Question
Consider an implementation of binary trees with Scheme lists, as in the following example: Before proceeding, it may be useful to define three auxiliary functions
Consider an implementation of binary trees with Scheme lists, as in the following example:
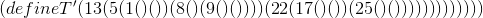
Before proceeding, it may be useful to define three auxiliary functions (val T), (left T) and (right T), which return the value in the root of tree T, its left subtree and its right subtree, respectively.
(a) Write a recursive function (tree-member? V T), which determines whether V apppears as an element in the tree T. The following example illustrates the use of this function:
> (tree-member? 17 T)
#t
(b) Write a recursive function (preorder T), which returns the list of all elements in the tree T corresponding to a preorder traversal of the tree. The following exapmle illustrates the use of this function:
>(preorder T)
(13 5 1 8 9 22 17 25)
(c) Write a recursive function (inorder T), which returns the list of all elements in the tree T corresponding to a inorder traversal of the tree. The following example illustrates the use of this function:
>(inorder T)
(1 5 8 9 13 17 22 25)
de fineT'135 100) 80900))(221700 250022)) de fineT'135 100) 80900))(221700 250022))Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


