Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Consider the natural join of the relation R(A,B) and S(A,C) on attribute A. Neither relations have any indexes built on them. Assume that R and
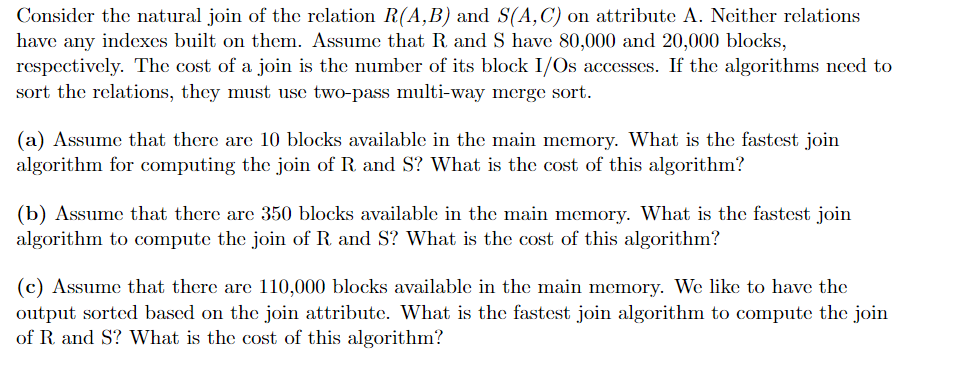 Consider the natural join of the relation R(A,B) and S(A,C) on attribute A. Neither relations have any indexes built on them. Assume that R and S have 80,000 and 20,000 blocks,
Consider the natural join of the relation R(A,B) and S(A,C) on attribute A. Neither relations have any indexes built on them. Assume that R and S have 80,000 and 20,000 blocks,
respectively. The cost of a join is the number of its block I/Os accesses. If the algorithms need to sort the relations, they must use two-pass multi-way merge sort.
(a)
Assume that there are 10 blocks available in the main memory. What is the fastest join algorithm for computing the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithm?
Consider the natural join of the relation R(A,B) and S(A,C) on attribute A. Neither relations have any indexes built on them. Assume that R and S have 80,000 and 20,000 blocks, respectively. The cost of a join is the number of its block I/Os accesses. If the algorithms need to sort the relations, they must use two-pass multi-way merge sort. (a) Assume that there are 10 blocks available in the main memory. What is the fastest join algorithm for computing the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithm? (b) Assume that there are 350 blocks available in the main memory. What is the fastest join algorithm to compute the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithm? (c) Assume that there are 110,000 blocks available in the main memory. We like to have the output sorted based on the join attribute. What is the fastest join algorithm to compute the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithm? Consider the natural join of the relation R(A,B) and S(A,C) on attribute A. Neither relations have any indexes built on them. Assume that R and S have 80,000 and 20,000 blocks, respectively. The cost of a join is the number of its block I/Os accesses. If the algorithms need to sort the relations, they must use two-pass multi-way merge sort. (a) Assume that there are 10 blocks available in the main memory. What is the fastest join algorithm for computing the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithm? (b) Assume that there are 350 blocks available in the main memory. What is the fastest join algorithm to compute the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithm? (c) Assume that there are 110,000 blocks available in the main memory. We like to have the output sorted based on the join attribute. What is the fastest join algorithm to compute the join of R and S? What is the cost of this algorithmStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


