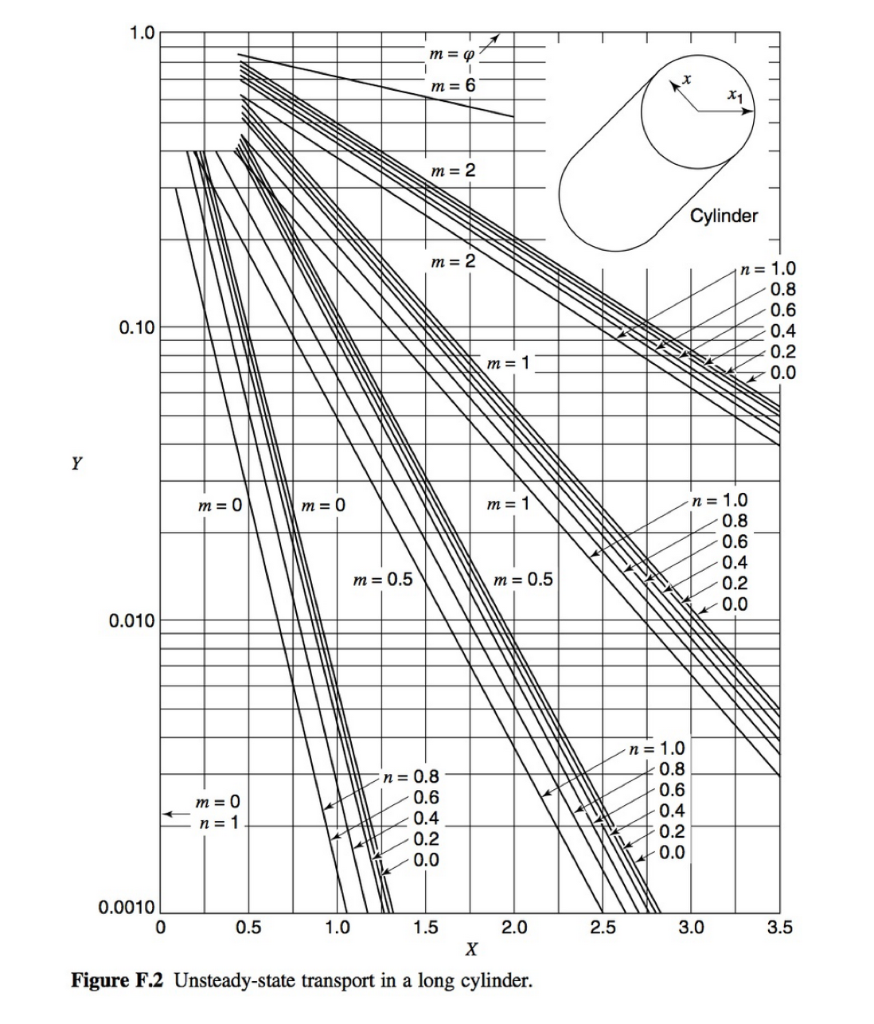
Consider a cylindrical-shaped absorbent material designed to selectively remove solute A from solution. The uptake of solute A through the homogeneous absorbent material is limited by molecular diffusion. Furthermore, the absorbent has a higher affinity for solute A relative to the surrounding solution that is described by the linear equilibrium relationship: CA = KCA where ca is the molar concentration of A in the absorbent, CA is molar concentration of A in the surrounding fluid, and K is a partition coefficient for solute A between the fluid and the absorbent material. The surrounding solution is very well mixed and has a constant concentration of C'Az = 2.00 gmol/m. The diffusion coefficient of A in the homogeneous absorbent material is 4 x 10 cmls, and the partition coefficient K = 1.5 cm fluid/cm absorbent. The cylindrical absorbent pellet is 1.0 cm in diameter and 5.0 cm in length. Initially, no solute A is absorbed into the absorbent material. a. Assume edge effects associated with the ends of the cylinder can be neglected. Under this assumption, how long will it take in hours) for the solute A concentration to reach 2.94 gmol/m' at a depth of 0.40 cm from the surface of the cylinder? To answer this question, first draw a picture of the control volume, select an appropriate coordinate system, write the simplified mass balance equation of species A in term of its concentration in the control volume, and specify boundary/initial conditions for solving the mass balance equation for species A. Then, use the appropriate Unsteady State Charts from Appendix F to find the solution to the problem. b. Assume that the edge effects associated with the cylinder ends cannot be neglected, how long will it take (in hours) for the solute A concentration to reach 2.94 gmol/m' at a radial position of 0.4 cm from the cylindrical surface, and at an axial position 1.0 cm from the end of the rod? To answer this question, first draw a picture of the control volume with appropriates coordinates labelled, write the simplified mass balance equation of species A in term of its concentration in the control volume, and specify boundary/initial conditions for solving the mass balance equation for species A. Then, use the appropriate Unsteady State Charts from Appendix F to find the solution to the problem. Appendix F Charts for Solution of Unsteady Transport Problems Table F.9 Symbols for unsteady-state charts Parameter symbol Molecular mass transfer Heat conduction Unaccomplished change, a dimensionless ratio Y T-T T - TO Relative time X at , CA CA - CAO DAB x} x Xi x Relative position X n Xi Relative resistance m k DAB kex1 hxi T = temperature CA = concentration of component A x=distance from center to any point 1 = time k = thermal conductivity h, kc = convective-transfer coefficients a= thermal diffusivity DAB = mass diffusivity Subscripts: 0= initial condition at time t = 0 1 = boundary A = component A 00 = reference condition for temperature 1.0 m = 00 m = 6 Ax Axi xay Slab m = 2 n=1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 UTII m = 2 | m = 1 0.10 m = 1 n = 1.0 0.8 -0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 oooo Y m = 0.5 m=0 m = 0 m = 0.5 0.010 . n = 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 m = 0 n=1 n = 0.8 -0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 0.0010 0 1.0 2.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 3.0 X Figure F.1 Unsteady-state transport in a large flat slab. 1.0 m = 0 m = 6 m = 2 Cylinder m = 2 0.10 n = 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 m=1 Y m = 0 m=0 m = 1 n = 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 FOOOOOT ON OOO m=0.5 m = 0.5 0.010 n = 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 n = 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 m = 0 n=1 0.0 0.0010 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 X Figure F.2 Unsteady-state transport in a long cylinder










