Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Consider a single-engine light private airplane Beechcraft Bonanza V-tailed, which has the following characteristics. Wing area: 16.82 m, aspect ratio: 6.2, Oswald efficiency factor:
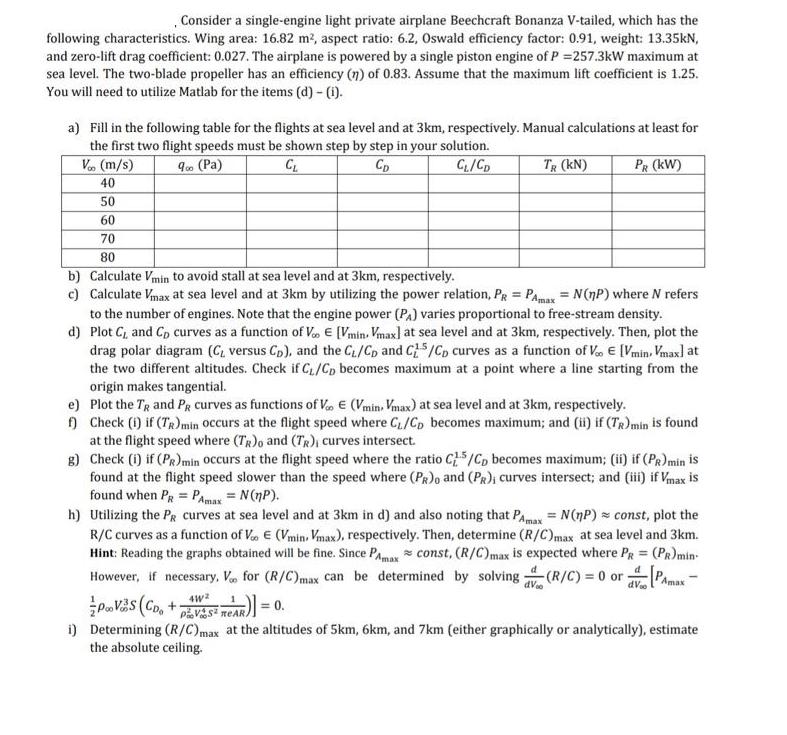
Consider a single-engine light private airplane Beechcraft Bonanza V-tailed, which has the following characteristics. Wing area: 16.82 m, aspect ratio: 6.2, Oswald efficiency factor: 0.91, weight: 13.35kN, and zero-lift drag coefficient: 0.027. The airplane is powered by a single piston engine of P =257.3kW maximum at sea level. The two-blade propeller has an efficiency (n) of 0.83. Assume that the maximum lift coefficient is 1.25. You will need to utilize Matlab for the items (d) - (i). a) Fill in the following table for the flights at sea level and at 3km, respectively. Manual calculations at least for the first two flight speeds must be shown step by step in your solution. V (m/s) 40 900 (Pa) CL CD CL/CD TR (KN) PR (KW) 50 60 70 80 b) Calculate Vmin to avoid stall at sea level and at 3km, respectively. c) Calculate Vmax at sea level and at 3km by utilizing the power relation, PR = PAmax = N(nP) where N refers to the number of engines. Note that the engine power (PA) varies proportional to free-stream density. d) Plot C, and Co curves as a function of Voo [Vmin. Vmax] at sea level and at 3km, respectively. Then, plot the drag polar diagram (C, versus Cp), and the C/CD and C5/CD curves as a function of V. [Vmin, Vmax] at the two different altitudes. Check if C/Cp becomes maximum at a point where a line starting from the origin makes tangential. e) f) Plot the TR and PR curves as functions of Voo (Vmin. Vmax) at sea level and at 3km, respectively. Check (1) if (TR) min occurs at the flight speed where C/CD becomes maximum; and (ii) if (TR) min is found at the flight speed where (TR)o and (TR), curves intersect. g) Check (i) if (PR) min occurs at the flight speed where the ratio CL5/CD becomes maximum; (ii) if (PR) min is found at the flight speed slower than the speed where (PR), and (PR); curves intersect; and (iii) if Vmax is found when PR PAmax = N(np). h) Utilizing the Pg curves at sea level and at 3km in d) and also noting that PAmax = N(nP) = const, plot the R/C curves as a function of Vo (Vmin, Vmax), respectively. Then, determine (R/C)max at sea level and 3km. Hint: Reading the graphs obtained will be fine. Since Pamax const, (R/C) max is expected where PR = (PR) min- However, if necessary, V for (R/C) max can be determined by solving (R/C) = 0 or Amax 4W PVS (CD + VS REAR)] = 0. i) Determining (R/C) max at the altitudes of 5km, 6km, and 7km (either graphically or analytically), estimate the absolute ceiling.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.32 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a V infty msq infty PaCLCDCLCDTRkNPR kW 4073550500135370368717609 509194062...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


