
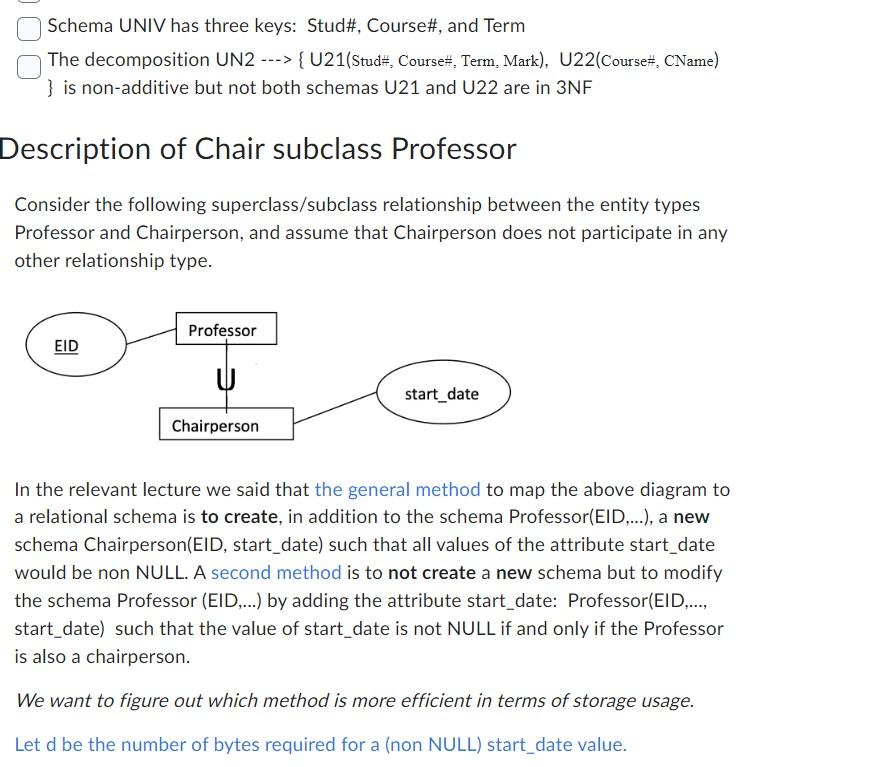
Consider below the schemas UNIV, UN1, UN2 and the functional dependencies F about students and courses: UNIV ( Stud\#, Sname, Email, Major, Advisor, Course\#, Cname, Term, Mark) UN1 (Stud\#, Sname, Email, Major, Advisor) UN2 (Stud\#, Course\#, Cname, Term, Mark) F={ Stud # Sname, Email, Major; Course\# --> Cname; Stud\#, Course\#, Term Mark; Stud\#, Major --> Advisor; Advisor > Major } Check below all the correct statements. The decomposition UN2 > \{ U21(Stud\#, Course\#, Term, Mark), U22(Course\#, CName) \} is non-additive and both schemas U21 and U22 are in 3NF The decomposition UN2 >{ U21(Stud\#, Course\#, Term, Mark), U22(Course\#, CName) \} is additive The decomposition UNIV >{ UN1, UN2 } is additive The decomposition UN1 > \{ U11(Stud\#, Sname, Email, Advisor), U12(Advisor, Major) \} is non-additive but not both schemas U11 and U12 are in 3NF The schema UNIV is not in 2NF, but UN1 and UN2 are in 2NF Schema UNIV has (exactly) one key: \{Stud\#,Course\#,Term,Advisor\} The decomposition UNIV UUN1, UN2 } is non-additive The decomposition UN1 ---> \{ U11(Stud\#, Sname, Email, Advisor), U12(Advisor, Major) \} is non-additive and both schemas U11 and U12 are in 3NF Schema UNIV has (exactly) one key: \{Stud\#,Course\#,Term\} The schema UNIV is not in 2 NF, but UN1 is in 2 NF Schema UNIV has three keys: Stud\#, Course\#, and Term The decomposition UN2 \{ U21(Stud\#, Course\#, Term, Mark), U22(Course\#, CName) \} is non-additive but not both schemas U21 and U22 are in 3NF escription of Chair subclass Professor Consider the following superclass/subclass relationship between the entity types Professor and Chairperson, and assume that Chairperson does not participate in any other relationship type. In the relevant lecture we said that the general method to map the above diagram to a relational schema is to create, in addition to the schema Professor(EID,..), a new schema Chairperson(EID, start_date) such that all values of the attribute start_date would be non NULL. A second method is to not create a new schema but to modify the schema Professor (EID,...) by adding the attribute start_date: Professor(EID,..., start_date) such that the value of start_date is not NULL if and only if the Professor is also a chairperson. We want to figure out which method is more efficient in terms of storage usage. Let d be the number of bytes required for a (non NULL) start_date value








