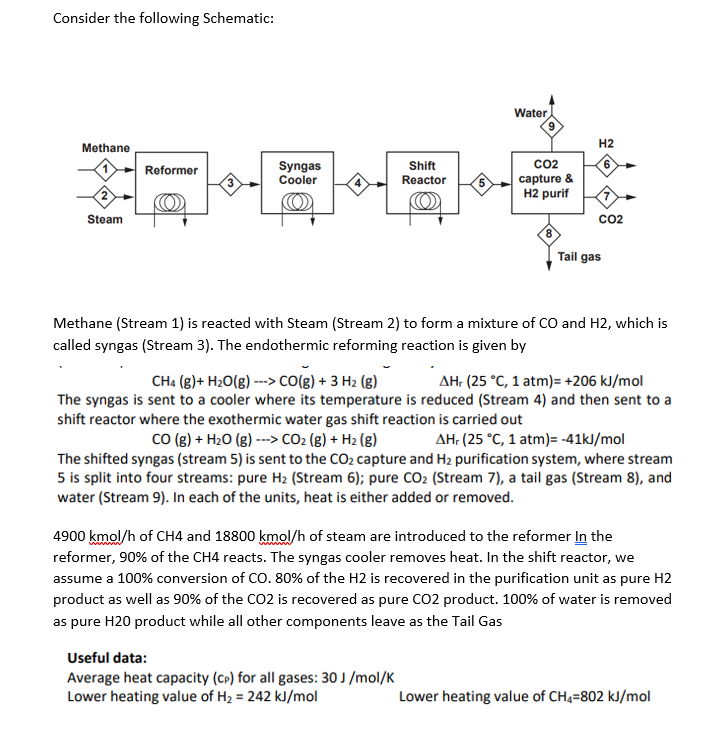
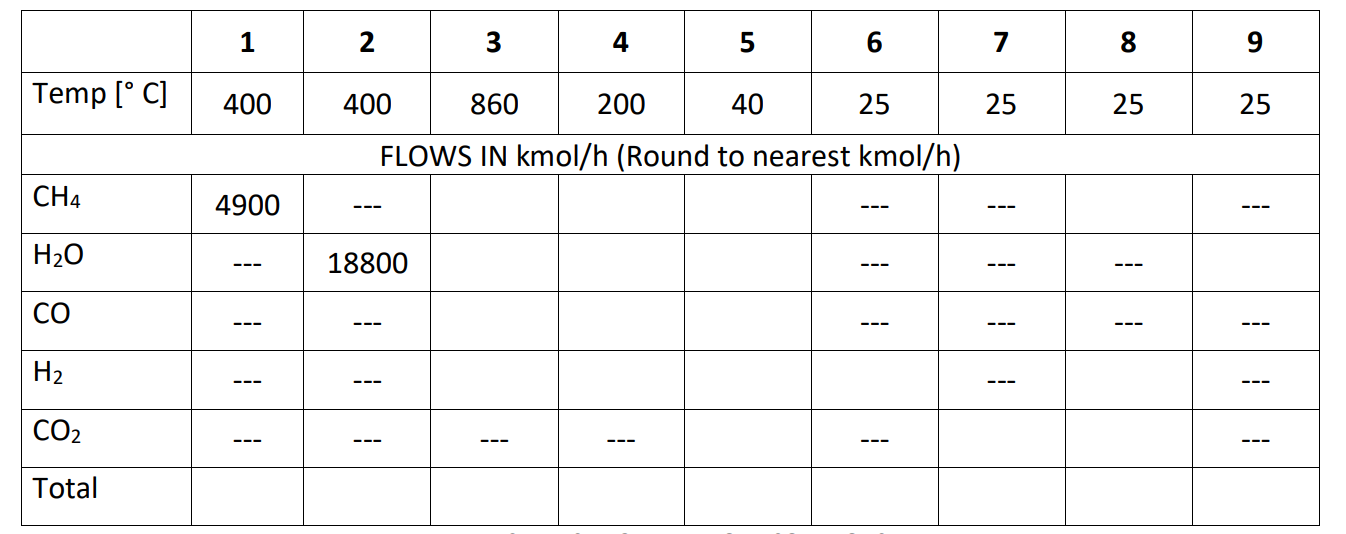

Consider the following Schematic: Water H2 Methane Reformer 6 Syngas Cooler Shift Reactor 3 5 CO2 capture & H2 purif Steam CO2 Tail gas Methane (Stream 1) is reacted with Steam (Stream 2) to form a mixture of CO and H2, which is called syngas (Stream 3). The endothermic reforming reaction is given by CH4 (g)+ H2O(g) ---> CO(g) + 3 H2 (g) AH (25 C, 1 atm)= +206 kJ/mol The syngas is sent to a cooler where its temperature is reduced (Stream 4) and then sent to a shift reactor where the exothermic water gas shift reaction is carried out CO(g) + H20 (8) ---> CO2 (g) + H2(g) AH (25 C, 1 atm)= -41kJ/mol The shifted syngas (stream 5) is sent to the CO2 capture and H2 purification system, where stream 5 is split into four streams: pure H2 (Stream 6); pure CO2 (Stream 7), a tail gas (Stream 8), and water (Stream 9). In each of the units, heat is either added or removed. 4900 kmol/h of CH4 and 18800 kmol/h of steam are introduced to the reformer In the reformer, 90% of the CH4 reacts. The syngas cooler removes heat. In the shift reactor, we assume a 100% conversion of CO. 80% of the H2 is recovered in the purification unit as pure H2 product as well as 90% of the CO2 is recovered as pure CO2 product. 100% of water is removed as pure H20 product while all other components leave as the Tail Gas Useful data: Average heat capacity (Cp) for all gases: 30 J/mol/K Lower heating value of H2 = 242 kJ/mol Lower heating value of CH4=802 kJ/mol 1 2 3 5 6 8 9 Temp [C] 400 400 860 200 40 25 25 25 25 FLOWS IN kmol/h (Round to nearest kmol/h) CH4 4900 --- --- H20 18800 CO --- H2 --- --- --- CO2 --- --- --- --- --- Total QUESTION 1: Is Steam or CH4 the limiting reactant entering the reformer? QUESTION 2: Complete the given stream table showing appropriate mass/energy balances. For energy balances, consider [25 C, 1 atm, gas) as a reference state and for those balances involving reactions, use the heat of reaction method. You can assume that enthalpy changes due to changes in pressure can be ignored. QUESTION 3: Find the rate (In MW) at which heat is added/removed from/to the reformer and the syn gas cooler. QUESTION 4: Tail gas can be burnt to provide heat and power the reformer. Find what percentage of heat required to power the reformer can be supplied by burning the tail gas. Show suitable calculations to justify your answer. QUESTION 5: If the tail gas is insufficient, explain how you could provide the extra heat energy to the reformer. QUESTION 6: Calculate the ratio of kg of CO2 produced per kg H2, including the CO2 that will be produced by burning the tail gas and additional gas that might need from Question 5









