Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Consider a two-period overlapping generation model economy where agents work when young and retire when old. Young agents supply inelastically labour to the competitive

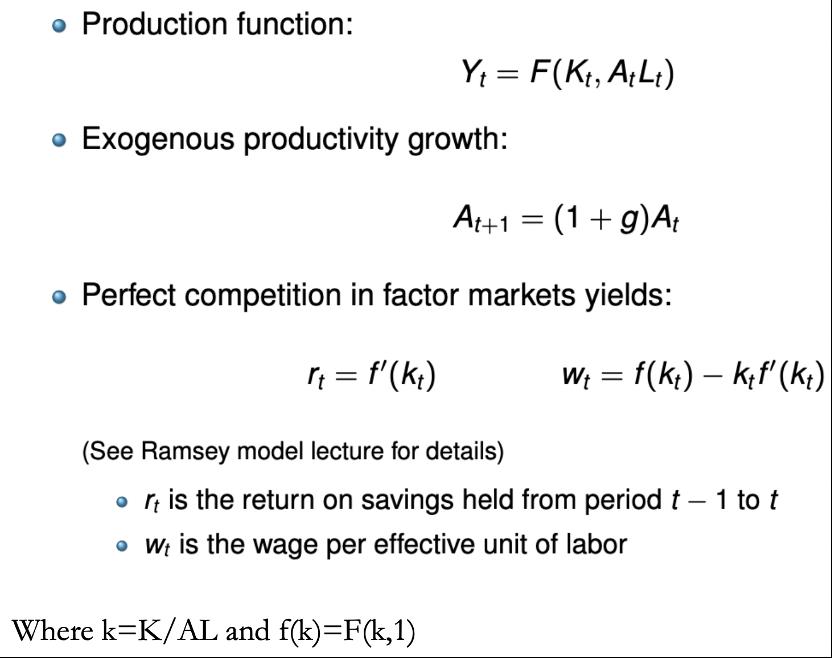
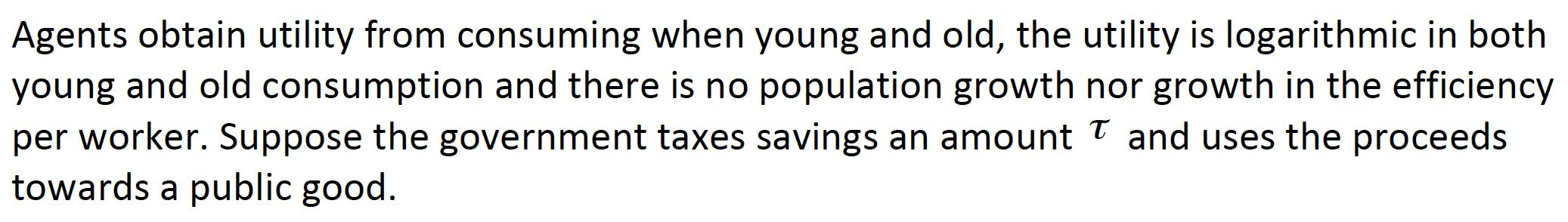

Consider a two-period overlapping generation model economy where agents work when young and retire when old. Young agents supply inelastically labour to the competitive firm who produces the only good in the economy using capital and labour through a Cobb-Douglas production function Production function: Yt = F(Kt, At Lt) Exogenous productivity growth: At+1 = (1 + g)At Perfect competition in factor markets yields: rt= f'(kt) Where k=K/AL and f(k)=F(k,1) Wt = f( kt) kt f' (kt) (See Ramsey model lecture for details) It is the return on savings held from period t - 1 to t Wt is the wage per effective unit of labor Agents obtain utility from consuming when young and old, the utility is logarithmic in both young and old consumption and there is no population growth nor growth in the efficiency per worker. Suppose the government taxes savings an amount and uses the proceeds towards a public good. (a) Write down the individual's utility maximization problem and explain each component. (b) Derive the optimal savings. (c) Find the impact of the tax on savings and explain this effect. (d) How much tax revenues are collected towards the public good? (e) Derive the per capita capital accumulation and find the corresponding steady state value. (f) Draw the corresponding diagram for the evolution of per capita capital if the initial per capita capital is smaller than the steady state value.
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.37 Rating (147 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
It seems like youre referring to a production function and some equations related to the ...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


