Question: Consider a random sample from N(u, 0.1082), and the null hypothesis Ho : u = 4.55. Suppose we observed a set of data with

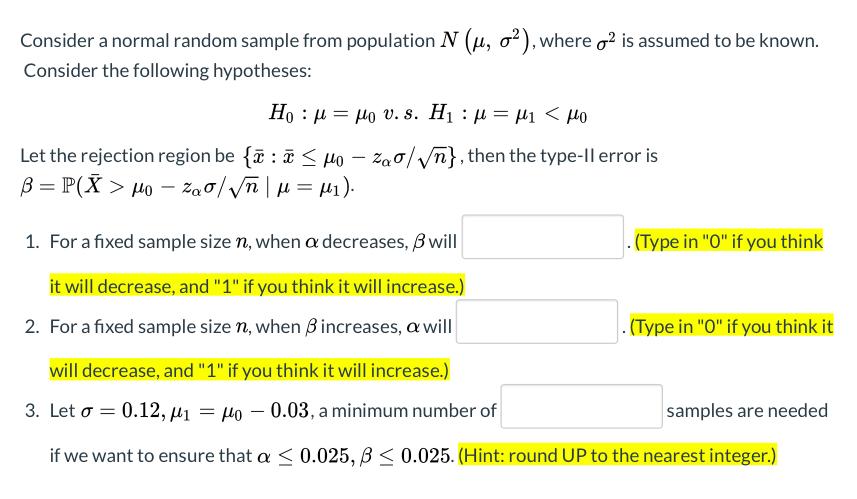
Consider a random sample from N(u, 0.1082), and the null hypothesis Ho : u = 4.55. Suppose we observed a set of data with n = 9, = 4.484. 1. Let H1 : + 4.55, the p-value of the observed = 4.484 is (Please round to 2 significant figures.) 2. Let H1 : u < 4.55, the p-value of the observed a 4.484 is (Please round to 2 significant figures.) Consider a normal random sample from population N (u, o?), where o2 is assumed to be known. Consider the following hypotheses: H : . . s. 1 : - Let the rejection region be { : < Ho - Zao/Vn},then the type-ll error is = P(X >- 2/ | = ). 1. For a fixed sample size n, when a decreases, B will (Type in "O" if you think it will decrease, and "1" if you think it will increase.) 2. For a fixed sample size n, when Bincreases, a will (Type in "O" if you think it will decrease, and "1" if you think it will increase.) 3. Let - 0.12, = lo 0.03, a minimum number of samples are needed if we want to ensure that a < 0.025, B < 0.025. (Hint: round UP to the nearest integer.)
Step by Step Solution
3.36 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Lets work through each question step by step Part 1 PValue Calculations Given mu0 455 sigma 0108 n 9 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


