Question
consider the java classes below: package binarySearchTree; public class BinaryTreeNode > { private BinaryTreeNode left; // the left child private BinaryTreeNode right; // the right
consider the java classes below:
package binarySearchTree;
public class BinaryTreeNode
private BinaryTreeNode
private BinaryTreeNode
private T data; // the data in this node
public BinaryTreeNode() {
this(null, null, null);
}
public BinaryTreeNode(T theData) {
this(theData, null, null);
}
public BinaryTreeNode(T theData, BinaryTreeNode
data = theData;
left = leftChild;
right = rightChild;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public BinaryTreeNode
return left;
}
public BinaryTreeNode
return right;
}
public void setLeft(BinaryTreeNode
left = newLeft;
}
public void setRight(BinaryTreeNode
right = newRight;
}
public void setData(T newData) {
data = newData;
}
public void preOrder() {
System.out.println(data);
if (left != null) {
left.preOrder();
}
if (right != null) {
right.preOrder();
}
}
public int height() {
int leftHeight = 0; // Height of the left subtree
int rightHeight = 0; // Height of the right subtree
int height = 0; // The height of this subtree
// If we have a left subtree, determine its height
if (left != null) {
leftHeight = left.height();
}
// If we have a right subtree, determine its height
if (right != null) {
rightHeight = right.height();
}
// The height of the tree rooted at this node is one more than the
// height of the 'taller' of its children.
if (leftHeight > rightHeight) {
height = 1 + leftHeight;
} else {
height = 1 + rightHeight;
}
// Return the answer
return height;
}
/**
* @param pathString
* @return the tree nodes in pre-order traversal
*/
public String toStringPreOrder(String pathString) {
String treeString = pathString + " : " + data + " ";
if (left != null) {
treeString += left.toStringPreOrder(pathString + "L");
}
if (right != null) {
treeString += right.toStringPreOrder(pathString + "R");
}
return treeString;
}
}
package binarySearchTree;
public class BinaryTree
private BinaryTreeNode
private BinaryTreeNode
/**
* Constructor for initializing a tree with node being set as the root of the
* tree.
*
* @param node
*/
public BinaryTree(BinaryTreeNode
root = node;
}
/**
* Moves the cursor to the root.
*/
public void toRoot() {
cursor = root;
}
/**
* Returns the cursor node.
*
* @return cursor
*/
public BinaryTreeNode
return cursor;
}
/**
* Sets the root to the provided node. ONLY USE IN THE DELETE METHOD
*
* @param node
*/
public void setRoot(BinaryTreeNode
root = node;
}
/**
* CS303 Lab Assignment 1 of 7 Checks if the tree node has a left child node
*
* @return true if left child exists else false
*/
public boolean hasLeftChild() {
return cursor.getLeft() != null;
}
/**
* Checks if the tree node has a right child node
*
* @return true if right child exists else false
*/
public boolean hasRightChild() {
return cursor.getRight() != null;
}
/**
* Move the cursor to the left child
*/
public void toLeftChild() {
cursor = cursor.getLeft();
}
/**
* Move the cursor to the right child
*/
public void toRightChild() {
cursor = cursor.getRight();
}
/**
* @return height of the tree
*/
public int height() {
if (root != null) {
return root.height();
} else {
return 0;
}
}
/*
* (non-Javadoc)
*
* @see java.lang.Object#toString()
*/
public String toString() {
if (root != null) {
return root.toStringPreOrder(".");
} else {
return "";
}
}
}
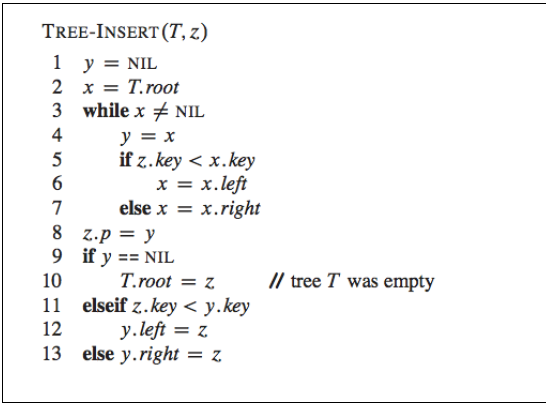
Use the classes above, implement a Tree-Insert that inserts a node having value of key = data in a Binary Search Tree. See the algorithm presented below
implement Inorder-tree-walk that prints the elements of the BST in an in-order format using the below algorithm:

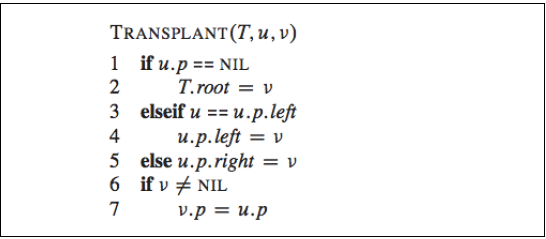
Also implement search, delete and transplant, algorithm for them is shown bellow:


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


