Consider the cylindrical catalyst pellet with dimensions shown in the figure below. The nonporous catalyst surface promotes the hydrogenation ethylene (CH) gas to ethane
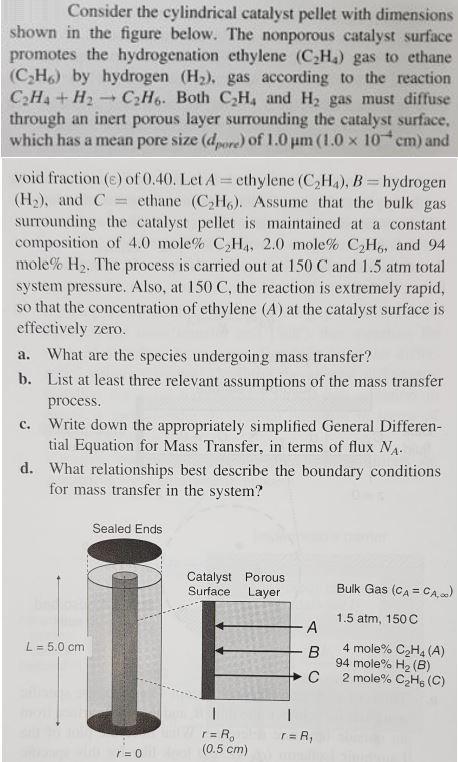
Consider the cylindrical catalyst pellet with dimensions shown in the figure below. The nonporous catalyst surface promotes the hydrogenation ethylene (CH) gas to ethane (CH6) by hydrogen (H). gas according to the reaction CH4 + H 1 CH6. Both CH4 and H gas must diffuse through an inert porous layer surrounding the catalyst surface. which has a mean pore size (dpore) of 1.0 m (1.0 x 10 cm) and void fraction (e) of 0.40. Let A = ethylene (CH4), B = hydrogen (H), and C= ethane (CH). Assume that the bulk gas surrounding the catalyst pellet is maintained at a constant composition of 4.0 mole% CH4, 2.0 mole % CH6, and 94 mole% H. The process is carried out at 150 C and 1.5 atm total system pressure. Also, at 150 C, the reaction is extremely rapid, so that the concentration of ethylene (A) at the catalyst surface is effectively zero. a. What are the species undergoing mass transfer? b. List at least three relevant assumptions of the mass transfer process. c. Write down the appropriately simplified General Differen- tial Equation for Mass Transfer, in terms of flux NA. What relationships best describe the boundary conditions for mass transfer in the system? d. L = 5.0 cm Sealed Ends Catalyst Porous. Surface Layer 1 r = R r = 0 (0.5 cm) A B C I r = R Bulk Gas (CA = CA,00) 1.5 atm, 150 C 4 mole% CH4 (A) 94 mole% H (B) 2 mole% CH, (C)
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (174 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a The species undergoing mass transfer are ethylene C2H4 hydrogen H2 and ethane C2H6 b Relevant assu...
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


